CAZypedia celebrates the life of Senior Curator Emeritus Harry Gilbert, a true giant in the field, who passed away in September 2025.
CAZypedia needs your help!
We have many unassigned pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators. See a page that's out-of-date and just needs a touch-up? - You are also welcome to become a CAZypedian. Here's how.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute.
Learn more about CAZypedia's misson here and in this article. Totally new to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
Difference between revisions of "Glycosyltransferase Family 38"
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
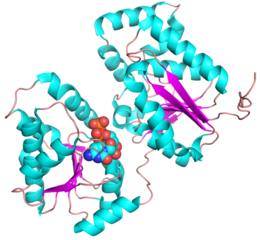
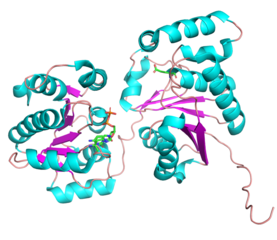
== Three-dimensional structures == | == Three-dimensional structures == | ||
| − | + | <gallery widths=320px heights=240px perrow=2 caption="PDB ID 5WC6 from GT38 (click images for large versions)"> | |
| + | File:GT38 3.png|top view | ||
| + | File:GT38 4.png|side view | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | == Family Firsts == | ||
| − | + | ; First general acid/base residue identification: E153, H291 | |
| + | ; First 3-D structure: PDB 5WC6 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| + | |||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
# Cho1994 pmid=7972078 | # Cho1994 pmid=7972078 | ||
| Line 63: | Line 65: | ||
# Devi1991 pmid=1898915 | # Devi1991 pmid=1898915 | ||
# Glode1977 pmid=64575 | # Glode1977 pmid=64575 | ||
| − | + | ||
# Lindhout2013 pmid=23922842 | # Lindhout2013 pmid=23922842 | ||
# Peterson2011 pmid=21278299 | # Peterson2011 pmid=21278299 | ||
| Line 72: | Line 74: | ||
# Willis2013 pmid=23610430 | # Willis2013 pmid=23610430 | ||
# Willis2008 pmid=18000029 | # Willis2008 pmid=18000029 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
# Lizak2017 pmid=28724897 | # Lizak2017 pmid=28724897 | ||
Revision as of 14:15, 27 May 2020
This page is currently under construction. This means that the Responsible Curator has deemed that the page's content is not quite up to CAZypedia's standards for full public consumption. All information should be considered to be under revision and may be subject to major changes.
- Author: ^^^Warren Wakarchuk^^^
- Responsible Curator: ^^^Warren Wakarchuk^^^
| Glycosyltransferase Family GT38 | |
| Clan | GT-B |
| Mechanisn | inverting |
| Active site residues | known |
| CAZy DB link | |
| https://www.cazy.org/GT38.html | |
Substrate specificities
Members of GT-38 are the bacterial polysialyltransferases (polySTs), which catalyze the addition of sialic acids from the activated sugar donor, CMP-sialic acid (CMP-Neu5Ac), to the nonreducing end of the growing polySia chain [1]. These enzymes build the polymer as a capsular polysaccharide on a specialized poly-β-KDO modified lyso-phosphatidyl glycerol anchor in the membrane of Gram negative bacteria [2]. Bacterial polySia capsules exist in three different flavours: Escherichia coli K1, Neisseria meningitidis serotype B, Moraxella nonliquefaciens, and Mannheimia haemolytica A2 synthesize α-2,8-linked polySia whereas N. meningitidis serotype C produces a α-2,9-linked polymer and E. coli K92 produces polymers with alternating α-2,8 and α-2,9 linkages [3] [4][5][6]. In vitro enzyme reactions have shown that the members of GT-38 require two sialic acids for elongation [7][8][9], presumably as this mimics the in vivo lipid primer. The enzymes have been used in applications to modify therapeutic proteins and prepare synthetic vaccines [10][11], where un-natural acceptors like protein N-glycans have been used.
Kinetics and Mechanism
Sialic acid transfer occurs with inversion of configuration (from the β-linked CMP-Neu5Ac donor to the α-2,8-linked polySia), and polyST has been proposed to follow a SN2-like direct displacement mechanism. While H291 could act as a catalytic acid to stabilize the nucleotide phosphate-leaving group.
Catalytic Residues
Residues involved in catalysis have been proposed from site-directed mutagensis and the X-ray crystal structure from the M. hemolytica serotype A2 enzyme [12]. The catalytic base E153 abstracts a proton from the C8′ hydroxyl group of the sialic acid acceptor concerted with the nucleophilic attack on the anomeric C2′ carbon of the CMP-sialic acid donor substrate, thereby generating an α-2,8 glycosidic linkage. The resulting negatively charged CMP leaving group is stabilized by H291 assisted by S339 and T340.
Three-dimensional structures
- PDB ID 5WC6 from GT38 (click images for large versions)
Family Firsts
- First general acid/base residue identification
- E153, H291
- First 3-D structure
- PDB 5WC6
References
Error fetching PMID 23610430:
Error fetching PMID 408435:
Error fetching PMID 10052589:
Error fetching PMID 1898915:
Error fetching PMID 64575:
Error fetching PMID 23922842:
Error fetching PMID 21278299:
Error fetching PMID 21502532:
Error fetching PMID 23949787:
Error fetching PMID 23610430:
Error fetching PMID 18000029:
Error fetching PMID 28724897:
- Error fetching PMID 7972078:
- Error fetching PMID 23610430:
- Error fetching PMID 23610430:
- Error fetching PMID 408435:
- Error fetching PMID 10052589:
- Error fetching PMID 1898915:
- Error fetching PMID 64575:
- Error fetching PMID 18000029:
- Error fetching PMID 21278299:
- Error fetching PMID 23922842:
- Error fetching PMID 21502532:
- Error fetching PMID 23949787:
- Error fetching PMID 28724897: