CAZypedia needs your help!
We have many unassigned pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators. See a page that's out-of-date and just needs a touch-up? - You are also welcome to become a CAZypedian. Here's how.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute.
Learn more about CAZypedia's misson here and in this article.
Totally new to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
Difference between revisions of "Glycoside hydrolases"
| (52 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{CuratorApproved}} | {{CuratorApproved}} | ||
| − | * Authors: | + | * Authors: [[User:Steve Withers|Steve Withers]], [[User:Spencer Williams|Spencer Williams]] |
| − | * Responsible Curator: | + | * Responsible Curator: [[User:Spencer Williams|Spencer Williams]] |
---- | ---- | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| − | |||
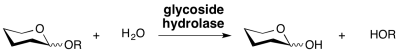
Glycoside hydrolases are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of the glycosidic linkage of glycosides, leading to the formation of a sugar hemiacetal or hemiketal and the corresponding free aglycon. Glycoside hydrolases are also referred to as glycosidases, and sometimes also as glycosyl hydrolases. Glycoside hydrolases can catalyze the hydrolysis of O-, N- and S-linked glycosides. | Glycoside hydrolases are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of the glycosidic linkage of glycosides, leading to the formation of a sugar hemiacetal or hemiketal and the corresponding free aglycon. Glycoside hydrolases are also referred to as glycosidases, and sometimes also as glycosyl hydrolases. Glycoside hydrolases can catalyze the hydrolysis of O-, N- and S-linked glycosides. | ||
| − | [[Image:GHs.png | + | [[Image:GHs.png|center|400px]] |
== Classification == | == Classification == | ||
| − | |||
Glycoside hydrolases can be classified in many different ways. The following paragraphs list several different ways, the utility of which depends on the context in which the classification is made and used. | Glycoside hydrolases can be classified in many different ways. The following paragraphs list several different ways, the utility of which depends on the context in which the classification is made and used. | ||
=== Endo/exo === | === Endo/exo === | ||
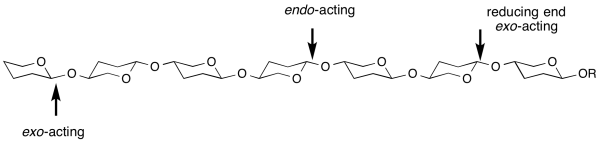
| − | ''exo''- and ''endo''- refers to the ability of a glycoside hydrolase to cleave a substrate at the end (most frequently, but not always the non-reducing end) or within the middle of a chain. For example, most cellulases are ''endo''-acting, whereas LacZ β-galactosidase from ''E. coli'' is ''exo''-acting. | + | ''exo''- and ''endo''- refers to the ability of a glycoside hydrolase to cleave a substrate at the end (most frequently, but not always the non-reducing end) or within the middle of a chain <cite>DaviesHenrissat1995</cite>. For example, most cellulases are ''endo''-acting, whereas LacZ β-galactosidase from ''E. coli'' is ''exo''-acting. A general [[sub-site nomenclature]] exists to demarcate substrate binding in glycosidase active-sites. |
| − | [[Image:exo_endo.png | + | [[Image:exo_endo.png|center|600px]] |
=== Enzyme Commission (EC) number === | === Enzyme Commission (EC) number === | ||
| Line 22: | Line 20: | ||
=== Mechanistic classification === | === Mechanistic classification === | ||
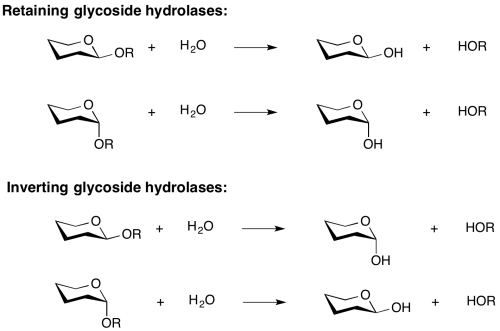
| + | Two reaction mechanisms are most commonly found for the retaining and inverting enzymes, as first outlined by Koshland and as described below.<cite>Gebler1992</cite> However several interesting variations on these mechanisms have been found, and one fundamentally different mechanism, catalyzed by an NADH cofactor, has been discovered in recent years, as discussed below. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Retaining&inverting_GH.png|center|500px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | [[Image:Retaining& | ||
=== Sequence-based classification === | === Sequence-based classification === | ||
| − | [[Sequence-based classification]] uses algorithmic methods to assign sequences to various families. The glycoside hydrolases have been classified into more than 100 families <cite> | + | [[Sequence-based classification]] uses algorithmic methods to assign sequences to various families. The glycoside hydrolases have been classified into more than 100 families <cite>Henrissat1991</cite>; this is permanently available through the Carbohydrate Active enZyme database <cite>CAZyURL</cite>. Each family (GH family) contains proteins that are related by sequence, and by corollary, fold. This allows a number of useful predictions to be made since it has long been noted that the catalytic machinery and molecular mechanism is conserved for the vast majority of the glycosidase families <cite>Gebler1992</cite> as well as the geometry around the glycosidic bond (irrespective of naming conventions) <cite>Henrissat1995</cite>. Usually, the mechanism used (ie [[retaining]] or [[inverting]]) is conserved within a GH family. One notable exception is the glycoside hydrolases of family [[GH97]], which contains both retaining and inverting enzymes; a glutamate acts as a [[general base]] in inverting members, whereas an aspartate likely acts as a [[catalytic nucleophile]] in retaining members <cite>Gloster2008</cite>. Another mechanistic curiosity are the glycoside hydrolases of familes [[GH4]] and [[GH109]] which operate through an [[NAD-dependent hydrolysis]] mechanism that proceeds through oxidation-elimination-addition-reduction steps via anionic [[transition state]]s <cite>Yip2007</cite>. This allows a single enzyme to hydrolyze both α- and β-glycosides. |
| − | Classification of families into larger groups, termed '[[clans]]' has been proposed <cite> | + | Classification of families into larger groups, termed '[[clans]]' has been proposed <cite>Henrissat1996</cite>. A '[[clan]]' is a group of families that possess significant similarity in their tertiary structure, catalytic residues and mechanism. Families within clans are thought to have a common evolutionary ancestry. For an updated table of glycoside hydrolase clans see the CAZy Database <cite>CAZyURL</cite>. |
== Mechanism == | == Mechanism == | ||
| − | + | Two reaction mechanisms are most commonly found for the retaining and inverting enzymes, as first outlined by Koshland and as described below <cite>Koshland1953</cite>. However several interesting variations on these mechanisms have been found, and one fundamentally different mechanism, catalyzed by an NADH cofactor, has been discovered in recent years. | |
| − | Two reaction mechanisms are most commonly found for the retaining and inverting enzymes, as first outlined by Koshland and as described below <cite> | ||
===Inverting glycoside hydrolases=== | ===Inverting glycoside hydrolases=== | ||
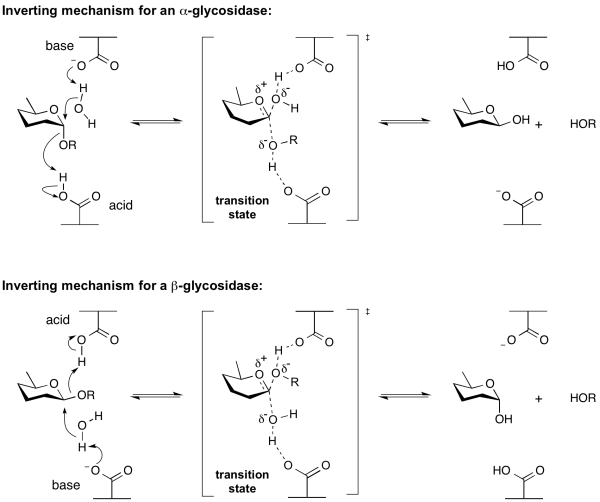
| + | Hydrolysis of a glycoside with net inversion of anomeric configuration is generally achieved via a one step, single-displacement mechanism involving [[oxocarbenium ion]]-like [[transition state]]s, as shown below. The reaction typically occurs with [[general acid]] and [[general base]] assistance from two amino acid side chains, normally glutamic or aspartic acids, that are typically located 6-11 A apart<cite>McCarter1994</cite>. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Inverting glucosidase mechanism.png|centre|600px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | [[Image:Inverting glucosidase mechanism.png|centre]] | ||
| − | |||
====Glycosyl-phosphate cleaving enzymes that lack a general acid==== | ====Glycosyl-phosphate cleaving enzymes that lack a general acid==== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
A subset of family [[GH92]] α-mannosidases catalyze the hydrolysis of mannose-1-phosphate linkages found in the mannose-1-phosphate-6-mannose groups of yeast mannoproteins. In these enzymes the usual [[general acid]] glutamic acid found in other members of this family is replaced by a glutamine. It has been suggested that the phosphate aglycon is a sufficiently good leaving group to be able to cleave in the first glycosylation step to form the glycosyl enzyme [[intermediate]] without the requirement of an acid catalyst <cite>Tiels2012</cite>. This replacement may also reduce charge repulsion between the glutamic acid residue and the anionic phosphate aglycon. A related example may be found in the case of the family [[GH1]] myrosinases. | A subset of family [[GH92]] α-mannosidases catalyze the hydrolysis of mannose-1-phosphate linkages found in the mannose-1-phosphate-6-mannose groups of yeast mannoproteins. In these enzymes the usual [[general acid]] glutamic acid found in other members of this family is replaced by a glutamine. It has been suggested that the phosphate aglycon is a sufficiently good leaving group to be able to cleave in the first glycosylation step to form the glycosyl enzyme [[intermediate]] without the requirement of an acid catalyst <cite>Tiels2012</cite>. This replacement may also reduce charge repulsion between the glutamic acid residue and the anionic phosphate aglycon. A related example may be found in the case of the family [[GH1]] myrosinases. | ||
===Retaining glycoside hydrolases=== | ===Retaining glycoside hydrolases=== | ||
| − | |||
====Classical Koshland retaining mechanism==== | ====Classical Koshland retaining mechanism==== | ||
| + | Hydrolysis with net retention of configuration is most commonly achieved via a two step, double-displacement mechanism involving a covalent glycosyl-enzyme [[intermediate]], as is shown in the figure below. Each step passes through an [[oxocarbenium ion]]-like [[transition state]]. Reaction occurs with acid/base and nucleophilic assistance provided by two amino acid side chains, typically glutamate or aspartate, located 5.5 A apart. In the first step (often called the glycosylation step), one residue plays the role of a nucleophile, attacking the anomeric centre to displace the aglycon and form a glycosyl enzyme [[intermediate]]. At the same time the other residue functions as an acid catalyst and protonates the glycosidic oxygen as the bond cleaves. In the second step (known as the deglycosylation step), the glycosyl enzyme is hydrolyzed by water, with the other residue now acting as a base catalyst deprotonating the water molecule as it attacks. The pKa value of the acid/base group cycles between high and low values during catalysis to optimize it for its role at each step of catalysis <cite>McIntosh1996</cite>. In the case of sialidases, the catalytic nucleophile is a tyrosine residue (see below). This mechanism was originally proposed by Dan Koshland, although at the time the identities of the residues was unclear <cite>Koshland1953</cite>. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Retaining_glycosidase_mechanism.png|centre|600px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | [[Image: | ||
====Neighboring group participation==== | ====Neighboring group participation==== | ||
| + | =====By a neighboring 2-acetamido group===== | ||
| + | Enzymes of [[GH18]], [[GH20]], [[GH25]], [[GH56]], [[GH84]], [[GH85]] and [[GH123]] hydrolyse substrates containing an ''N''-acetyl (acetamido) or ''N''-glycolyl group at the 2-position. These enzymes have no catalytic nucleophile: rather they utilize a mechanism in which the 2-acetamido group acts as an intramolecular nucleophile. Neighboring group participation by the 2-acetamido group leads to formation of an oxazoline (or more strictly an [[oxazolinium ion]]) [[intermediate]]. This mechanism was deduced from X-ray structures of complexes of chitinases with natural inhibitors <cite>Terwisscha1995</cite>, from the potent inhibition afforded by a stable thiazoline analogue of the oxazoline <cite>Knapp1996 Mark2001</cite>, and from detailed mechanistic analyses using substrates of modified reactivity <cite>Vocadlo2005</cite>. Typically, a stabilizing residue (a carboxylate) stabilizes the charge development in the [[transition state]]. Not all enzymes that cleave substrates possessing a 2-acetamido group utilize a neighboring groups participation mechanism; enzymes from [[GH3]] and [[GH22]] utilize a classical retaining mechanism with an enzymic nucleophile. Other hexosaminidases such as those of [[Glycoside Hydrolase Family 19]] utilize an inverting mechanism. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Hex_neighboring_mechanism.png|centre|700px]] | |
| − | [[ | + | =====By a neighboring 2-hydroxyl group===== |
| + | Enzymes of [[Glycoside Hydrolase Family 99]] hydrolyse α-mannoside substrates and lack a enzymic catalytic nucleophile. These enzymes use a mechanism in which the 2-hydroxyl group acts as an intramolecular nucleophile. Neighboring group participation by the 2-hydroxy group leads to formation of an epoxide (or more strictly a 1,2-anhydro sugar). This mechanism was implicated from 3D X-ray structures of complexes of bacterial endomannosidase/endomannanase with iminosugar inhibitors <cite>Thompson2012</cite>. Detailed mechanistic analyses using carbocyclic analogues of the 1,2-anhydro sugar, quantum mechanic/molecular mechanics computational modelling, and kinetic isotope effects <cite>Sobala2020</cite>. | ||
====Myrosinases: Retaining glycoside hydrolases that lack a general acid and utilize an exogenous base==== | ====Myrosinases: Retaining glycoside hydrolases that lack a general acid and utilize an exogenous base==== | ||
| + | Glycoside hydrolases termed myrosinases catalyze the hydrolysis of anionic thioglycosides (glucosinolates) found in plants. They are found in [[Glycoside Hydrolase Family 1]]. In these enzymes the usual acid/base glutamic acid found in other members of this family is replaced by a glutamine. This likely reduces charge repulsion between the anionic aglycon sulfate. The unusual aglycon is a sufficiently good leaving group to be able to cleave in the first glycosylation step to form the glycosyl enzyme [[intermediate]] without the requirement of an acid catalyst. However, since a base catalyst is required for the second step (hydrolysis or deglycosylation) these enzymes require an alternative basic group. This is provided by the co-enzyme L-ascorbate <cite>Burmeister2000</cite>. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:myrosinase.png|centre|550px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | [[Image:myrosinase.png|centre]] | ||
====Alternative nucleophiles==== | ====Alternative nucleophiles==== | ||
| + | Several groups of retaining glycosidases use atypical nucleophiles. These include the sialidases and trans-sialidases of [[GH33]] and [[GH34]], and 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-lyxo-heptulosaric acid hydrolases of [[GH143]] <cite>Ndeh2017</cite>. Glycoside hydrolases of these families utilize a tyrosine as a catalytic nucleophile, which is believed to be activated by an adjacent base residue. A rationale for this unusual difference is that the use of a negatively charged carboxylate as a nucelophile will be disfavoured as the anomeric centre is itself negatively charged, and thus charge repulsion interferes. A tyrosine residue is a neutral nucleophile, but requires a general base to enhance its nucleophilicity. This mechanism was implied from X-ray structures, and was supported by experiments involving trapping of the [[intermediate]] with fluorosugars followed by peptide mapping and then crystallography <cite>Amaya2004 Watts2003</cite>, as well as via mechanistic studies on mutants <cite>Watson2003</cite>. A cysteine nucleophile has been demonstrated for Zn<sup>2+</sup>-dependent arabinofuranosidases of families [[GH127]] and [[GH146]] through X-ray crystallography of the covalently labelled nucleophilic cysteine and MD and QM/MM simulations <cite>#McGregor2021</cite>. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:sialidase_mechanism.png|center|700px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | [[Image:sialidase_mechanism.png|center]] | ||
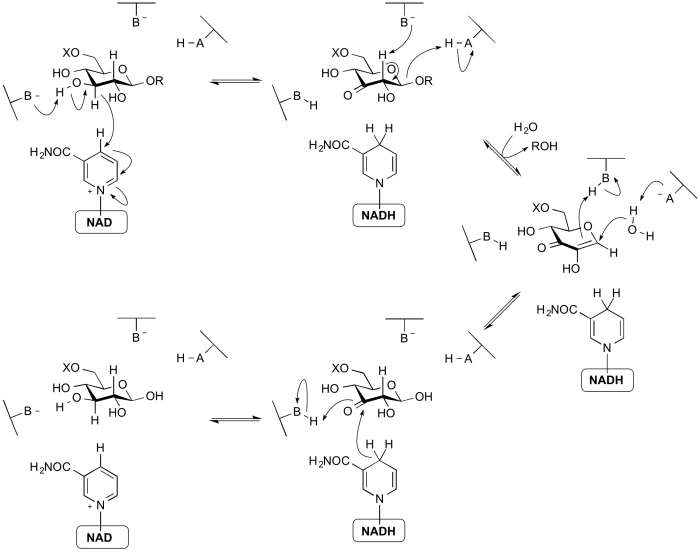
====NAD-dependent hydrolysis==== | ====NAD-dependent hydrolysis==== | ||
| + | The members of [[GH4]], [[GH109]], [[GH177]] and [[GH179]] use a mechanism that requires an NAD cofactor, which remains tightly bound throughout catalysis. The mechanism proceeds via anionic [[transition state]]s with elimination and redox steps rather than the classical mechanisms proceeding through[[oxocarbenium ion]]-like transition states. As shown below for a 6-phospho-β-glucosidase, the mechanism involves an initial oxidation of the 3-hydroxyl of the substrate by the enzyme-bound NAD cofactor. This increases the acidity of the C2 proton such that an E1<sub>cb</sub> elimination can occur with assistance from an enzymatic base. The α,β-unsaturated [[intermediate]] formed then undergoes addition of water at the anomeric centre and finally the ketone at C3 is reduced to generate the free sugar product. Thus, even though glycosidic bond cleavage occurred via an elimination mechanism, the overall reaction is hydrolysis. This mechanism was elucidated through a combination of stereochemical studies by NMR, kinetic isotope effects, linear free energy relationships, X-ray crystallography and UV/Vis spectrophotometry <cite>Yip2004 Rajan2004</cite>. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Family_4_mechanism.png|center|700px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | [[Image:Family_4_mechanism.png|center]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
| − | # | + | #McCarter1994 pmid=7712292 |
| − | # | + | #Koshland1953 Koshland, D. (1953) ''Biol. Rev.'' 28, 416. |
| − | # | + | #McIntosh1996 pmid=8756457 |
| − | # | + | #Gebler1992 pmid=1618761 |
| − | # | + | #Henrissat1995 pmid=7624375 |
| − | # | + | #Terwisscha1995 pmid=7495789 |
| − | # | + | #Mark2001 pmid=11124970 |
| − | # | + | #Knapp1996 Knapp, S., Vocadlo, D., Gao, Z. N., Kirk, B., Lou, J. P., and Withers, S. G. (1996) ''Journal of the American Chemical Society 118'', 6804-6805. |
| − | # | + | #Vocadlo2005 pmid=16171396 |
| − | # | + | #Burmeister2000 pmid=10978344 |
| − | # | + | #Amaya2004 pmid=15130470 |
| − | # | + | #Watts2003 pmid=12812490 |
| − | # | + | #Watson2003 pmid=14580216 |
| − | # | + | #Yip2004 pmid=15237973 |
| − | # | + | #Rajan2004 pmid=15341727 |
| + | #CAZyURL Carbohydrate Active Enzymes database; URL http://www.cazy.org/ | ||
| + | #Henrissat1991 pmid=1747104 | ||
| + | #Henrissat1996 pmid=8687420 | ||
| + | #Gloster2008 pmid=18848471 | ||
| + | #Yip2007 pmid=17676871 | ||
| + | #Tiels2012 pmid=23159880 | ||
| + | #DaviesHenrissat1995 pmid=8535779 | ||
| + | #Ndeh2017 pmid=28329766 | ||
| + | #Sobala2020 pmid=32490192 | ||
| + | #McGregor2021 pmid=33528085 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
[[Category:Definitions and explanations]] | [[Category:Definitions and explanations]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:29, 17 December 2023
This page has been approved by the Responsible Curator as essentially complete. CAZypedia is a living document, so further improvement of this page is still possible. If you would like to suggest an addition or correction, please contact the page's Responsible Curator directly by e-mail.
- Authors: Steve Withers, Spencer Williams
- Responsible Curator: Spencer Williams
Overview
Glycoside hydrolases are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of the glycosidic linkage of glycosides, leading to the formation of a sugar hemiacetal or hemiketal and the corresponding free aglycon. Glycoside hydrolases are also referred to as glycosidases, and sometimes also as glycosyl hydrolases. Glycoside hydrolases can catalyze the hydrolysis of O-, N- and S-linked glycosides.
Classification
Glycoside hydrolases can be classified in many different ways. The following paragraphs list several different ways, the utility of which depends on the context in which the classification is made and used.
Endo/exo
exo- and endo- refers to the ability of a glycoside hydrolase to cleave a substrate at the end (most frequently, but not always the non-reducing end) or within the middle of a chain [1]. For example, most cellulases are endo-acting, whereas LacZ β-galactosidase from E. coli is exo-acting. A general sub-site nomenclature exists to demarcate substrate binding in glycosidase active-sites.
Enzyme Commission (EC) number
EC numbers are codes representing the Enzyme Commission number. This is a numerical classification scheme for enzymes, based on the chemical reactions they catalyze. Every EC number is associated with a recommended name for the respective enzyme. EC numbers do not specify enzymes, but enzyme-catalyzed reactions. If different enzymes (for instance from different organisms) catalyze the same reaction, then they receive the same EC number. A necessary consequence of the EC classification scheme is that codes can be applied only to enzymes for which a function has been biochemically identified. Additionally, certain enzymes can catalyze reactions that fall in more than one class. These enzymes must bear more than one EC number.
Mechanistic classification
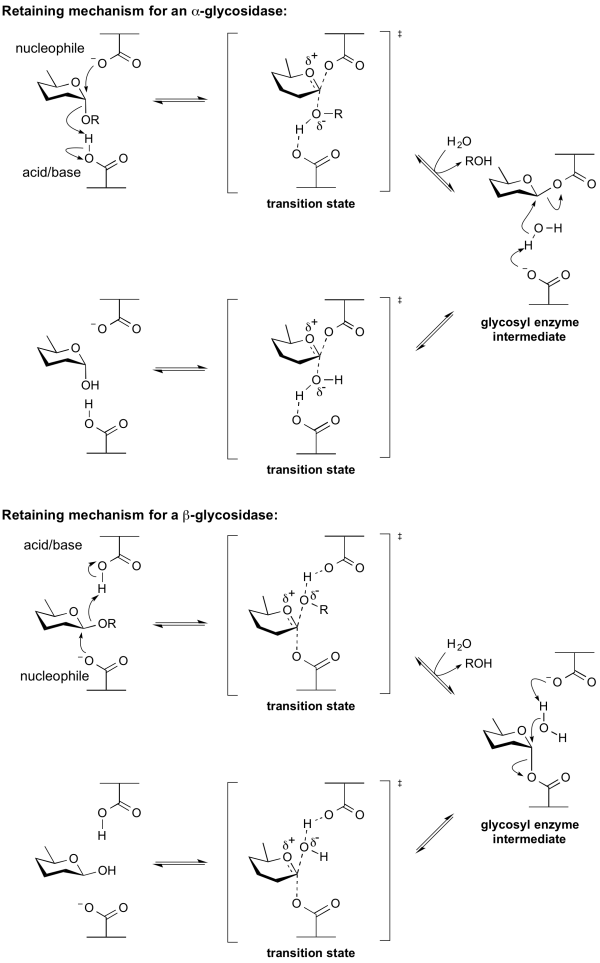
Two reaction mechanisms are most commonly found for the retaining and inverting enzymes, as first outlined by Koshland and as described below.[2] However several interesting variations on these mechanisms have been found, and one fundamentally different mechanism, catalyzed by an NADH cofactor, has been discovered in recent years, as discussed below.
Sequence-based classification
Sequence-based classification uses algorithmic methods to assign sequences to various families. The glycoside hydrolases have been classified into more than 100 families [3]; this is permanently available through the Carbohydrate Active enZyme database [4]. Each family (GH family) contains proteins that are related by sequence, and by corollary, fold. This allows a number of useful predictions to be made since it has long been noted that the catalytic machinery and molecular mechanism is conserved for the vast majority of the glycosidase families [2] as well as the geometry around the glycosidic bond (irrespective of naming conventions) [5]. Usually, the mechanism used (ie retaining or inverting) is conserved within a GH family. One notable exception is the glycoside hydrolases of family GH97, which contains both retaining and inverting enzymes; a glutamate acts as a general base in inverting members, whereas an aspartate likely acts as a catalytic nucleophile in retaining members [6]. Another mechanistic curiosity are the glycoside hydrolases of familes GH4 and GH109 which operate through an NAD-dependent hydrolysis mechanism that proceeds through oxidation-elimination-addition-reduction steps via anionic transition states [7]. This allows a single enzyme to hydrolyze both α- and β-glycosides.
Classification of families into larger groups, termed 'clans' has been proposed [8]. A 'clan' is a group of families that possess significant similarity in their tertiary structure, catalytic residues and mechanism. Families within clans are thought to have a common evolutionary ancestry. For an updated table of glycoside hydrolase clans see the CAZy Database [4].
Mechanism
Two reaction mechanisms are most commonly found for the retaining and inverting enzymes, as first outlined by Koshland and as described below [9]. However several interesting variations on these mechanisms have been found, and one fundamentally different mechanism, catalyzed by an NADH cofactor, has been discovered in recent years.
Inverting glycoside hydrolases
Hydrolysis of a glycoside with net inversion of anomeric configuration is generally achieved via a one step, single-displacement mechanism involving oxocarbenium ion-like transition states, as shown below. The reaction typically occurs with general acid and general base assistance from two amino acid side chains, normally glutamic or aspartic acids, that are typically located 6-11 A apart[10].
Glycosyl-phosphate cleaving enzymes that lack a general acid
A subset of family GH92 α-mannosidases catalyze the hydrolysis of mannose-1-phosphate linkages found in the mannose-1-phosphate-6-mannose groups of yeast mannoproteins. In these enzymes the usual general acid glutamic acid found in other members of this family is replaced by a glutamine. It has been suggested that the phosphate aglycon is a sufficiently good leaving group to be able to cleave in the first glycosylation step to form the glycosyl enzyme intermediate without the requirement of an acid catalyst [11]. This replacement may also reduce charge repulsion between the glutamic acid residue and the anionic phosphate aglycon. A related example may be found in the case of the family GH1 myrosinases.
Retaining glycoside hydrolases
Classical Koshland retaining mechanism
Hydrolysis with net retention of configuration is most commonly achieved via a two step, double-displacement mechanism involving a covalent glycosyl-enzyme intermediate, as is shown in the figure below. Each step passes through an oxocarbenium ion-like transition state. Reaction occurs with acid/base and nucleophilic assistance provided by two amino acid side chains, typically glutamate or aspartate, located 5.5 A apart. In the first step (often called the glycosylation step), one residue plays the role of a nucleophile, attacking the anomeric centre to displace the aglycon and form a glycosyl enzyme intermediate. At the same time the other residue functions as an acid catalyst and protonates the glycosidic oxygen as the bond cleaves. In the second step (known as the deglycosylation step), the glycosyl enzyme is hydrolyzed by water, with the other residue now acting as a base catalyst deprotonating the water molecule as it attacks. The pKa value of the acid/base group cycles between high and low values during catalysis to optimize it for its role at each step of catalysis [12]. In the case of sialidases, the catalytic nucleophile is a tyrosine residue (see below). This mechanism was originally proposed by Dan Koshland, although at the time the identities of the residues was unclear [9].
Neighboring group participation
By a neighboring 2-acetamido group
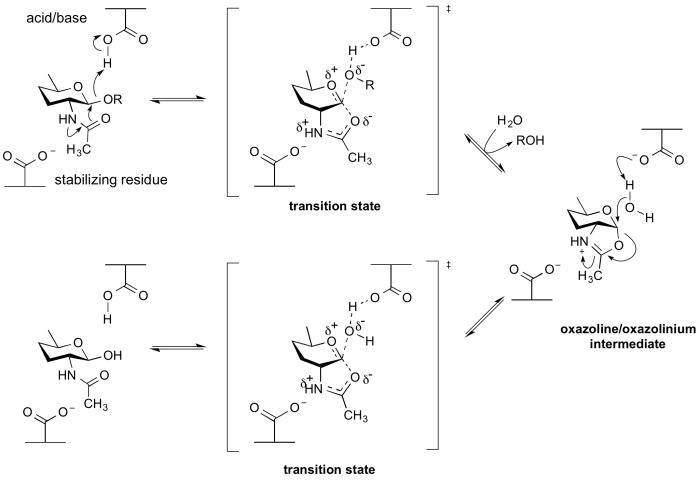
Enzymes of GH18, GH20, GH25, GH56, GH84, GH85 and GH123 hydrolyse substrates containing an N-acetyl (acetamido) or N-glycolyl group at the 2-position. These enzymes have no catalytic nucleophile: rather they utilize a mechanism in which the 2-acetamido group acts as an intramolecular nucleophile. Neighboring group participation by the 2-acetamido group leads to formation of an oxazoline (or more strictly an oxazolinium ion) intermediate. This mechanism was deduced from X-ray structures of complexes of chitinases with natural inhibitors [13], from the potent inhibition afforded by a stable thiazoline analogue of the oxazoline [14, 15], and from detailed mechanistic analyses using substrates of modified reactivity [16]. Typically, a stabilizing residue (a carboxylate) stabilizes the charge development in the transition state. Not all enzymes that cleave substrates possessing a 2-acetamido group utilize a neighboring groups participation mechanism; enzymes from GH3 and GH22 utilize a classical retaining mechanism with an enzymic nucleophile. Other hexosaminidases such as those of Glycoside Hydrolase Family 19 utilize an inverting mechanism.
By a neighboring 2-hydroxyl group
Enzymes of Glycoside Hydrolase Family 99 hydrolyse α-mannoside substrates and lack a enzymic catalytic nucleophile. These enzymes use a mechanism in which the 2-hydroxyl group acts as an intramolecular nucleophile. Neighboring group participation by the 2-hydroxy group leads to formation of an epoxide (or more strictly a 1,2-anhydro sugar). This mechanism was implicated from 3D X-ray structures of complexes of bacterial endomannosidase/endomannanase with iminosugar inhibitors [17]. Detailed mechanistic analyses using carbocyclic analogues of the 1,2-anhydro sugar, quantum mechanic/molecular mechanics computational modelling, and kinetic isotope effects [18].
Myrosinases: Retaining glycoside hydrolases that lack a general acid and utilize an exogenous base
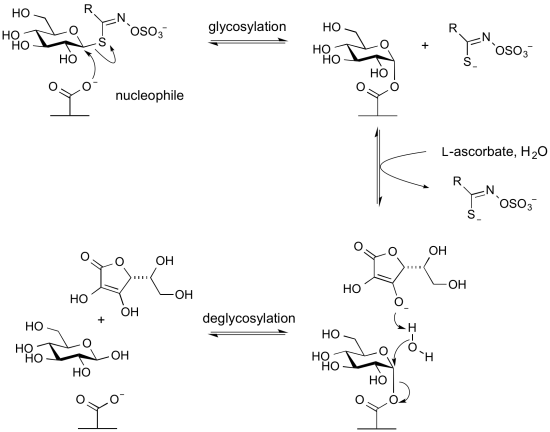
Glycoside hydrolases termed myrosinases catalyze the hydrolysis of anionic thioglycosides (glucosinolates) found in plants. They are found in Glycoside Hydrolase Family 1. In these enzymes the usual acid/base glutamic acid found in other members of this family is replaced by a glutamine. This likely reduces charge repulsion between the anionic aglycon sulfate. The unusual aglycon is a sufficiently good leaving group to be able to cleave in the first glycosylation step to form the glycosyl enzyme intermediate without the requirement of an acid catalyst. However, since a base catalyst is required for the second step (hydrolysis or deglycosylation) these enzymes require an alternative basic group. This is provided by the co-enzyme L-ascorbate [19].
Alternative nucleophiles
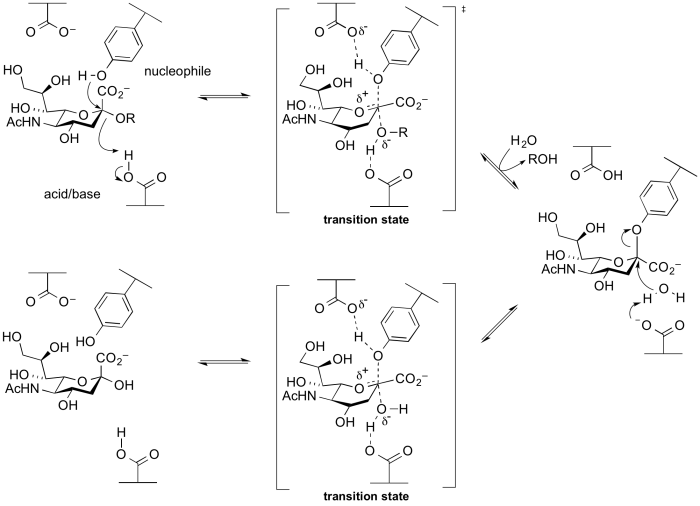
Several groups of retaining glycosidases use atypical nucleophiles. These include the sialidases and trans-sialidases of GH33 and GH34, and 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-lyxo-heptulosaric acid hydrolases of GH143 [20]. Glycoside hydrolases of these families utilize a tyrosine as a catalytic nucleophile, which is believed to be activated by an adjacent base residue. A rationale for this unusual difference is that the use of a negatively charged carboxylate as a nucelophile will be disfavoured as the anomeric centre is itself negatively charged, and thus charge repulsion interferes. A tyrosine residue is a neutral nucleophile, but requires a general base to enhance its nucleophilicity. This mechanism was implied from X-ray structures, and was supported by experiments involving trapping of the intermediate with fluorosugars followed by peptide mapping and then crystallography [21, 22], as well as via mechanistic studies on mutants [23]. A cysteine nucleophile has been demonstrated for Zn2+-dependent arabinofuranosidases of families GH127 and GH146 through X-ray crystallography of the covalently labelled nucleophilic cysteine and MD and QM/MM simulations [24].
NAD-dependent hydrolysis
The members of GH4, GH109, GH177 and GH179 use a mechanism that requires an NAD cofactor, which remains tightly bound throughout catalysis. The mechanism proceeds via anionic transition states with elimination and redox steps rather than the classical mechanisms proceeding throughoxocarbenium ion-like transition states. As shown below for a 6-phospho-β-glucosidase, the mechanism involves an initial oxidation of the 3-hydroxyl of the substrate by the enzyme-bound NAD cofactor. This increases the acidity of the C2 proton such that an E1cb elimination can occur with assistance from an enzymatic base. The α,β-unsaturated intermediate formed then undergoes addition of water at the anomeric centre and finally the ketone at C3 is reduced to generate the free sugar product. Thus, even though glycosidic bond cleavage occurred via an elimination mechanism, the overall reaction is hydrolysis. This mechanism was elucidated through a combination of stereochemical studies by NMR, kinetic isotope effects, linear free energy relationships, X-ray crystallography and UV/Vis spectrophotometry [25, 26].
References
- Davies G and Henrissat B. (1995). Structures and mechanisms of glycosyl hydrolases. Structure. 1995;3(9):853-9. DOI:10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00220-9 |
- Gebler J, Gilkes NR, Claeyssens M, Wilson DB, Béguin P, Wakarchuk WW, Kilburn DG, Miller RC Jr, Warren RA, and Withers SG. (1992). Stereoselective hydrolysis catalyzed by related beta-1,4-glucanases and beta-1,4-xylanases. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(18):12559-61. | Google Books | Open Library
- Henrissat B (1991). A classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem J. 1991;280 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):309-16. DOI:10.1042/bj2800309 |
-
Carbohydrate Active Enzymes database; URL http://www.cazy.org/
- Henrissat B, Callebaut I, Fabrega S, Lehn P, Mornon JP, and Davies G. (1995). Conserved catalytic machinery and the prediction of a common fold for several families of glycosyl hydrolases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(15):7090-4. DOI:10.1073/pnas.92.15.7090 |
- Gloster TM, Turkenburg JP, Potts JR, Henrissat B, and Davies GJ. (2008). Divergence of catalytic mechanism within a glycosidase family provides insight into evolution of carbohydrate metabolism by human gut flora. Chem Biol. 2008;15(10):1058-67. DOI:10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.09.005 |
- Yip VL, Thompson J, and Withers SG. (2007). Mechanism of GlvA from Bacillus subtilis: a detailed kinetic analysis of a 6-phospho-alpha-glucosidase from glycoside hydrolase family 4. Biochemistry. 2007;46(34):9840-52. DOI:10.1021/bi700536p |
- Henrissat B and Bairoch A. (1996). Updating the sequence-based classification of glycosyl hydrolases. Biochem J. 1996;316 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):695-6. DOI:10.1042/bj3160695 |
-
Koshland, D. (1953) Biol. Rev. 28, 416.
- McCarter JD and Withers SG. (1994). Mechanisms of enzymatic glycoside hydrolysis. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1994;4(6):885-92. DOI:10.1016/0959-440x(94)90271-2 |
- Tiels P, Baranova E, Piens K, De Visscher C, Pynaert G, Nerinckx W, Stout J, Fudalej F, Hulpiau P, Tännler S, Geysens S, Van Hecke A, Valevska A, Vervecken W, Remaut H, and Callewaert N. (2012). A bacterial glycosidase enables mannose-6-phosphate modification and improved cellular uptake of yeast-produced recombinant human lysosomal enzymes. Nat Biotechnol. 2012;30(12):1225-31. DOI:10.1038/nbt.2427 |
- McIntosh LP, Hand G, Johnson PE, Joshi MD, Körner M, Plesniak LA, Ziser L, Wakarchuk WW, and Withers SG. (1996). The pKa of the general acid/base carboxyl group of a glycosidase cycles during catalysis: a 13C-NMR study of bacillus circulans xylanase. Biochemistry. 1996;35(31):9958-66. DOI:10.1021/bi9613234 |
- Terwisscha van Scheltinga AC, Armand S, Kalk KH, Isogai A, Henrissat B, and Dijkstra BW. (1995). Stereochemistry of chitin hydrolysis by a plant chitinase/lysozyme and X-ray structure of a complex with allosamidin: evidence for substrate assisted catalysis. Biochemistry. 1995;34(48):15619-23. DOI:10.1021/bi00048a003 |
-
Knapp, S., Vocadlo, D., Gao, Z. N., Kirk, B., Lou, J. P., and Withers, S. G. (1996) Journal of the American Chemical Society 118, 6804-6805.
- Mark BL, Vocadlo DJ, Knapp S, Triggs-Raine BL, Withers SG, and James MN. (2001). Crystallographic evidence for substrate-assisted catalysis in a bacterial beta-hexosaminidase. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(13):10330-7. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M011067200 |
- Vocadlo DJ and Withers SG. (2005). Detailed comparative analysis of the catalytic mechanisms of beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases from families 3 and 20 of glycoside hydrolases. Biochemistry. 2005;44(38):12809-18. DOI:10.1021/bi051121k |
- Sobala LF, Speciale G, Zhu S, Raich L, Sannikova N, Thompson AJ, Hakki Z, Lu D, Shamsi Kazem Abadi S, Lewis AR, Rojas-Cervellera V, Bernardo-Seisdedos G, Zhang Y, Millet O, Jiménez-Barbero J, Bennet AJ, Sollogoub M, Rovira C, Davies GJ, and Williams SJ. (2020). An Epoxide Intermediate in Glycosidase Catalysis. ACS Cent Sci. 2020;6(5):760-770. DOI:10.1021/acscentsci.0c00111 |
- Burmeister WP, Cottaz S, Rollin P, Vasella A, and Henrissat B. (2000). High resolution X-ray crystallography shows that ascorbate is a cofactor for myrosinase and substitutes for the function of the catalytic base. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(50):39385-93. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M006796200 |
- Ndeh D, Rogowski A, Cartmell A, Luis AS, Baslé A, Gray J, Venditto I, Briggs J, Zhang X, Labourel A, Terrapon N, Buffetto F, Nepogodiev S, Xiao Y, Field RA, Zhu Y, O'Neil MA, Urbanowicz BR, York WS, Davies GJ, Abbott DW, Ralet MC, Martens EC, Henrissat B, and Gilbert HJ. (2017). Complex pectin metabolism by gut bacteria reveals novel catalytic functions. Nature. 2017;544(7648):65-70. DOI:10.1038/nature21725 |
- Amaya MF, Watts AG, Damager I, Wehenkel A, Nguyen T, Buschiazzo A, Paris G, Frasch AC, Withers SG, and Alzari PM. (2004). Structural insights into the catalytic mechanism of Trypanosoma cruzi trans-sialidase. Structure. 2004;12(5):775-84. DOI:10.1016/j.str.2004.02.036 |
- Watts AG, Damager I, Amaya ML, Buschiazzo A, Alzari P, Frasch AC, and Withers SG. (2003). Trypanosoma cruzi trans-sialidase operates through a covalent sialyl-enzyme intermediate: tyrosine is the catalytic nucleophile. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125(25):7532-3. DOI:10.1021/ja0344967 |
- Watson JN, Dookhun V, Borgford TJ, and Bennet AJ. (2003). Mutagenesis of the conserved active-site tyrosine changes a retaining sialidase into an inverting sialidase. Biochemistry. 2003;42(43):12682-90. DOI:10.1021/bi035396g |
- McGregor NGS, Coines J, Borlandelli V, Amaki S, Artola M, Nin-Hill A, Linzel D, Yamada C, Arakawa T, Ishiwata A, Ito Y, van der Marel GA, Codée JDC, Fushinobu S, Overkleeft HS, Rovira C, and Davies GJ. (2021). Cysteine Nucleophiles in Glycosidase Catalysis: Application of a Covalent β-l-Arabinofuranosidase Inhibitor. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021;60(11):5754-5758. DOI:10.1002/anie.202013920 |
- Yip VL, Varrot A, Davies GJ, Rajan SS, Yang X, Thompson J, Anderson WF, and Withers SG. (2004). An unusual mechanism of glycoside hydrolysis involving redox and elimination steps by a family 4 beta-glycosidase from Thermotoga maritima. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126(27):8354-5. DOI:10.1021/ja047632w |
- Rajan SS, Yang X, Collart F, Yip VL, Withers SG, Varrot A, Thompson J, Davies GJ, and Anderson WF. (2004). Novel catalytic mechanism of glycoside hydrolysis based on the structure of an NAD+/Mn2+ -dependent phospho-alpha-glucosidase from Bacillus subtilis. Structure. 2004;12(9):1619-29. DOI:10.1016/j.str.2004.06.020 |