CAZypedia celebrates the life of Senior Curator Emeritus Harry Gilbert, a true giant in the field, who passed away in September 2025.
CAZypedia needs your help!
We have many unassigned pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators. See a page that's out-of-date and just needs a touch-up? - You are also welcome to become a CAZypedian. Here's how.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute.
Learn more about CAZypedia's misson here and in this article. Totally new to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
Difference between revisions of "Auxiliary Activity Family 5"
Harry Brumer (talk | contribs) (deleted double Forget2020 citation in biblio section) |
|||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{CuratorApproved}} | |
| − | + | * [[Author]]: [[User:Maria Cleveland|Maria Cleveland]] and [[User:Yann Mathieu|Yann Mathieu]] | |
| − | * [[Author]]: | + | * [[Responsible Curator]]: [[User:Harry Brumer|Harry Brumer]] |
| − | * [[Responsible Curator]]: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 28: | Line 27: | ||
== Substrate Specificities == | == Substrate Specificities == | ||
| − | Enzymes from Auxiliary Activity Family 5 (AA5) are mononuclear copper-radical oxidases (CROs) that perform the two-electron oxidation of substrates using oxygen as the final electron acceptor ([{{EClink}}1.1.3.- EC 1.1.3.-]) <cite>Kersten2014</cite>. AA5 members are further classified into two major subfamilies <cite>Levasseur2013</cite> | + | Enzymes from Auxiliary Activity Family 5 (AA5) are mononuclear copper-radical oxidases (CROs) that perform the two-electron oxidation of substrates using oxygen as the final electron acceptor ([{{EClink}}1.1.3.- EC 1.1.3.-]) <cite>Kersten2014</cite>. AA5 members are further classified into two major subfamilies <cite>Levasseur2013</cite>. Subfamily AA5_1 contains characterized glyoxal oxidases ([{{EClink}}1.2.3.15 EC 1.2.3.15]) <cite>Daou2017</cite>. Subfamily AA5_2 contains galactose 6-oxidases ([{{EClink}}1.1.3.9 EC 1.1.3.9]), which oxidize the C-6 hydroxyl of diverse galactosides to the corresponding aldehyde <cite>Whittaker2003,Andberg2017,Cleveland2021b</cite>. AA5_2 also contains the more recently discovered general alcohol oxidases ([{{EClink}}1.1.3.13 EC 1.1.3.13]) <cite>Yin2015,Oide2019,Cleveland2021b</cite> and aryl alcohol oxidases ([{{EClink}}1.1.3.7 EC 1.1.3.7]) <cite>Mathieu2020,Cleveland2021a</cite>. The first biochemically characterized member of AA5 was the galactose 6-oxidase from the phytopathogenic fungus ''Fusarium graminearum'' (previously known as ''Polyporus circinatus'' and ''Cladobotryum (Dactylium) dendroides'' <cite>Ogel1994</cite>), which was originally reported in 1959 following isolation from cultures <cite>Cooper1959 Avigad1962</cite>. Subsequently, the ''Fusarium graminearum'' galactose 6-oxidase became the defining member of AA5_2 <cite>Levasseur2013</cite>. The first characterized member of what is now known as AA5_1 is the glyoxal oxidase from ''Phanerochaete chrysosporium'', which was likewise isolated from fungal culture <cite>Kersten1987</cite>. |
In contrast to their fungal and bacterial counterparts, plant AA5 members do not fall within the two defined subfamilies. An AA5 enzyme from ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' has been demonstrated ''in vivo'' to have galactose 6-oxidase activity and promote cell-to-cell adhesion in the seed coat epidermis <cite>Sola2019</cite> (see also <cite>Sola2021</cite>). Additionally, a ''Streptomyces lividans'' enzyme, GlxA, which is distantly related to AA5, has been shown to oxidize glycolaldehyde and a deletion mutant showed a loss of glycan accumulation at hyphal tips <cite>Chaplin2015</cite>. | In contrast to their fungal and bacterial counterparts, plant AA5 members do not fall within the two defined subfamilies. An AA5 enzyme from ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' has been demonstrated ''in vivo'' to have galactose 6-oxidase activity and promote cell-to-cell adhesion in the seed coat epidermis <cite>Sola2019</cite> (see also <cite>Sola2021</cite>). Additionally, a ''Streptomyces lividans'' enzyme, GlxA, which is distantly related to AA5, has been shown to oxidize glycolaldehyde and a deletion mutant showed a loss of glycan accumulation at hyphal tips <cite>Chaplin2015</cite>. | ||
=== AA5_1 === | === AA5_1 === | ||
| − | The AA5_1 members are generally known as glyoxal oxidases ([{{EClink}}1.2.3.15 EC 1.2.3.15]), characterized | + | The AA5_1 members are generally known as glyoxal oxidases ([{{EClink}}1.2.3.15 EC 1.2.3.15]), characterized examples of which typically accept a range of simple aldehydes, α-hydroxycarbonyl, and α-dicarbonyl compounds as substrates, with the highest activities observed on glyoxal, methylglyoxal and glycolaldehyde <cite>Whittaker1996,Whittaker1999,Kersten1987,Leuthner2004,Kersten2014</cite>. In contrast, two glyoxal oxidases form ''Pycnoporus cinnabarinus'' demonstrated the highest catalytic efficiency on glyoxylic acid <cite>Daou2016</cite>. An apparent distinction between the AA5_1 and AA5_2 subfamilies is that while AA5_1 enzymes catalyze the oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids <cite>Kersten2014</cite>, AA5_2 members oxidize primary alcohols to the corresponding aldehyde (and, in some instances, also oxidize the aldehyde to the acid, albeit much more slowly) <cite>Whittaker2003,Parikka2015</cite>. Consequently, the oxidation of aldehydes by AA5 CROs has been suggested to proceed through the hydrated, ''gem''-diol species <cite>Whittaker1996</cite>. |
=== AA5_2 === | === AA5_2 === | ||
| − | The archetypal CRO and AA5 member is the ''Fusarium graminearum'' galactose 6-oxidase (''Fgr''GalOx), which catalyzes the regioselective oxidation of the C6-hydroxyl group on the monosaccharide galactose ([{{EClink}}1.1.3.7 EC 1.3.3.7]) <cite>Cooper1959 Avigad1962</cite>. The range of substrates oxidized by ''Fgr''GalOx also includes galactosides as methyl beta-galactopyranoside <cite>Paukner2015</cite>, and galactose-containing di-, oligo-, and polysaccharides, including lactose, melibiose, raffinose, galactoxyloglucan, galactomannan and galactoglucomannan <cite>Parikka2015,Parikka2010</cite>. Several other AA5_2 members from ''Fusarium'' species, such as those from ''F. oxysporum'' <cite>Paukner2014</cite>, ''F. sambucinum'' <cite>Paukner2015</cite>, and ''F. acuminatum'' <cite>Alberton2007</cite> have substrate specificities similar to ''Fgr''GalOx. | + | The archetypal CRO and AA5 member is the ''Fusarium graminearum'' galactose 6-oxidase (''Fgr''GalOx), which catalyzes the regioselective oxidation of the C6-hydroxyl group on the monosaccharide galactose ([{{EClink}}1.1.3.7 EC 1.3.3.7]) <cite>Cooper1959 Avigad1962</cite>. The range of substrates oxidized by ''Fgr''GalOx also includes galactosides as methyl beta-galactopyranoside <cite>Paukner2015</cite>, and galactose-containing di-, oligo-, and polysaccharides, including lactose, melibiose, raffinose, galactoxyloglucan, galactomannan and galactoglucomannan <cite>Parikka2015,Parikka2010</cite>. Several other AA5_2 members from ''Fusarium'' species, such as those from ''F. oxysporum'' <cite>Paukner2014</cite>, ''F. sambucinum'' <cite>Paukner2015</cite>, and ''F. acuminatum'' <cite>Alberton2007</cite> have substrate specificities similar to ''Fgr''GalOx. Other AA5_2 orthologs exhibit specificity for the alpha-galactosyl unit of the di- and trisaccharides mellibiose and raffinose, respectively, over galactose <cite>Andberg2017,Cleveland2021b</cite>. For many decades following their discovery, galactose 6-oxidase activity was thought to be the defining feature of this family, although a limited ability of ''Fgr''GalOx to oxidize non-carbohydrate alcohols had been noted <cite>Minasian2004 Siebum2006</cite> |
In 2015, two AA5_2 orthologs from the fungi ''Colletotrichum graminicola'' and ''Colletotrichum gloeosporioides'' were characterized (''Cgr''AlcOx and ''Cgl''AlcOx, respectively), which were essentially inactive on galactose and galactosides, but efficiently oxidized the hydroxyl group of diverse aliphatic and aromatic primary alcohols <cite>Yin2015</cite>. These enzymes exhibited high catalytic efficiency towards, e.g., ''n''-butan-1-ol, 2,4-hexadiene-1-ol, benzyl alcohol, and cinnamyl alcohol, and were therefore denoted as general alcohol oxidases ([{{EClink}}1.1.3.13 EC 1.3.3.13]) <cite>Yin2015</cite>. Likewise, two AA5_2 members were characterized from the pathogenic fungi ''Pyricularia oryzae'' (''Por''AlcOx) and ''Colletotrichum higginsianum'' (''Chi''AlcOx), which exhibited prominent activity on ''n''-butan-1-ol, ethanol, 1,3-butanediol, and glycerol <cite>Oide2019</cite>. Since then, additional AA5_2 enzymes from various fungi have been characterized as general alcohol oxidases, some of which efficiently oxidize both carbohydrate and non-carbohydrate substrates <cite>Cleveland2021b</cite>. More specifically, several fungal AA5_2 members, including homologs from ''Colletotrichum/Glomerella'' and ''Fusarium'' species, have been characterized as aryl alcohol oxidases due to predominant specificities toward substituted benzyl alcohols and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) (see [{{EClink}}1.1.3.7 EC 1.1.3.7] and [{{EClink}}1.1.3.47 EC 1.1.3.47]) <cite>Mathieu2020 Cleveland2021a Cleveland2021b</cite>. | In 2015, two AA5_2 orthologs from the fungi ''Colletotrichum graminicola'' and ''Colletotrichum gloeosporioides'' were characterized (''Cgr''AlcOx and ''Cgl''AlcOx, respectively), which were essentially inactive on galactose and galactosides, but efficiently oxidized the hydroxyl group of diverse aliphatic and aromatic primary alcohols <cite>Yin2015</cite>. These enzymes exhibited high catalytic efficiency towards, e.g., ''n''-butan-1-ol, 2,4-hexadiene-1-ol, benzyl alcohol, and cinnamyl alcohol, and were therefore denoted as general alcohol oxidases ([{{EClink}}1.1.3.13 EC 1.3.3.13]) <cite>Yin2015</cite>. Likewise, two AA5_2 members were characterized from the pathogenic fungi ''Pyricularia oryzae'' (''Por''AlcOx) and ''Colletotrichum higginsianum'' (''Chi''AlcOx), which exhibited prominent activity on ''n''-butan-1-ol, ethanol, 1,3-butanediol, and glycerol <cite>Oide2019</cite>. Since then, additional AA5_2 enzymes from various fungi have been characterized as general alcohol oxidases, some of which efficiently oxidize both carbohydrate and non-carbohydrate substrates <cite>Cleveland2021b</cite>. More specifically, several fungal AA5_2 members, including homologs from ''Colletotrichum/Glomerella'' and ''Fusarium'' species, have been characterized as aryl alcohol oxidases due to predominant specificities toward substituted benzyl alcohols and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) (see [{{EClink}}1.1.3.7 EC 1.1.3.7] and [{{EClink}}1.1.3.47 EC 1.1.3.47]) <cite>Mathieu2020 Cleveland2021a Cleveland2021b</cite>. | ||
| − | The specificity of AA5 CROs has been harnessed for a range of biotechnological applications. The earliest examples include glycoprotein labelling via oxidation of galactosyl residues with ''Fgr''GalOx <cite>Roberts1965</cite>. Likewise, ''Fgr''GalOx has been utilized for the production of functionalized carbohydrates from biomass sources <cite>Yalpani1982 Kelleher1986 Schoevaart2004 Leppanen2014 Xu2012 Parikka2012 Mikkonen2014 Derikvand2016</cite>. Several mutants of ''Fgr''GalOx have been developed to attempt to change the substrate preference showing increased activity on glucose (M<sub>3 </sub>with R330K, Q406T, and W290F in M<sub>1</sub> background and Des 3-2 with Q326E, Y329K and R330K in WT background), fructose (R330K in WT background), mannose (variant H<sub>1</sub> with R330K mutation in M<sub>1</sub> background) and N-acetylglucosamine (variant F<sub>2</sub> with R330K, W290F, Q406E, Y405F mutations in M<sub>1</sub> background), secondary alcohols (variant M<sub>3-5 </sub>similar to M<sub>3</sub> with a methionine at the 330 position), and amino alcohols (variants F<sub>2</sub> and M<sub>3-5</sub>) | + | The specificity of AA5 CROs has been harnessed for a range of biotechnological applications. The earliest examples include glycoprotein labelling via oxidation of galactosyl residues with ''Fgr''GalOx <cite>Roberts1965</cite>. Likewise, ''Fgr''GalOx has been utilized for the production of functionalized carbohydrates from biomass sources <cite>Yalpani1982 Kelleher1986 Schoevaart2004 Leppanen2014 Xu2012 Parikka2012 Mikkonen2014 Derikvand2016</cite>. Several mutants of ''Fgr''GalOx have been developed to attempt to change the substrate preference showing increased activity on glucose (M<sub>3 </sub>with R330K, Q406T, and W290F in M<sub>1</sub> background and Des 3-2 with Q326E, Y329K and R330K in WT background), fructose (R330K in WT background), mannose (variant H<sub>1</sub> with R330K mutation in M<sub>1</sub> background) and N-acetylglucosamine (variant F<sub>2</sub> with R330K, W290F, Q406E, Y405F mutations in M<sub>1</sub> background), secondary alcohols (variant M<sub>3-5 </sub>similar to M<sub>3</sub> with a methionine at the 330 position), and amino alcohols (variants F<sub>2</sub> and M<sub>3-5</sub>) <cite>Sun2002,Lippow2010,Deacon2004,Rannes2011,Escalettes2008,Herter2015, Birmingham2018</cite>. Some of these variants have been explored for the labelling of galactose-containing carbohydrates (M<sub>1</sub>), mannose-containing carbohydrates (H<sub>1</sub>), N-acetylglucosamine and the human xeno-autoantigen N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc) (F<sub>2</sub>) <cite>Rannes2011,Mattey2019</cite>. |
| + | |||
| + | The ability of specific AA5 members to oxidize aliphatic and aromatic alcohols to the corresponding aldehydes, including stereoselectively, has biocatalytic applications in chemical production, e.g. for the pharmaceutical and food and fragrance industries <cite>Huffman2019 Toftgaard2015 Birmingham2018 Forget2020 Monosik2012 Schoevaart2004 Ribeaucourt2021a Ribeaucourt2021b Ribeaucourt2021c Roncal2012 Vilim2018</cite>. Similarly, the ability of CROs to convert HMF into the bi-functional precursors diformylfuran (DFF) and 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA) may find application in polymer manufacturing <cite>Mathieu2020 Cleveland2021a Cleveland2021b Rosatella2011 Sousa2015 Birmingham2021</cite>. | ||
| − | |||
== Kinetics and Mechanism == | == Kinetics and Mechanism == | ||
[[File:CRO_mechanism.png|thumb|400px|right|'''Figure 1.''' Reaction mechanism of copper radical oxidases. A. First half-reaction – oxidation of substrate. B. Second-half reaction – regeneration of active site radical. PT – proton transfer, HAT – hydrogen atom transfer, ET – electron transfer. This figure is reproduced from <cite>Yin2015</cite> (CC BY 4.0).]] | [[File:CRO_mechanism.png|thumb|400px|right|'''Figure 1.''' Reaction mechanism of copper radical oxidases. A. First half-reaction – oxidation of substrate. B. Second-half reaction – regeneration of active site radical. PT – proton transfer, HAT – hydrogen atom transfer, ET – electron transfer. This figure is reproduced from <cite>Yin2015</cite> (CC BY 4.0).]] | ||
| − | The majority of what is known about the mechanism of AA5 enzymes comes from studies on the archetype, ''Fgr''GalOx. AA5 enzymes oxidize their substrates through a ping-pong mechanism involving a corresponding reduction of oxygen to hydrogen peroxide mediated by a mononuclear copper center, which is complexed via a distinct, crosslinked tyrosyl-cysteine residue (see below) <cite>Whittaker2003,Whittaker2005,Baron1994,Humphreys2009,Whittaker1993,Whittaker1996,Whittaker1999,Kersten2014</cite>. The first half-reaction results in a two-electron oxidation of the substrate and corresponding reduction of the Cu[II]-tyrosyl radical to a Cu[I]-tyrosine (phenol). The second half-reaction regenerates the oxidation state of the active-site through reduction of molecular oxygen to hydrogen peroxide. Detailed kinetic studies, including kinetic isotope effects, suggest that each half reaction consists of three steps: proton transfer (PT), hydrogen atom transfer (HAT), and electron transfer (ET) <cite>Whittaker2004 Humphreys2009</cite>. Due to its fundamental uniqueness, the mechanism of AA5 CROs has received significant theoretical treatment and the synthesis of many chemical mimetics has been attempted <cite>Wang1998 | + | The majority of what is known about the mechanism of AA5 enzymes comes from studies on the archetype, ''Fgr''GalOx. AA5 enzymes oxidize their substrates through a ping-pong mechanism involving a corresponding reduction of oxygen to hydrogen peroxide mediated by a mononuclear copper center, which is complexed via a distinct, crosslinked tyrosyl-cysteine residue (see below) <cite>Whittaker2003,Whittaker2005,Baron1994,Humphreys2009,Whittaker1993,Whittaker1996,Whittaker1999,Kersten2014</cite>. The first half-reaction results in a two-electron oxidation of the substrate and corresponding reduction of the Cu[II]-tyrosyl radical to a Cu[I]-tyrosine (phenol). The second half-reaction regenerates the oxidation state of the active-site through reduction of molecular oxygen to hydrogen peroxide. Detailed kinetic studies, including kinetic isotope effects, suggest that each half reaction consists of three steps: proton transfer (PT), hydrogen atom transfer (HAT), and electron transfer (ET) <cite>Whittaker2004 Humphreys2009</cite>. Due to its fundamental uniqueness, the mechanism of AA5 CROs has received significant theoretical treatment and the synthesis of many chemical mimetics has been attempted <cite>Wang1998 Itoh2000 Himo2000</cite>. |
Practically, AA5 enzymes are conveniently assayed by measuring hydrogen peroxide (co-product) generatation, e.g. in coupled reactions with horseradish peroxidase and a chromogenic substrate. In preparative reactions, catalase is typically added to prevent accumulation of hydrogen peroxide. AA5 enzymes are prone to inactivation by one-electron reduction to a Cu[I]-tyrosyl radical. The resulting off-cycle species can be rescued by oxidation by peroxidases or transition metal ions (ferricyanide, Mg(III), etc.), the inclusion of which in reactions is required to obtain maximal activity and substrate conversion <cite>Kersten1990 Cleveland1975 Hamilton1978 Pedersen2015 Forget2020 Johnson2021 Roncal2012</cite>. | Practically, AA5 enzymes are conveniently assayed by measuring hydrogen peroxide (co-product) generatation, e.g. in coupled reactions with horseradish peroxidase and a chromogenic substrate. In preparative reactions, catalase is typically added to prevent accumulation of hydrogen peroxide. AA5 enzymes are prone to inactivation by one-electron reduction to a Cu[I]-tyrosyl radical. The resulting off-cycle species can be rescued by oxidation by peroxidases or transition metal ions (ferricyanide, Mg(III), etc.), the inclusion of which in reactions is required to obtain maximal activity and substrate conversion <cite>Kersten1990 Cleveland1975 Hamilton1978 Pedersen2015 Forget2020 Johnson2021 Roncal2012</cite>. | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
== Catalytic Residues == | == Catalytic Residues == | ||
[[File: FgrGalOx_Active_site_CAZY.png|thumb|250px|right|'''Figure 2.''' Active site residues of copper radical oxidases FgrGalOx, Cu ion in orange (PDB ID [{{PDBlink}}1gof 1GOF]). ]] | [[File: FgrGalOx_Active_site_CAZY.png|thumb|250px|right|'''Figure 2.''' Active site residues of copper radical oxidases FgrGalOx, Cu ion in orange (PDB ID [{{PDBlink}}1gof 1GOF]). ]] | ||
| − | The redox-active center of AA5 oxidases comprises a copper ion that coordinated by two tyrosine sidechains and two histidine sidechains (in ''Fgr''GalOx these are Tyr495, Tyr272, His496, and His581, respectively), resulting in a distorted square pyramidal geometry <cite>Ito1991 Ito1994 Yin2015 Mathieu2020</cite>. Based on the copper coordination environment, AA5 proteins are type 2 "non-blue" copper enzymes due to the nitrogen and oxygen ligands <cite>Ito1994</cite>. | + | The redox-active center of AA5 oxidases comprises a copper ion that coordinated by two tyrosine sidechains and two histidine sidechains (in the archetype ''Fgr''GalOx these are Tyr495, Tyr272, His496, and His581, respectively), resulting in a distorted square pyramidal geometry <cite>Ito1991 Ito1994 Yin2015 Mathieu2020</cite>. Based on the copper coordination environment, AA5 proteins are type 2 "non-blue" copper enzymes due to the nitrogen and oxygen ligands <cite>Ito1994</cite>. |
| − | The unique feature of AA5 enzymes is the covalently linked equatorial tyrosine with an adjacent cysteine by a thioether bond (Tyr272 and Cys228 in | + | The unique feature of AA5 enzymes is the covalently linked equatorial tyrosine with an adjacent cysteine by a thioether bond (Tyr272 and Cys228 in ''Fgr''GalOx) <cite>Ito1991</cite>. The thioether linkage forms spontaneously in the presence of copper and has been shown to stabilize the radical though delocalization onto the equatorial tyrosine during catalysis <cite>Rogers2008</cite>. |
Another important feature of AA5 enzymes is a secondary shell amino acid that is located on top of the tyrosine-cysteine cofactor (Trp290 in ''Fgr''GalOx). It has been speculated to be critical in determining the substrate specificity, radical stability and redox activity of ''Fgr''GalOx. W290 has been speculated to be involved in hydrogen bonding to the substrate, the delocalization of the radical located on the Cys-Tyr moiety, and/or protecting the thioether bond from solvent <cite>Whittaker2003,Rogers2007,Kersten2014, Daou2017</cite>. This residue in AA5_1, based on sequence alignments, has been conserved as a histidine <cite>Kersten2014</cite>, while characterized AA5_2 enzymes have an aromatic residue at this position: a tryptophan in galactose oxidases (W290 in ''Fgr''GalOx) <cite>Rogers2007,Cleveland2021b</cite>, a phenylalanine in the ''Colletotrichum'' aliphatic alcohol oxidases <cite>Yin2015</cite>, whereas a tyrosine is present in the raffinose oxidases <cite>Andberg2017,Cleveland2021b</cite> and in the aryl alcohol oxidase from ''Colletotrichum graminicola'' <cite>Mathieu2020</cite>. Furthermore, an AA5 enzyme from ''Streptomyces lividans'' with activity on glycolaldehyde also possesses a tryptophan at this position, similar to ''Fgr''GalOx, however the indole ring has a different orientation compared to ''Fgr''GalOx, which may affect the substrate specificity <cite>Chaplin2015,Chaplin2017</cite>. | Another important feature of AA5 enzymes is a secondary shell amino acid that is located on top of the tyrosine-cysteine cofactor (Trp290 in ''Fgr''GalOx). It has been speculated to be critical in determining the substrate specificity, radical stability and redox activity of ''Fgr''GalOx. W290 has been speculated to be involved in hydrogen bonding to the substrate, the delocalization of the radical located on the Cys-Tyr moiety, and/or protecting the thioether bond from solvent <cite>Whittaker2003,Rogers2007,Kersten2014, Daou2017</cite>. This residue in AA5_1, based on sequence alignments, has been conserved as a histidine <cite>Kersten2014</cite>, while characterized AA5_2 enzymes have an aromatic residue at this position: a tryptophan in galactose oxidases (W290 in ''Fgr''GalOx) <cite>Rogers2007,Cleveland2021b</cite>, a phenylalanine in the ''Colletotrichum'' aliphatic alcohol oxidases <cite>Yin2015</cite>, whereas a tyrosine is present in the raffinose oxidases <cite>Andberg2017,Cleveland2021b</cite> and in the aryl alcohol oxidase from ''Colletotrichum graminicola'' <cite>Mathieu2020</cite>. Furthermore, an AA5 enzyme from ''Streptomyces lividans'' with activity on glycolaldehyde also possesses a tryptophan at this position, similar to ''Fgr''GalOx, however the indole ring has a different orientation compared to ''Fgr''GalOx, which may affect the substrate specificity <cite>Chaplin2015,Chaplin2017</cite>. | ||
| − | In AA5_2 the Tyr-Cys cofactor exhibits an unusually low reduction potential (+275 mV) <cite>Cowley2016,Thomas2002,Wright2001</cite> compared to unmodified tyrosine in solution (> +800 mV) or in other enzymatic systems <cite>Itoh2000</cite>. Several factors such as the increased stability of the protein free radical through π-stacking with aromatic residues and the electron donating effect of the thioether linkage could contribute to this phenomenon <cite>Jazdzewski2000,Whittaker2003,Rogers2007</cite>. In contrast, AA5_1 have a reduction potential around +640 mV <cite>Whittaker1996</cite> possibly caysed by the substitution of the secondary shell amino acid Trpin AA5_2 with a His in AA5_1 leading to the different oxidizing power of these two subfamilies <cite>Wright2001,Kersten2014</cite>. Furthermore, in the archetypal AA5_2 member, ''Fgr''GalOx, the Trp290His substitution increased the reduction potential of the resulting enzyme from +400 mV to +730 mV <cite>Saysell1997</cite>; however, it also decreased the catalytic efficiency by 1000-fold <cite>Baron1994</cite> and affected the stability of the [Cu2+ Tyr·] metallo-radical complex at neutral pH <cite>Rogers1998</cite>. ''Cgr''AlcOx and ''Cgr''AAO have been speculated to have a lower reduction potential than ''Fgr''GalOx due to their secondary shell amino acid substitutions (Phe in ''Cgr''AlcOx and Tyr in ''Cgr''AAO) <cite>Yin2015,Mathieu2020</cite>. | + | In AA5_2 the Tyr-Cys cofactor exhibits an unusually low reduction potential (+275 mV) <cite>Cowley2016,Thomas2002,Wright2001</cite> compared to unmodified tyrosine in solution (> +800 mV) or in other enzymatic systems <cite>Itoh2000</cite>. Several factors such as the increased stability of the protein free radical through π-stacking with aromatic residues and the electron donating effect of the thioether linkage could contribute to this phenomenon <cite>Jazdzewski2000,Whittaker2003,Rogers2007</cite>. In contrast, AA5_1 have a reduction potential around +640 mV <cite>Whittaker1996</cite> possibly caysed by the substitution of the secondary shell amino acid Trpin AA5_2 with a His in AA5_1 leading to the different oxidizing power of these two subfamilies <cite>Wright2001,Kersten2014</cite>. Furthermore, in the archetypal AA5_2 member, ''Fgr''GalOx, the Trp290His substitution increased the reduction potential of the resulting enzyme from +400 mV to +730 mV <cite>Saysell1997</cite>; however, it also decreased the catalytic efficiency by 1000-fold <cite>Baron1994</cite> and affected the stability of the [Cu2+ Tyr·] metallo-radical complex at neutral pH <cite>Rogers1998</cite>. ''Cgr''AlcOx and ''Cgr''AAO have been speculated to have a lower reduction potential than ''Fgr''GalOx due to their secondary shell amino acid substitutions (Phe in ''Cgr''AlcOx and Tyr in ''Cgr''AAO) <cite>Yin2015,Mathieu2020</cite>. |
== Three-dimensional Structures == | == Three-dimensional Structures == | ||
[[File:CRO_tertiary_structure.png|thumb|400px|right|'''Figure 3.''' Crystal structure of copper radical oxidases. A. ''Fgr''GalOx (PDB ID [{{PDBlink}}1gof 1GOF]), Copper ion in orange and B. ''Cgr''AlcOx (PDB ID [{{PDBlink}}5c86 5C86]), Copper ion in grey. This figure is reproduced from <cite>Yin2015</cite> (CC BY 4.0).]] | [[File:CRO_tertiary_structure.png|thumb|400px|right|'''Figure 3.''' Crystal structure of copper radical oxidases. A. ''Fgr''GalOx (PDB ID [{{PDBlink}}1gof 1GOF]), Copper ion in orange and B. ''Cgr''AlcOx (PDB ID [{{PDBlink}}5c86 5C86]), Copper ion in grey. This figure is reproduced from <cite>Yin2015</cite> (CC BY 4.0).]] | ||
| − | AA5 members share a core seven-bladed β-propeller fold containing the active site (Figure 3) <cite>Ito1994 Yin2015 Mathieu2020</cite>. The structure of the archetype, ''Fgr''GalOx, was first reported in 1991 and comprises three domains: Domain 1 has a beta-sandwich structure now known as [[Carbohydrate Binding Module Family 32]], Domain 2 is the catalytic domain, and Domain 3 is a small, β-strand domain that packs against the catalytic domain on the side opposite from the active-site | + | AA5 members share a core seven-bladed β-propeller fold containing the active site (Figure 3) <cite>Ito1991 Ito1994 Yin2015 Mathieu2020</cite>. The structure of the archetype, ''Fgr''GalOx, was first reported in 1991 and comprises three domains: Domain 1 has a beta-sandwich structure now known as [[Carbohydrate Binding Module Family 32]], Domain 2 is the catalytic domain, and Domain 3 is a small, β-strand domain that packs against the catalytic domain on the side opposite from the active-site <cite>Ito1991 Ito1994</cite>. Notably, the original structural analysis of ''Fgr''GalOx revealed the distinct crosslinked Tyr-Cys active site residue of CROs, provided the first [[CBM32]] tertiary structure, and indicated the ability of Domain 1/[[CBM32]] to bind galactose <cite>Ito1991</cite>. |
| − | The [[CBM32]] domain is widely, but not exclusively, conserved among many AA5_2 members, especially from ''Fusarium'' species <cite>Paukner2014 Paukner2015 Faria2019 Cleveland2021b</cite> (including some that do not posses predominant galactose 6-oxidase activity, e.g. ''Fgr''AAO and ''Fox''AAO <cite>Cleveland2021a Cleveland2021b</cite>.) In other cases, PAN and WSC domains are found in place of the [[CBM32]]. The function of PAN domains in ''Colletotrichum graminicola'' aryl alchohol oxidase and raffinose oxidase is unclear <cite>Mathieu2020 Andberg2017</cite>, while the WSC domain in ''Pyricularia oryzae'' alchohol oxidase was able to bind xylans and fungal chitin/β-1,3-glucan, implicating the involvement of this domain in enzyme anchoring <cite>Oide2019</cite>. Finally, several general alcohol oxidases (i.e. those with little activity toward galactosides) do not possess a corresponding N-terminal domain, but rather comprise only the seven-bladed β-propeller and C-terminal domain (Figure 3) <cite>Yin2015 Oide2019</cite>. Glyoxal oxidases of AA5_1 also appear to lack the N-terminal [[CBM32]] domain found in ''Fgr''GalOx <cite>Whittaker1999</cite>. | + | The [[CBM32]] domain is widely, but not exclusively, conserved among many AA5_2 members, especially from ''Fusarium'' species <cite>Paukner2014 Paukner2015 Faria2019 Cleveland2021b</cite> (including some that do not posses predominant galactose 6-oxidase activity, e.g. ''Fgr''AAO and ''Fox''AAO <cite>Cleveland2021a Cleveland2021b</cite>.) In other cases, PAN and WSC domains are found in place of the [[CBM32]]. The function of PAN domains in ''Colletotrichum graminicola'' aryl alchohol oxidase and raffinose oxidase is unclear <cite>Mathieu2020 Andberg2017</cite>, while the WSC domain in ''Pyricularia oryzae'' alchohol oxidase was able to bind xylans and fungal chitin/β-1,3-glucan, implicating the involvement of this domain in enzyme anchoring <cite>Oide2019</cite>. Finally, several general alcohol oxidases (i.e. those with little activity toward galactosides) do not possess a corresponding N-terminal domain, but rather comprise only the core seven-bladed β-propeller and the C-terminal domain (Figure 3) <cite>Yin2015 Oide2019</cite>. Glyoxal oxidases of AA5_1 also appear to lack the N-terminal [[CBM32]] domain found in ''Fgr''GalOx <cite>Whittaker1999</cite>. |
== Family Firsts == | == Family Firsts == | ||
;First AA5_1 enzyme discovered: The glyoxal oxidase from ''Phanerochaete chrysosporium'' discovered in 1987 <cite>Kersten1987</cite>. | ;First AA5_1 enzyme discovered: The glyoxal oxidase from ''Phanerochaete chrysosporium'' discovered in 1987 <cite>Kersten1987</cite>. | ||
;First AA5_2 enzyme discovered: The archetypal galactose-6 oxidase from ''Fusarium graminearum'' (''Fgr''GalOx) discovered in 1959 <cite>Cooper1959</cite>. | ;First AA5_2 enzyme discovered: The archetypal galactose-6 oxidase from ''Fusarium graminearum'' (''Fgr''GalOx) discovered in 1959 <cite>Cooper1959</cite>. | ||
| − | ;Copper requirement confirmed: While | + | ;Copper requirement confirmed: While the original report established FgrGalOx as a metalloenzyme <cite>Cooper1959</cite>, its copper requirement was later confirmed <cite>Amaral1963</cite>. |
| − | ;First 3-D structure: The first | + | ;First 3-D structure: The first crystallographic structure of AA5 was of ''Fgr''GalOx in 1991 <cite>Ito1991</cite>. |
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
#Amaral1963 pmid=14012475 | #Amaral1963 pmid=14012475 | ||
#Cleveland2021a pmid=34134727 | #Cleveland2021a pmid=34134727 | ||
| − | #Cleveland2021b pmid= | + | #Cleveland2021b pmid=34738149 |
#Paukner2014 pmid=24967652 | #Paukner2014 pmid=24967652 | ||
#Paukner2015 pmid=25543085 | #Paukner2015 pmid=25543085 | ||
| Line 141: | Line 141: | ||
#Roncal2012 pmid=22226201 | #Roncal2012 pmid=22226201 | ||
#Schoevaart2004 Schoevaart, R., Kieboom, T. (2004) Application of galactose oxidase in chemoenzymatic one-pot cascade reactions without intermediate recovery steps. ''Topics in Catalysis'', '''27''', 3–9. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1023/B:TOCA.0000013536.27551.13 DOI:10.1023/B:TOCA.0000013536.27551.13] | #Schoevaart2004 Schoevaart, R., Kieboom, T. (2004) Application of galactose oxidase in chemoenzymatic one-pot cascade reactions without intermediate recovery steps. ''Topics in Catalysis'', '''27''', 3–9. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1023/B:TOCA.0000013536.27551.13 DOI:10.1023/B:TOCA.0000013536.27551.13] | ||
| − | |||
#Sun2002 pmid=12203977 | #Sun2002 pmid=12203977 | ||
| − | |||
#Lippow2010 pmid=21168766 | #Lippow2010 pmid=21168766 | ||
| − | |||
#Deacon2004 pmid=15239055 | #Deacon2004 pmid=15239055 | ||
| − | |||
#Rannes2011 pmid=21526835 | #Rannes2011 pmid=21526835 | ||
| − | |||
#Escalettes2008 pmid=18330849 | #Escalettes2008 pmid=18330849 | ||
| − | + | #Herter2015 Herter, S.; McKenna, S. M.; Frazer, A. R.; Leimkühler, S.; Carnell, A. J.; Turner, N. J. (2015) Galactose Oxidase Variants for the Oxidation of Amino Alcohols in Enzyme Cascade Synthesis. ''ChemCatChem.'' '''''7''''', 2313-2317. [https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201500218 DOI:10.1002/cctc.201500218] | |
| − | #Herter2015 Herter, S.; McKenna, S. M.; Frazer, A. R.; Leimkühler, S.; Carnell, A. J.; Turner, N. J. (2015) Galactose Oxidase Variants for the Oxidation of Amino Alcohols in Enzyme Cascade Synthesis. ''ChemCatChem.'' '''''7''''', 2313-2317 | + | #Birmingham2018 Birmingham, W. R.; Turner, N. J. (2018) A Single Enzyme Oxidative “Cascade” via a Dual-Functional Galactose Oxidase. ''ACS Catal.'' '''8''', 4025-4032. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b00043 DOI:10.1021/acscatal.8b00043] |
| − | + | #Mattey2019 Mattey, A. P.; Birmingham, W. R.; Both, P.; Kress, N.; Huang, K.; van Munster, J. M.; Bulmer, G. S.; Parmeggiani, F.; Voglmeir, J.; Martinez, J. E. R.; Turner, N. J.; Flitsch, S. L. (2019) Selective Oxidation of N-Glycolylneuraminic Acid Using an Engineered Galactose Oxidase Variant. ''ACS Catal.'' '''9''', 8208-8212. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b02873 DOI:10.1021/acscatal.9b02873] | |
| − | #Birmingham2018 Birmingham, W. R.; Turner, N. J. (2018) A Single Enzyme Oxidative “Cascade” via a Dual-Functional Galactose Oxidase. ''ACS Catal.'' '''8''', 4025-4032. | ||
| − | |||
| − | #Mattey2019 Mattey, A. P.; Birmingham, W. R.; Both, P.; Kress, N.; Huang, K.; van Munster, J. M.; Bulmer, G. S.; Parmeggiani, F.; Voglmeir, J.; Martinez, J. E. R.; Turner, N. J.; Flitsch, S. L. (2019) Selective Oxidation of N-Glycolylneuraminic Acid Using an Engineered Galactose Oxidase Variant. ''ACS Catal.'' '''9''', 8208-8212 | ||
#Roberts1965 pmid=4161238 | #Roberts1965 pmid=4161238 | ||
| + | #Sousa2015 Sousa, A. F.; Vilela, C.; Fonseca, A. C.; Matos, M.; Freire, C. S. R.; Gruter, G.-J. M.; Coelho, J. F. J.; Silvestre, A. J. D. (2015) Biobased polyesters and other polymers from 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid: a tribute to furan excellency. ''Polym. Chem.'' '''6''', 5961-5983. [https://doi.org/10.1039/C5PY00686D DOI:10.1039/C5PY00686D] | ||
| + | #Rosatella2011 Rosatella, A. A.; Simeonov, S. P.; Frade, R. F. M.; Afonso, C. A. M. (2011) 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) as a building block platform: Biological properties, synthesis and synthetic applications. ''Green Chem.'' '''13''', 754-793. [https://doi.org/10.1039/C0GC00401D DOI:10.1039/C0GC00401D] | ||
| + | #Monosik2012 Monosik, R.; Stredansky, M.; Tkac, J.; Sturdik, E. (2012) Application of Enzyme Biosensors in Analysis of Food and Beverages. ''Food Anal. Methods.'' '''5''', 40-53. [https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-011-9222-4 DOI:10.1007/s12161-011-9222-4] | ||
| + | #Huffman2019 pmid=31806816 | ||
| + | #Toftgaard2015 Toftgaard Pedersen, A.; Birmingham, W. R.; Rehn, G.; Charnock, S. J.; Turner, N. J.; Woodley, J. M. (2015) Process Requirements of Galactose Oxidase Catalyzed Oxidation of Alcohols. ''Org. Process Res. Dev.'' '''19''', 1580-1589. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.oprd.5b00278 DOI:10.1021/acs.oprd.5b00278] | ||
| + | #McKenna2017 McKenna, S. M.; Mines, P.; Law, P.; Kovacs-Schreiner, K.; Birmingham, W. R.; Turner, N. J.; Leimkühler, S.; Carnell, A. J. (2017) The continuous oxidation of HMF to FDCA and the immobilisation and stabilisation of periplasmic aldehyde oxidase (PaoABC). ''Green Chem.'' '''19''', 4660-4665. [https://doi.org/10.1039/C7GC01696D DOI:10.1039/C7GC01696D] | ||
| + | #Birmingham2021 pmid=34400632 | ||
| + | #Ribeaucourt2021c Ribeaucourt, D.; Bissaro, B.; Guallar, V.; Yemloul, M.; Haon, M.; Grisel, S.; Alphand, V.; Brumer, H.; Lambert, F.; Berrin, J-G.; Lafond, M. (2021) Comprehensive Insights into the Production of Long Chain Aliphatic Aldehydes Using a Copper-Radical Alcohol Oxidase as Biocatalyst. ''ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng''. '''9''', 4411-4421 [https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c07 DOI:10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c07] | ||
#Vilim2018 pmid=30176101 | #Vilim2018 pmid=30176101 | ||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
[[Category:Auxiliary Activity Families|AA005]] | [[Category:Auxiliary Activity Families|AA005]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:17, 19 April 2022
This page has been approved by the Responsible Curator as essentially complete. CAZypedia is a living document, so further improvement of this page is still possible. If you would like to suggest an addition or correction, please contact the page's Responsible Curator directly by e-mail.
| Auxiliary Activity Family AA5 | |
| Fold | Seven-bladed β-propeller |
| Mechanism | Copper Radical Oxidase |
| Active site residues | known |
| CAZy DB link | |
| https://www.cazy.org/AA5.html | |
Substrate Specificities
Enzymes from Auxiliary Activity Family 5 (AA5) are mononuclear copper-radical oxidases (CROs) that perform the two-electron oxidation of substrates using oxygen as the final electron acceptor (EC 1.1.3.-) [1]. AA5 members are further classified into two major subfamilies [2]. Subfamily AA5_1 contains characterized glyoxal oxidases (EC 1.2.3.15) [3]. Subfamily AA5_2 contains galactose 6-oxidases (EC 1.1.3.9), which oxidize the C-6 hydroxyl of diverse galactosides to the corresponding aldehyde [4, 5, 6]. AA5_2 also contains the more recently discovered general alcohol oxidases (EC 1.1.3.13) [6, 7, 8] and aryl alcohol oxidases (EC 1.1.3.7) [9, 10]. The first biochemically characterized member of AA5 was the galactose 6-oxidase from the phytopathogenic fungus Fusarium graminearum (previously known as Polyporus circinatus and Cladobotryum (Dactylium) dendroides [11]), which was originally reported in 1959 following isolation from cultures [12, 13]. Subsequently, the Fusarium graminearum galactose 6-oxidase became the defining member of AA5_2 [2]. The first characterized member of what is now known as AA5_1 is the glyoxal oxidase from Phanerochaete chrysosporium, which was likewise isolated from fungal culture [14].
In contrast to their fungal and bacterial counterparts, plant AA5 members do not fall within the two defined subfamilies. An AA5 enzyme from Arabidopsis thaliana has been demonstrated in vivo to have galactose 6-oxidase activity and promote cell-to-cell adhesion in the seed coat epidermis [15] (see also [16]). Additionally, a Streptomyces lividans enzyme, GlxA, which is distantly related to AA5, has been shown to oxidize glycolaldehyde and a deletion mutant showed a loss of glycan accumulation at hyphal tips [17].
AA5_1
The AA5_1 members are generally known as glyoxal oxidases (EC 1.2.3.15), characterized examples of which typically accept a range of simple aldehydes, α-hydroxycarbonyl, and α-dicarbonyl compounds as substrates, with the highest activities observed on glyoxal, methylglyoxal and glycolaldehyde [1, 14, 18, 19, 20]. In contrast, two glyoxal oxidases form Pycnoporus cinnabarinus demonstrated the highest catalytic efficiency on glyoxylic acid [21]. An apparent distinction between the AA5_1 and AA5_2 subfamilies is that while AA5_1 enzymes catalyze the oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids [1], AA5_2 members oxidize primary alcohols to the corresponding aldehyde (and, in some instances, also oxidize the aldehyde to the acid, albeit much more slowly) [4, 22]. Consequently, the oxidation of aldehydes by AA5 CROs has been suggested to proceed through the hydrated, gem-diol species [18].
AA5_2
The archetypal CRO and AA5 member is the Fusarium graminearum galactose 6-oxidase (FgrGalOx), which catalyzes the regioselective oxidation of the C6-hydroxyl group on the monosaccharide galactose (EC 1.3.3.7) [12, 13]. The range of substrates oxidized by FgrGalOx also includes galactosides as methyl beta-galactopyranoside [23], and galactose-containing di-, oligo-, and polysaccharides, including lactose, melibiose, raffinose, galactoxyloglucan, galactomannan and galactoglucomannan [22, 24]. Several other AA5_2 members from Fusarium species, such as those from F. oxysporum [25], F. sambucinum [23], and F. acuminatum [26] have substrate specificities similar to FgrGalOx. Other AA5_2 orthologs exhibit specificity for the alpha-galactosyl unit of the di- and trisaccharides mellibiose and raffinose, respectively, over galactose [5, 6]. For many decades following their discovery, galactose 6-oxidase activity was thought to be the defining feature of this family, although a limited ability of FgrGalOx to oxidize non-carbohydrate alcohols had been noted [27, 28]
In 2015, two AA5_2 orthologs from the fungi Colletotrichum graminicola and Colletotrichum gloeosporioides were characterized (CgrAlcOx and CglAlcOx, respectively), which were essentially inactive on galactose and galactosides, but efficiently oxidized the hydroxyl group of diverse aliphatic and aromatic primary alcohols [7]. These enzymes exhibited high catalytic efficiency towards, e.g., n-butan-1-ol, 2,4-hexadiene-1-ol, benzyl alcohol, and cinnamyl alcohol, and were therefore denoted as general alcohol oxidases (EC 1.3.3.13) [7]. Likewise, two AA5_2 members were characterized from the pathogenic fungi Pyricularia oryzae (PorAlcOx) and Colletotrichum higginsianum (ChiAlcOx), which exhibited prominent activity on n-butan-1-ol, ethanol, 1,3-butanediol, and glycerol [8]. Since then, additional AA5_2 enzymes from various fungi have been characterized as general alcohol oxidases, some of which efficiently oxidize both carbohydrate and non-carbohydrate substrates [6]. More specifically, several fungal AA5_2 members, including homologs from Colletotrichum/Glomerella and Fusarium species, have been characterized as aryl alcohol oxidases due to predominant specificities toward substituted benzyl alcohols and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) (see EC 1.1.3.7 and EC 1.1.3.47) [6, 9, 10].
The specificity of AA5 CROs has been harnessed for a range of biotechnological applications. The earliest examples include glycoprotein labelling via oxidation of galactosyl residues with FgrGalOx [29]. Likewise, FgrGalOx has been utilized for the production of functionalized carbohydrates from biomass sources [30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37]. Several mutants of FgrGalOx have been developed to attempt to change the substrate preference showing increased activity on glucose (M3 with R330K, Q406T, and W290F in M1 background and Des 3-2 with Q326E, Y329K and R330K in WT background), fructose (R330K in WT background), mannose (variant H1 with R330K mutation in M1 background) and N-acetylglucosamine (variant F2 with R330K, W290F, Q406E, Y405F mutations in M1 background), secondary alcohols (variant M3-5 similar to M3 with a methionine at the 330 position), and amino alcohols (variants F2 and M3-5) [38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44]. Some of these variants have been explored for the labelling of galactose-containing carbohydrates (M1), mannose-containing carbohydrates (H1), N-acetylglucosamine and the human xeno-autoantigen N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc) (F2) [41, 45].
The ability of specific AA5 members to oxidize aliphatic and aromatic alcohols to the corresponding aldehydes, including stereoselectively, has biocatalytic applications in chemical production, e.g. for the pharmaceutical and food and fragrance industries [32, 44, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54]. Similarly, the ability of CROs to convert HMF into the bi-functional precursors diformylfuran (DFF) and 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA) may find application in polymer manufacturing [6, 9, 10, 55, 56, 57].
Kinetics and Mechanism
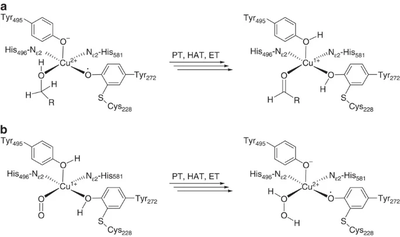
The majority of what is known about the mechanism of AA5 enzymes comes from studies on the archetype, FgrGalOx. AA5 enzymes oxidize their substrates through a ping-pong mechanism involving a corresponding reduction of oxygen to hydrogen peroxide mediated by a mononuclear copper center, which is complexed via a distinct, crosslinked tyrosyl-cysteine residue (see below) [1, 4, 18, 19, 58, 59, 60, 61]. The first half-reaction results in a two-electron oxidation of the substrate and corresponding reduction of the Cu[II]-tyrosyl radical to a Cu[I]-tyrosine (phenol). The second half-reaction regenerates the oxidation state of the active-site through reduction of molecular oxygen to hydrogen peroxide. Detailed kinetic studies, including kinetic isotope effects, suggest that each half reaction consists of three steps: proton transfer (PT), hydrogen atom transfer (HAT), and electron transfer (ET) [60, 62]. Due to its fundamental uniqueness, the mechanism of AA5 CROs has received significant theoretical treatment and the synthesis of many chemical mimetics has been attempted [63, 64, 65].
Practically, AA5 enzymes are conveniently assayed by measuring hydrogen peroxide (co-product) generatation, e.g. in coupled reactions with horseradish peroxidase and a chromogenic substrate. In preparative reactions, catalase is typically added to prevent accumulation of hydrogen peroxide. AA5 enzymes are prone to inactivation by one-electron reduction to a Cu[I]-tyrosyl radical. The resulting off-cycle species can be rescued by oxidation by peroxidases or transition metal ions (ferricyanide, Mg(III), etc.), the inclusion of which in reactions is required to obtain maximal activity and substrate conversion [48, 53, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70].
Catalytic Residues
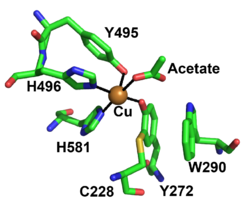
The redox-active center of AA5 oxidases comprises a copper ion that coordinated by two tyrosine sidechains and two histidine sidechains (in the archetype FgrGalOx these are Tyr495, Tyr272, His496, and His581, respectively), resulting in a distorted square pyramidal geometry [7, 9, 71, 72]. Based on the copper coordination environment, AA5 proteins are type 2 "non-blue" copper enzymes due to the nitrogen and oxygen ligands [72]. The unique feature of AA5 enzymes is the covalently linked equatorial tyrosine with an adjacent cysteine by a thioether bond (Tyr272 and Cys228 in FgrGalOx) [71]. The thioether linkage forms spontaneously in the presence of copper and has been shown to stabilize the radical though delocalization onto the equatorial tyrosine during catalysis [73].
Another important feature of AA5 enzymes is a secondary shell amino acid that is located on top of the tyrosine-cysteine cofactor (Trp290 in FgrGalOx). It has been speculated to be critical in determining the substrate specificity, radical stability and redox activity of FgrGalOx. W290 has been speculated to be involved in hydrogen bonding to the substrate, the delocalization of the radical located on the Cys-Tyr moiety, and/or protecting the thioether bond from solvent [1, 3, 4, 74]. This residue in AA5_1, based on sequence alignments, has been conserved as a histidine [1], while characterized AA5_2 enzymes have an aromatic residue at this position: a tryptophan in galactose oxidases (W290 in FgrGalOx) [6, 74], a phenylalanine in the Colletotrichum aliphatic alcohol oxidases [7], whereas a tyrosine is present in the raffinose oxidases [5, 6] and in the aryl alcohol oxidase from Colletotrichum graminicola [9]. Furthermore, an AA5 enzyme from Streptomyces lividans with activity on glycolaldehyde also possesses a tryptophan at this position, similar to FgrGalOx, however the indole ring has a different orientation compared to FgrGalOx, which may affect the substrate specificity [17, 75].
In AA5_2 the Tyr-Cys cofactor exhibits an unusually low reduction potential (+275 mV) [76, 77, 78] compared to unmodified tyrosine in solution (> +800 mV) or in other enzymatic systems [64]. Several factors such as the increased stability of the protein free radical through π-stacking with aromatic residues and the electron donating effect of the thioether linkage could contribute to this phenomenon [4, 74, 79]. In contrast, AA5_1 have a reduction potential around +640 mV [18] possibly caysed by the substitution of the secondary shell amino acid Trpin AA5_2 with a His in AA5_1 leading to the different oxidizing power of these two subfamilies [1, 78]. Furthermore, in the archetypal AA5_2 member, FgrGalOx, the Trp290His substitution increased the reduction potential of the resulting enzyme from +400 mV to +730 mV [80]; however, it also decreased the catalytic efficiency by 1000-fold [59] and affected the stability of the [Cu2+ Tyr·] metallo-radical complex at neutral pH [81]. CgrAlcOx and CgrAAO have been speculated to have a lower reduction potential than FgrGalOx due to their secondary shell amino acid substitutions (Phe in CgrAlcOx and Tyr in CgrAAO) [7, 9].
Three-dimensional Structures
AA5 members share a core seven-bladed β-propeller fold containing the active site (Figure 3) [7, 9, 71, 72]. The structure of the archetype, FgrGalOx, was first reported in 1991 and comprises three domains: Domain 1 has a beta-sandwich structure now known as Carbohydrate Binding Module Family 32, Domain 2 is the catalytic domain, and Domain 3 is a small, β-strand domain that packs against the catalytic domain on the side opposite from the active-site [71, 72]. Notably, the original structural analysis of FgrGalOx revealed the distinct crosslinked Tyr-Cys active site residue of CROs, provided the first CBM32 tertiary structure, and indicated the ability of Domain 1/CBM32 to bind galactose [71].
The CBM32 domain is widely, but not exclusively, conserved among many AA5_2 members, especially from Fusarium species [6, 23, 25, 82] (including some that do not posses predominant galactose 6-oxidase activity, e.g. FgrAAO and FoxAAO [6, 10].) In other cases, PAN and WSC domains are found in place of the CBM32. The function of PAN domains in Colletotrichum graminicola aryl alchohol oxidase and raffinose oxidase is unclear [5, 9], while the WSC domain in Pyricularia oryzae alchohol oxidase was able to bind xylans and fungal chitin/β-1,3-glucan, implicating the involvement of this domain in enzyme anchoring [8]. Finally, several general alcohol oxidases (i.e. those with little activity toward galactosides) do not possess a corresponding N-terminal domain, but rather comprise only the core seven-bladed β-propeller and the C-terminal domain (Figure 3) [7, 8]. Glyoxal oxidases of AA5_1 also appear to lack the N-terminal CBM32 domain found in FgrGalOx [19].
Family Firsts
- First AA5_1 enzyme discovered
- The glyoxal oxidase from Phanerochaete chrysosporium discovered in 1987 [14].
- First AA5_2 enzyme discovered
- The archetypal galactose-6 oxidase from Fusarium graminearum (FgrGalOx) discovered in 1959 [12].
- Copper requirement confirmed
- While the original report established FgrGalOx as a metalloenzyme [12], its copper requirement was later confirmed [83].
- First 3-D structure
- The first crystallographic structure of AA5 was of FgrGalOx in 1991 [71].
References
- Kersten P and Cullen D. (2014). Copper radical oxidases and related extracellular oxidoreductases of wood-decay Agaricomycetes. Fungal Genet Biol. 2014;72:124-130. DOI:10.1016/j.fgb.2014.05.011 |
- Levasseur A, Drula E, Lombard V, Coutinho PM, and Henrissat B. (2013). Expansion of the enzymatic repertoire of the CAZy database to integrate auxiliary redox enzymes. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2013;6(1):41. DOI:10.1186/1754-6834-6-41 |
- Daou M and Faulds CB. (2017). Glyoxal oxidases: their nature and properties. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017;33(5):87. DOI:10.1007/s11274-017-2254-1 |
- Whittaker JW (2003). Free radical catalysis by galactose oxidase. Chem Rev. 2003;103(6):2347-63. DOI:10.1021/cr020425z |
- Andberg M, Mollerup F, Parikka K, Koutaniemi S, Boer H, Juvonen M, Master E, Tenkanen M, and Kruus K. (2017). A Novel Colletotrichum graminicola Raffinose Oxidase in the AA5 Family. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017;83(20). DOI:10.1128/AEM.01383-17 |
- Cleveland ME, Mathieu Y, Ribeaucourt D, Haon M, Mulyk P, Hein JE, Lafond M, Berrin JG, and Brumer H. (2021). A survey of substrate specificity among Auxiliary Activity Family 5 copper radical oxidases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78(24):8187-8208. DOI:10.1007/s00018-021-03981-w |
- Yin DT, Urresti S, Lafond M, Johnston EM, Derikvand F, Ciano L, Berrin JG, Henrissat B, Walton PH, Davies GJ, and Brumer H. (2015). Structure-function characterization reveals new catalytic diversity in the galactose oxidase and glyoxal oxidase family. Nat Commun. 2015;6:10197. DOI:10.1038/ncomms10197 |
- Oide S, Tanaka Y, Watanabe A, and Inui M. (2019). Carbohydrate-binding property of a cell wall integrity and stress response component (WSC) domain of an alcohol oxidase from the rice blast pathogen Pyricularia oryzae. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2019;125:13-20. DOI:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2019.02.009 |
-
Mathieu, Y., Offen, W. A., Forget, S. M., Ciano, L., Viborg, A. H., Blagova, E., Henrissat, B., Walton, P.H, Davies, G.J, and Brumer, H. (2020). Discovery of a fungal copper radical oxidase with high catalytic efficiency toward 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and benzyl alcohols for bioprocessing. ACS Catalysis, 10, 3042-3058. DOI:10.1021/acscatal.9b04727
- Cleveland M, Lafond M, Xia FR, Chung R, Mulyk P, Hein JE, and Brumer H. (2021). Two Fusarium copper radical oxidases with high activity on aryl alcohols. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021;14(1):138. DOI:10.1186/s13068-021-01984-0 |
-
Ögel, Z. B.; Brayford, D.; McPherson, M. J., (1994). Cellulose-triggered sporulation in the galactose oxidase-producing fungus Cladobotryum (Dactylium) dendroides NRRL 2903 and its re-identification as a species of Fusarium. Mycol. Res., 98, 474-480. DOI:10.1016/S0953-7562(09)81207-0
- COOPER JA, SMITH W, BACILA M, and MEDINA H. (1959). Galactose oxidase from Polyporus circinatus, Fr. J Biol Chem. 1959;234(3):445-8. | Google Books | Open Library
- AVIGAD G, AMARAL D, ASENSIO C, and HORECKER BL. (1962). The D-galactose oxidase of Polyporus circinatus. J Biol Chem. 1962;237:2736-43. | Google Books | Open Library
- Kersten PJ and Kirk TK. (1987). Involvement of a new enzyme, glyoxal oxidase, in extracellular H2O2 production by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Bacteriol. 1987;169(5):2195-201. DOI:10.1128/jb.169.5.2195-2201.1987 |
- Šola K, Gilchrist EJ, Ropartz D, Wang L, Feussner I, Mansfield SD, Ralet MC, and Haughn GW. (2019). RUBY, a Putative Galactose Oxidase, Influences Pectin Properties and Promotes Cell-To-Cell Adhesion in the Seed Coat Epidermis of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2019;31(4):809-831. DOI:10.1105/tpc.18.00954 |
- Šola K, Dean GH, Li Y, Lohmann J, Movahedan M, Gilchrist EJ, Adams KL, and Haughn GW. (2021). Expression Patterns and Functional Characterization of Arabidopsis Galactose Oxidase-Like Genes Suggest Specialized Roles for Galactose Oxidases in Plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2021;62(12):1927-1943. DOI:10.1093/pcp/pcab073 |
- Chaplin AK, Petrus ML, Mangiameli G, Hough MA, Svistunenko DA, Nicholls P, Claessen D, Vijgenboom E, and Worrall JA. (2015). GlxA is a new structural member of the radical copper oxidase family and is required for glycan deposition at hyphal tips and morphogenesis of Streptomyces lividans. Biochem J. 2015;469(3):433-44. DOI:10.1042/BJ20150190 |
- Whittaker MM, Kersten PJ, Nakamura N, Sanders-Loehr J, Schweizer ES, and Whittaker JW. (1996). Glyoxal oxidase from Phanerochaete chrysosporium is a new radical-copper oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1996;271(2):681-7. DOI:10.1074/jbc.271.2.681 |
- Whittaker MM, Kersten PJ, Cullen D, and Whittaker JW. (1999). Identification of catalytic residues in glyoxal oxidase by targeted mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(51):36226-32. DOI:10.1074/jbc.274.51.36226 |
- Leuthner B, Aichinger C, Oehmen E, Koopmann E, Müller O, Müller P, Kahmann R, Bölker M, and Schreier PH. (2005). A H2O2-producing glyoxal oxidase is required for filamentous growth and pathogenicity in Ustilago maydis. Mol Genet Genomics. 2005;272(6):639-50. DOI:10.1007/s00438-004-1085-6 |
- Daou M, Piumi F, Cullen D, Record E, and Faulds CB. (2016). Heterologous Production and Characterization of Two Glyoxal Oxidases from Pycnoporus cinnabarinus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016;82(16):4867-75. DOI:10.1128/AEM.00304-16 |
-
Parikka, K.; Master, E.; Tenkanen, M., (2015) Oxidation with galactose oxidase: Multifunctional enzymatic catalysis. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 120, 47-59. DOI:10.1016/j.molcatb.2015.06.006
- Paukner R, Staudigl P, Choosri W, Haltrich D, and Leitner C. (2015). Expression, purification, and characterization of galactose oxidase of Fusarium sambucinum in E. coli. Protein Expr Purif. 2015;108:73-79. DOI:10.1016/j.pep.2014.12.010 |
- Parikka K, Leppänen AS, Pitkänen L, Reunanen M, Willför S, and Tenkanen M. (2010). Oxidation of polysaccharides by galactose oxidase. J Agric Food Chem. 2010;58(1):262-71. DOI:10.1021/jf902930t |
- Paukner R, Staudigl P, Choosri W, Sygmund C, Halada P, Haltrich D, and Leitner C. (2014). Galactose oxidase from Fusarium oxysporum--expression in E. coli and P. pastoris and biochemical characterization. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e100116. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0100116 |
- Alberton D, Silva de Oliveira L, Peralta RM, and Barbosa-Tessmann IP. (2007). Production, purification, and characterization of a novel galactose oxidase from Fusarium acuminatum. J Basic Microbiol. 2007;47(3):203-12. DOI:10.1002/jobm.200610290 |
- Minasian SG, Whittaker MM, and Whittaker JW. (2004). Stereoselective hydrogen abstraction by galactose oxidase. Biochemistry. 2004;43(43):13683-93. DOI:10.1021/bi048554s |
-
Siebum, A., van Wijk, A., Schoevaart, R. & Kieboom, T. (2006) Galactose oxidase and alcohol oxidase: scope and limitations for the enzymatic synthesis of aldehydes. J. Mol. Catal. B, 41, 141–145. DOI:10.1016/j.molcatb.2006.04.003
- Roberts GP and Gupta SK. (1965). Use of galactose oxidase in the histochemical examination of mucus-secreting cells. Nature. 1965;207(995):425-6. DOI:10.1038/207425a0 |
-
Yalpani, M.; Hall, L. D., (1982) Some chemical and analytical aspects of polysaccharide modifications. II. A high-yielding, specific method for the chemical derivatization of galactose-containing polysaccharides: Oxidation with galactose oxidase followed by reductive amination. J. Polym. Sci., Polym. Chem. Ed. 20, 3399-3420. DOI:10.1002/pol.1982.170201213
- Kelleher FM and Bhavanandan VP. (1986). Preparation and characterization of beta-D-fructofuranosyl O-(alpha-D-galactopyranosyl uronic acid)-(1----6)-O-alpha-D-glucopyranoside and O-(alpha-D-galactopyranosyl uronic acid)-(1----6)-D-glucose. Carbohydr Res. 1986;155:89-97. DOI:10.1016/s0008-6215(00)90135-6 |
-
Schoevaart, R., Kieboom, T. (2004) Application of galactose oxidase in chemoenzymatic one-pot cascade reactions without intermediate recovery steps. Topics in Catalysis, 27, 3–9. DOI:10.1023/B:TOCA.0000013536.27551.13
- Leppänen AS, Xu C, Parikka K, Eklund P, Sjöholm R, Brumer H, Tenkanen M, and Willför S. (2014). Targeted allylation and propargylation of galactose-containing polysaccharides in water. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;100:46-54. DOI:10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.11.053 |
- Xu C, Spadiut O, Araújo AC, Nakhai A, and Brumer H. (2012). Chemo-enzymatic assembly of clickable cellulose surfaces via multivalent polysaccharides. ChemSusChem. 2012;5(4):661-5. DOI:10.1002/cssc.201100522 |
- Parikka K, Leppänen AS, Xu C, Pitkänen L, Eronen P, Osterberg M, Brumer H, Willför S, and Tenkanen M. (2012). Functional and anionic cellulose-interacting polymers by selective chemo-enzymatic carboxylation of galactose-containing polysaccharides. Biomacromolecules. 2012;13(8):2418-28. DOI:10.1021/bm300679a |
-
Mikkonen, K. S.; Parikka, K.; Suuronen, J.-P.; Ghafar, A.; Serimaa, R.; Tenkanen, M., (2014) Enzymatic oxidation as a potential new route to produce polysaccharide aerogels. RSC Advances. 4, 11884-11892. DOI:10.1039/C3RA47440B
- Derikvand F, Yin DT, Barrett R, and Brumer H. (2016). Cellulose-Based Biosensors for Esterase Detection. Anal Chem. 2016;88(6):2989-93. DOI:10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04661 |
- Sun L, Bulter T, Alcalde M, Petrounia IP, and Arnold FH. (2002). Modification of galactose oxidase to introduce glucose 6-oxidase activity. Chembiochem. 2002;3(8):781-3. DOI:10.1002/1439-7633(20020802)3:8<781::AID-CBIC781>3.0.CO;2-8 |
- Lippow SM, Moon TS, Basu S, Yoon SH, Li X, Chapman BA, Robison K, Lipovšek D, and Prather KL. (2010). Engineering enzyme specificity using computational design of a defined-sequence library. Chem Biol. 2010;17(12):1306-15. DOI:10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.10.012 |
- Deacon SE, Mahmoud K, Spooner RK, Firbank SJ, Knowles PF, Phillips SE, and McPherson MJ. (2004). Enhanced fructose oxidase activity in a galactose oxidase variant. Chembiochem. 2004;5(7):972-9. DOI:10.1002/cbic.200300810 |
- Rannes JB, Ioannou A, Willies SC, Grogan G, Behrens C, Flitsch SL, and Turner NJ. (2011). Glycoprotein labeling using engineered variants of galactose oxidase obtained by directed evolution. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133(22):8436-9. DOI:10.1021/ja2018477 |
- Escalettes F and Turner NJ. (2008). Directed evolution of galactose oxidase: generation of enantioselective secondary alcohol oxidases. Chembiochem. 2008;9(6):857-60. DOI:10.1002/cbic.200700689 |
-
Herter, S.; McKenna, S. M.; Frazer, A. R.; Leimkühler, S.; Carnell, A. J.; Turner, N. J. (2015) Galactose Oxidase Variants for the Oxidation of Amino Alcohols in Enzyme Cascade Synthesis. ChemCatChem. 7, 2313-2317. DOI:10.1002/cctc.201500218
-
Birmingham, W. R.; Turner, N. J. (2018) A Single Enzyme Oxidative “Cascade” via a Dual-Functional Galactose Oxidase. ACS Catal. 8, 4025-4032. DOI:10.1021/acscatal.8b00043
-
Mattey, A. P.; Birmingham, W. R.; Both, P.; Kress, N.; Huang, K.; van Munster, J. M.; Bulmer, G. S.; Parmeggiani, F.; Voglmeir, J.; Martinez, J. E. R.; Turner, N. J.; Flitsch, S. L. (2019) Selective Oxidation of N-Glycolylneuraminic Acid Using an Engineered Galactose Oxidase Variant. ACS Catal. 9, 8208-8212. DOI:10.1021/acscatal.9b02873
- Huffman MA, Fryszkowska A, Alvizo O, Borra-Garske M, Campos KR, Canada KA, Devine PN, Duan D, Forstater JH, Grosser ST, Halsey HM, Hughes GJ, Jo J, Joyce LA, Kolev JN, Liang J, Maloney KM, Mann BF, Marshall NM, McLaughlin M, Moore JC, Murphy GS, Nawrat CC, Nazor J, Novick S, Patel NR, Rodriguez-Granillo A, Robaire SA, Sherer EC, Truppo MD, Whittaker AM, Verma D, Xiao L, Xu Y, and Yang H. (2019). Design of an in vitro biocatalytic cascade for the manufacture of islatravir. Science. 2019;366(6470):1255-1259. DOI:10.1126/science.aay8484 |
-
Toftgaard Pedersen, A.; Birmingham, W. R.; Rehn, G.; Charnock, S. J.; Turner, N. J.; Woodley, J. M. (2015) Process Requirements of Galactose Oxidase Catalyzed Oxidation of Alcohols. Org. Process Res. Dev. 19, 1580-1589. DOI:10.1021/acs.oprd.5b00278
- Forget SM, Xia FR, Hein JE, and Brumer H. (2020). Determination of biocatalytic parameters of a copper radical oxidase using real-time reaction progress monitoring. Org Biomol Chem. 2020;18(11):2076-2084. DOI:10.1039/c9ob02757b |
-
Monosik, R.; Stredansky, M.; Tkac, J.; Sturdik, E. (2012) Application of Enzyme Biosensors in Analysis of Food and Beverages. Food Anal. Methods. 5, 40-53. DOI:10.1007/s12161-011-9222-4
- Ribeaucourt D, Saker S, Navarro D, Bissaro B, Drula E, Correia LO, Haon M, Grisel S, Lapalu N, Henrissat B, O'Connell RJ, Lambert F, Lafond M, and Berrin JG. (2021). Identification of Copper-Containing Oxidoreductases in the Secretomes of Three Colletotrichum Species with a Focus on Copper Radical Oxidases for the Biocatalytic Production of Fatty Aldehydes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021;87(24):e0152621. DOI:10.1128/AEM.01526-21 |
- Ribeaucourt D, Bissaro B, Lambert F, Lafond M, and Berrin JG. (2022). Biocatalytic oxidation of fatty alcohols into aldehydes for the flavors and fragrances industry. Biotechnol Adv. 2022;56:107787. DOI:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2021.107787 |
-
Ribeaucourt, D.; Bissaro, B.; Guallar, V.; Yemloul, M.; Haon, M.; Grisel, S.; Alphand, V.; Brumer, H.; Lambert, F.; Berrin, J-G.; Lafond, M. (2021) Comprehensive Insights into the Production of Long Chain Aliphatic Aldehydes Using a Copper-Radical Alcohol Oxidase as Biocatalyst. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 9, 4411-4421 DOI:10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c07
- Roncal T, Muñoz C, Lorenzo L, Maestro B, and Díaz de Guereñu Mdel M. (2012). Two-step oxidation of glycerol to glyceric acid catalyzed by the Phanerochaete chrysosporium glyoxal oxidase. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2012;50(2):143-50. DOI:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2011.11.007 |
- Vilím J, Knaus T, and Mutti FG. (2018). Catalytic Promiscuity of Galactose Oxidase: A Mild Synthesis of Nitriles from Alcohols, Air, and Ammonia. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018;57(43):14240-14244. DOI:10.1002/anie.201809411 |
-
Rosatella, A. A.; Simeonov, S. P.; Frade, R. F. M.; Afonso, C. A. M. (2011) 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) as a building block platform: Biological properties, synthesis and synthetic applications. Green Chem. 13, 754-793. DOI:10.1039/C0GC00401D
-
Sousa, A. F.; Vilela, C.; Fonseca, A. C.; Matos, M.; Freire, C. S. R.; Gruter, G.-J. M.; Coelho, J. F. J.; Silvestre, A. J. D. (2015) Biobased polyesters and other polymers from 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid: a tribute to furan excellency. Polym. Chem. 6, 5961-5983. DOI:10.1039/C5PY00686D
- Birmingham WR, Toftgaard Pedersen A, Dias Gomes M, Bøje Madsen M, Breuer M, Woodley JM, and Turner NJ. (2021). Toward scalable biocatalytic conversion of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural by galactose oxidase using coordinated reaction and enzyme engineering. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4946. DOI:10.1038/s41467-021-25034-3 |
- Whittaker JW (2005). The radical chemistry of galactose oxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005;433(1):227-39. DOI:10.1016/j.abb.2004.08.034 |
- Baron AJ, Stevens C, Wilmot C, Seneviratne KD, Blakeley V, Dooley DM, Phillips SE, Knowles PF, and McPherson MJ. (1994). Structure and mechanism of galactose oxidase. The free radical site. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(40):25095-105. | Google Books | Open Library
- Humphreys KJ, Mirica LM, Wang Y, and Klinman JP. (2009). Galactose oxidase as a model for reactivity at a copper superoxide center. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131(13):4657-63. DOI:10.1021/ja807963e |
- Whittaker MM and Whittaker JW. (1993). Ligand interactions with galactose oxidase: mechanistic insights. Biophys J. 1993;64(3):762-72. DOI:10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81437-1 |
- Whittaker MM, Ballou DP, and Whittaker JW. (1998). Kinetic isotope effects as probes of the mechanism of galactose oxidase. Biochemistry. 1998;37(23):8426-36. DOI:10.1021/bi980328t |
- Wang Y, DuBois JL, Hedman B, Hodgson KO, and Stack TD. (1998). Catalytic galactose oxidase models: biomimetic Cu(II)-phenoxyl-radical reactivity. Science. 1998;279(5350):537-40. DOI:10.1126/science.279.5350.537 |
-
Itoh, S.; Taki, M.; Fukuzumi, S., (2000). Active site models for galactose oxidase and related enzymes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 198, 3-20. DOI:10.1016/S0010-8545(99)00209-X
-
Himo, F.; Eriksson, L. A.; Maseras, F.; Siegbahn, P. E. M., (2000). Catalytic Mechanism of Galactose Oxidase: A Theoretical Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 8031-8036. DOI:10.1021/ja994527r
- Kersten PJ (1990). Glyoxal oxidase of Phanerochaete chrysosporium: its characterization and activation by lignin peroxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87(8):2936-40. DOI:10.1073/pnas.87.8.2936 |
- Cleveland L, Coffman RE, Coon P, and Davis L. (1975). An investigation of the role of the copper in galactose oxidase. Biochemistry. 1975;14(6):1108-15. DOI:10.1021/bi00677a003 |
- Hamilton GA, Dyrkacz GR, and Libby RD. (1976). The involvement of superoxide and trivalent copper in the galactose oxidase reaction. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;74:489-504. DOI:10.1007/978-1-4684-3270-1_42 |
-
Toftgaard Pedersen, A.; Birmingham, W. R.; Rehn, G.; Charnock, S. J.; Turner, N. J.; Woodley, J. M., (2015) Process Requirements of Galactose Oxidase Catalyzed Oxidation of Alcohols. Org. Process Res. Dev. 19, 1580-1589. DOI:10.1021/acs.oprd.5b00278
- Johnson HC, Zhang S, Fryszkowska A, Ruccolo S, Robaire SA, Klapars A, Patel NR, Whittaker AM, Huffman MA, and Strotman NA. (2021). Biocatalytic oxidation of alcohols using galactose oxidase and a manganese(III) activator for the synthesis of islatravir. Org Biomol Chem. 2021;19(7):1620-1625. DOI:10.1039/d0ob02395g |
- Ito N, Phillips SE, Stevens C, Ogel ZB, McPherson MJ, Keen JN, Yadav KD, and Knowles PF. (1991). Novel thioether bond revealed by a 1.7 A crystal structure of galactose oxidase. Nature. 1991;350(6313):87-90. DOI:10.1038/350087a0 |
- Ito N, Phillips SE, Yadav KD, and Knowles PF. (1994). Crystal structure of a free radical enzyme, galactose oxidase. J Mol Biol. 1994;238(5):794-814. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1994.1335 |
- Rogers MS, Hurtado-Guerrero R, Firbank SJ, Halcrow MA, Dooley DM, Phillips SE, Knowles PF, and McPherson MJ. (2008). Cross-link formation of the cysteine 228-tyrosine 272 catalytic cofactor of galactose oxidase does not require dioxygen. Biochemistry. 2008;47(39):10428-39. DOI:10.1021/bi8010835 |
- Rogers MS, Tyler EM, Akyumani N, Kurtis CR, Spooner RK, Deacon SE, Tamber S, Firbank SJ, Mahmoud K, Knowles PF, Phillips SE, McPherson MJ, and Dooley DM. (2007). The stacking tryptophan of galactose oxidase: a second-coordination sphere residue that has profound effects on tyrosyl radical behavior and enzyme catalysis. Biochemistry. 2007;46(15):4606-18. DOI:10.1021/bi062139d |
- Chaplin AK, Svistunenko DA, Hough MA, Wilson MT, Vijgenboom E, and Worrall JA. (2017). Active-site maturation and activity of the copper-radical oxidase GlxA are governed by a tryptophan residue. Biochem J. 2017;474(5):809-825. DOI:10.1042/BCJ20160968 |
- Cowley RE, Cirera J, Qayyum MF, Rokhsana D, Hedman B, Hodgson KO, Dooley DM, and Solomon EI. (2016). Structure of the Reduced Copper Active Site in Preprocessed Galactose Oxidase: Ligand Tuning for One-Electron O(2) Activation in Cofactor Biogenesis. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138(40):13219-13229. DOI:10.1021/jacs.6b05792 |
- Thomas F, Gellon G, Gautier-Luneau I, Saint-Aman E, and Pierre JL. (2002). A structural and functional model of galactose oxidase: control of the one-electron oxidized active form through two differentiated phenolic arms in a tripodal ligand. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2002;41(16):3047-50. DOI:10.1002/1521-3773(20020816)41:16<3047::AID-ANIE3047>3.0.CO;2-W |
- Wright C and Sykes AG. (2001). Interconversion of Cu(I) and Cu(II) forms of galactose oxidase: comparison of reduction potentials. J Inorg Biochem. 2001;85(4):237-43. DOI:10.1016/s0162-0134(01)00214-8 |
-
Jazdzewski, B. A.; Tolman, W. B., (2000). Understanding the copper–phenoxyl radical array in galactose oxidase: contributions from synthetic modeling studies. Coord. Chem. Rev. 200-202, 633-685. DOI:10.1016/S0010-8545(00)00342-8
-
Saysell, C. G.; Barna, T.; Borman, C. D.; Baron, A. J.; McPherson, M. J.; Sykes, A. G., P(1997). Properties of the Trp290His variant of Fusarium NRRL 2903 galactose oxidase: interactions of the GOasesemi state with different buffers, its redox activity and ability to bind azide. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2, 702-709. DOI:10.1007/s007750050186
-
Rogers, M. S.; Knowles, P. F.; Baron, A. J.; McPherson, M. J.; Dooley, D. M., (1998). Characterization of the active site of galactose oxidase and its active site mutational variants Y495F/H/K and W290H by circular dichroism spectroscopy. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 275-276, 175-181. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-1693(97)06142-2
- Faria CB, de Castro FF, Martim DB, Abe CAL, Prates KV, de Oliveira MAS, and Barbosa-Tessmann IP. (2019). Production of Galactose Oxidase Inside the Fusarium fujikuroi Species Complex and Recombinant Expression and Characterization of the Galactose Oxidase GaoA Protein from Fusarium subglutinans. Mol Biotechnol. 2019;61(9):633-649. DOI:10.1007/s12033-019-00190-6 |
- AMARAL D, BERNSTEIN L, MORSE D, and HORECKER BL. (1963). Galactose oxidase of Polyporus circinatus: a copper enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1963;238:2281-4. | Google Books | Open Library
- Mollerup F and Master E. (2016). Influence of a family 29 carbohydrate binding module on the recombinant production of galactose oxidase in Pichia pastoris. Data Brief. 2016;6:176-83. DOI:10.1016/j.dib.2015.11.032 |
-
McKenna, S. M.; Mines, P.; Law, P.; Kovacs-Schreiner, K.; Birmingham, W. R.; Turner, N. J.; Leimkühler, S.; Carnell, A. J. (2017) The continuous oxidation of HMF to FDCA and the immobilisation and stabilisation of periplasmic aldehyde oxidase (PaoABC). Green Chem. 19, 4660-4665. DOI:10.1039/C7GC01696D
