CAZypedia celebrates the life of Senior Curator Emeritus Harry Gilbert, a true giant in the field, who passed away in September 2025.
CAZypedia needs your help!
We have many unassigned pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators. See a page that's out-of-date and just needs a touch-up? - You are also welcome to become a CAZypedian. Here's how.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute.
Learn more about CAZypedia's misson here and in this article. Totally new to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
Difference between revisions of "Carbohydrate Binding Module Family 32"
| (64 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!-- RESPONSIBLE CURATORS: Please replace the {{UnderConstruction}} tag below with {{CuratorApproved}} when the page is ready for wider public consumption --> | <!-- RESPONSIBLE CURATORS: Please replace the {{UnderConstruction}} tag below with {{CuratorApproved}} when the page is ready for wider public consumption --> | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{CuratorApproved}} |
| − | * [[Author]]: | + | * [[Author]]s: [[User:Elizabeth Ficko-Blean|Elizabeth Ficko-Blean]] and [[User:Al Boraston|Al Boraston]] |
| − | * [[Responsible Curator]]: | + | * [[Responsible Curator]]: [[User:Elizabeth Ficko-Blean|Elizabeth Ficko-Blean]] |
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
== Ligand specificities == | == Ligand specificities == | ||
| − | In 1994 the first | + | In 1994, the first structure of a [[carbohydrate-binding modules|carbohydrate-binding module]] of family 32, in complex with D-galactose, was determined from a fungal galactose oxidase <cite>Ito1994</cite>. Following that, a CBM32 from a multi-modular sialidase produced by ''Micromonospora viridifaciens'' was shown to demonstrate galactose and lactose binding specificity <cite>Gaskell1995 Newstead2005</cite>. A CBM32 from a ''Cellvibrio mixtus'' family 16 glycoside hydrolase binds laminarin and pustulan <cite>Centeno2006</cite>, while a CBM32 from a ''Clostridium thermocellum'' mannanase has demonstrable binding on the non-reducing end of β-mannans and β-1,4-linked mannooligosaccharides <cite>Mizutani2012</cite>. A periplasmic-binding protein, YeCBM32, from ''Yersinia enterolitica'' shares sequence identity with the CBM32 family and binds the polygalaturonic acid components of pectin <cite>Abbott2007</cite>. A CBM32 from ''Persicobacter sp'' alginate lyase AlyQ binds 4,5-unsaturated uronic acid on the non-reducing end of alginate oligosaccharides <cite>Teh2020</cite>. The ''Clostridium perfringens'' CBM32s have been well studied and many of their ligand specificities were determined as follows: D-galactose, N-acetyl-D-galactosamine <cite>Boraston2007 Ficko-Blean2012 Ficko-Blean2006 </cite>, D-galactose-β-1,4-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (LacNAc), L-fucose-α-1,2-D-galactose-β-1,4-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (type II blood group H-trisaccharide) <cite>Ficko-Blean2006</cite>, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-β-1,3-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-β-1,2-D-mannose, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-β-1,3-D-mannose (non-biological) <cite>Ficko-Blean2009</cite>, and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-α-1,4-D-galactose <cite>Ficko-Blean2012</cite>. Some members of CBM family 32 have exhibited a degree of substrate promiscuity; these include CpCBM32-2 from the NagH enzyme and CpCBM32C from the NagJ enzyme of ''Clostridium perfringens'' <cite>Ficko-Blean2009 Ficko-Blean2006</cite>. This CBM family has a very diverse set of ligand specificities that is reflected in the notable amino acid sequence divergence throughout the family <cite>AbbottMolBiolEvol</cite>. |
| − | + | == Structural Features == | |
| + | [[File:Cbm32C.png|thumb|300px|right|'''Figure 1.''' A secondary structure representation of the ''C. perfringens'' NagJ CpCBM32C [{{PDBlink}}2j1e 2J1e] showing the tryptophan platform, found in the terminal loop region, interacting with D-galactose from LacNac. A calcium is shown as a grey sphere. ]] | ||
| − | + | The CBM32s share the common beta sandwich fold and have a bound structural metal ion that is most often attributed to be calcium <cite>Boraston2004</cite>. Most family members have fairly weak binding affinities (''K''<sub>a</sub> values in the mM<sup>-1</sup> and low μM<sup>-1</sup> range) <cite>Ficko-Blean2009 Ficko-Blean2006 Mizutani2012</cite>. These binding site are located at the terminal loop region within the CBM32 family. The binding sites are, in some cases, quite shallow and designed to bind monosaccharides or short oligosaccharides, making these [[Carbohydrate-binding_modules#Types|type C]] CBMs <cite>Ficko-Blean2009 Ficko-Blean2006 Boraston2007 Ficko-Blean2012</cite>. Variability within the apical loop region within the family confers the different ligand specificities. Characteristically, there is one residue, commonly Trp but also Tyr, which provides an important hydrophobic platform for interaction with the ring of one of the sugar moieties (Figure 1) <cite>Gaskell1995 Ficko-Blean2006 Ficko-Blean2012</cite>. In most cases, the CBM32 members interact with the saturated non-reducing end of oligosaccharides <cite>Ficko-Blean2009 Ficko-Blean2006 Boraston2007 Ficko-Blean2012 Mizutani2012</cite>. However, this is not always the case, as demonstrated by the periplasmic-binding protein from ''Y. enterocolitica'', which shares sequence identity with the CBM32 family <cite>Cantarel2009</cite> and binds polygalacturonic acid polymers <cite>Abbott2007</cite> or the CBM32 domain of the alginate lyase AlyQ, which specifically recognizes a 4,5-unsaturated uronate at the non-reducing end <cite>Teh2020</cite>. | |
| − | The CBM32s share the common beta sandwich fold and have a bound structural metal ion most often attributed to be calcium <cite>Boraston2004</cite>. Most family members | + | |
| + | Some structural examples of the complex oligosaccharide binding sites of the CBM32s can be found in the following PDB entries: [{{PDBlink}}1euu 1EUU] <cite>Gaskell1995</cite>, [{{PDBlink}}7d29 7D29]<cite>Teh2020</cite>,[{{PDBlink}}2j7m 2J7M] <cite>Ficko-Blean2006</cite>, [{{PDBlink}}4a45 4A45] <cite>Ficko-Blean2012</cite>, [{{PDBlink}}4a6o 4A6O] <cite>Ficko-Blean2012</cite>, and [{{PDBlink}}2w1u 2W1U] <cite>Ficko-Blean2009</cite>, to name just a few. An updated list of available three-dimensional structures is available on the [http://www.cazy.org/CBM32_structure.html CBM32 page of the CAZy Database]. | ||
== Functionalities == | == Functionalities == | ||
| − | + | CBMs, in general, are thought to [[Carbohydrate-binding modules|target pendant catalytic modules to their respective substrates]]. CtCBM32 from a ''C. thermocellum'' manannase potentiates the hydrolytic function of the enzyme and prevents transglycosylation reactions by preferentially binding the non-reducing end of β-mannans. Thus, the CBM32 may sterically block the access of longer manno-oligosaccharide acceptor molecules to the enzyme active site thereby enhancing hydrolysis and affecting the products of catalysis <cite>Mizutani2012</cite>. | |
| − | The | + | Alginate lyases may be mannuronate (EC 4.2.2.3), guluronate (EC 4.2.2.11) or mixed link (EC 4.2.2.-) specific lyases. The β-elimination of the 4-OH of the C5 epimers mannuronate or guluronate during alginate lyase activity results in the same 4,5-unsaturated uronate residue on the non-reducing end. Thus, alginate lyase released non-reducing end 4,5-unsaturated ManA and GulA have the same configuration and are identical. The ''Persicobacter sp'' CBM32 from AlyQ, a [[PL7]], specifically targets this unsaturated non-reducing end uronate rather than the individual mannuronate or guluronate residues <cite>Teh2020, Sim2017</cite>. |
| − | + | CBM32s from the Gram-positive pathogen ''C. perfringens'' may well have a dual role as many of the enzymes containing CBM32s have an LPXTG motif at their C-terminal end, which generally signals for sortase-mediated anchoring to the bacterial cell wall <cite>Mazmanian1999</cite>. Thus, not only would the catalytic modules be targeted to substrate, but also the bacterium as a whole, suggesting an adhesin-like activity for these CBMs <cite>Ficko-BleanPortraitOfAnEnzyme</cite>. | |
| − | + | The types of catalytic modules that the CBM32 members are associated with vary widely and include sialidases <cite>Boraston2007</cite>, β-N-acetylglucosaminidases <cite>Rao</cite>, α-N-acetylglucosaminidases <cite>Ficko-BleanGH89</cite>, alginate lyases <cite>Teh2020</cite>, mannanases <cite>Mizutani2012</cite> and galactose oxidases <cite>Ito1994</cite>. In enteric bacteria the CBM32 motif may occur more than once in the same enzyme and they may or may not share the same ligand specifities; this suggests the possibility of heterogenic multivalent binding events <cite>Boraston2007 Ficko-Blean2012 AbbottMolBiolEvol</cite>. Other modules that may be associated in the same enzymes are different families of CBMs, FNIII domains, and cohesin and dockerin domains <cite>Ficko-BleanPortraitOfAnEnzyme Chitayat2008 Adams2008 Ficko-Blean2012</cite>. There are now examples of CBM32s that are independent of a catalytic module, such as the YeCBM32 periplasmic-binding protein <cite>Abbott2007</cite>. | |
| + | |||
| + | As an example of an unusual biotechnological application, the ligand binding loops from CpCBM32-2 from the NagH enzyme were modified to create polyol-responsive antibody mimetics for affinity purification of specific proteins <cite>Suderman2017</cite>. This CBM32 application speaks to the plasticity within the loop binding region. | ||
== Family Firsts == | == Family Firsts == | ||
| − | ;First Identified | + | ;First Identified: The galactose-binding function of CBM32 was first suggested by crystallography of a galactose oxidase from the fungus ''Fusarium graminearum'' <cite>Ito1994</cite> (previously ''Dactylium dendroides'' <cite>Ogel1994</cite>). |
| − | The | + | ;First Structural Characterization: In 1991, the first crystal structures of a galactose oxidase from the fungus ''F. graminearum'' (''e.g.'' PDB ID [{{PDBlink}}1gof 1GOF]) revealed an N-terminal CBM32, although this study did not explore the carbohydrate-binding function of this module <cite>Ito1991</cite>. The first available complex structure of a CBM32 is from the same galactose oxidase soaked with galactose <cite>Ito1994</cite>; unfortunately, a corresponding entry in the RCSB Protein Data Bank is lacking. |
| − | ;First Structural Characterization | ||
| − | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 52: | Line 54: | ||
#Mizutani2012 pmid=22562994 | #Mizutani2012 pmid=22562994 | ||
#Mazmanian1999 pmid=10427003 | #Mazmanian1999 pmid=10427003 | ||
| − | #Ficko-BleanGH89 pmid= | + | #Ficko-BleanGH89 pmid=22090394 |
#Ficko-Blean2012 pmid=22479408 | #Ficko-Blean2012 pmid=22479408 | ||
#Ficko-Blean2009 pmid=19422833 | #Ficko-Blean2009 pmid=19422833 | ||
#Ficko-Blean2006 pmid=16990278 | #Ficko-Blean2006 pmid=16990278 | ||
#Ficko-BleanPortraitOfAnEnzyme pmid=19193644 | #Ficko-BleanPortraitOfAnEnzyme pmid=19193644 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
#Rao pmid=16541109 | #Rao pmid=16541109 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
#Ito1991 pmid=2002850 | #Ito1991 pmid=2002850 | ||
| − | # | + | #Ogel1994 Ögel, Z.B. Brayford, D. and McPherson, M.J. (1994) ''Cellulose-Triggered Sporulation in the Galactose Oxidase-Producing Fungus Cladobotryum (Dactylium) Dendroides Nrrl-2903 and Its Reidentification as a Species of Fusarium.'' Mycological Research, 98(4):474-480. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0953-7562(09)81207-0 DOI:10.1016/S0953-7562(09)81207-0] |
| + | #Suderman2017 pmid=28428153 | ||
| + | #Teh2020 pmid=33010888 | ||
| + | |||
| + | #Sim2017 pmid=29057942 | ||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
[[Category:Carbohydrate Binding Module Families|CBM032]] | [[Category:Carbohydrate Binding Module Families|CBM032]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:38, 25 August 2022
This page has been approved by the Responsible Curator as essentially complete. CAZypedia is a living document, so further improvement of this page is still possible. If you would like to suggest an addition or correction, please contact the page's Responsible Curator directly by e-mail.
| CAZy DB link | |
| https://www.cazy.org/CBM32.html |
Ligand specificities
In 1994, the first structure of a carbohydrate-binding module of family 32, in complex with D-galactose, was determined from a fungal galactose oxidase [1]. Following that, a CBM32 from a multi-modular sialidase produced by Micromonospora viridifaciens was shown to demonstrate galactose and lactose binding specificity [2, 3]. A CBM32 from a Cellvibrio mixtus family 16 glycoside hydrolase binds laminarin and pustulan [4], while a CBM32 from a Clostridium thermocellum mannanase has demonstrable binding on the non-reducing end of β-mannans and β-1,4-linked mannooligosaccharides [5]. A periplasmic-binding protein, YeCBM32, from Yersinia enterolitica shares sequence identity with the CBM32 family and binds the polygalaturonic acid components of pectin [6]. A CBM32 from Persicobacter sp alginate lyase AlyQ binds 4,5-unsaturated uronic acid on the non-reducing end of alginate oligosaccharides [7]. The Clostridium perfringens CBM32s have been well studied and many of their ligand specificities were determined as follows: D-galactose, N-acetyl-D-galactosamine [8, 9, 10], D-galactose-β-1,4-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (LacNAc), L-fucose-α-1,2-D-galactose-β-1,4-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (type II blood group H-trisaccharide) [10], N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-β-1,3-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-β-1,2-D-mannose, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-β-1,3-D-mannose (non-biological) [11], and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-α-1,4-D-galactose [9]. Some members of CBM family 32 have exhibited a degree of substrate promiscuity; these include CpCBM32-2 from the NagH enzyme and CpCBM32C from the NagJ enzyme of Clostridium perfringens [10, 11]. This CBM family has a very diverse set of ligand specificities that is reflected in the notable amino acid sequence divergence throughout the family [12].
Structural Features
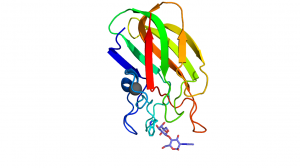
The CBM32s share the common beta sandwich fold and have a bound structural metal ion that is most often attributed to be calcium [13]. Most family members have fairly weak binding affinities (Ka values in the mM-1 and low μM-1 range) [5, 10, 11]. These binding site are located at the terminal loop region within the CBM32 family. The binding sites are, in some cases, quite shallow and designed to bind monosaccharides or short oligosaccharides, making these type C CBMs [8, 9, 10, 11]. Variability within the apical loop region within the family confers the different ligand specificities. Characteristically, there is one residue, commonly Trp but also Tyr, which provides an important hydrophobic platform for interaction with the ring of one of the sugar moieties (Figure 1) [2, 9, 10]. In most cases, the CBM32 members interact with the saturated non-reducing end of oligosaccharides [5, 8, 9, 10, 11]. However, this is not always the case, as demonstrated by the periplasmic-binding protein from Y. enterocolitica, which shares sequence identity with the CBM32 family [14] and binds polygalacturonic acid polymers [6] or the CBM32 domain of the alginate lyase AlyQ, which specifically recognizes a 4,5-unsaturated uronate at the non-reducing end [7].
Some structural examples of the complex oligosaccharide binding sites of the CBM32s can be found in the following PDB entries: 1EUU [2], 7D29[7],2J7M [10], 4A45 [9], 4A6O [9], and 2W1U [11], to name just a few. An updated list of available three-dimensional structures is available on the CBM32 page of the CAZy Database.
Functionalities
CBMs, in general, are thought to target pendant catalytic modules to their respective substrates. CtCBM32 from a C. thermocellum manannase potentiates the hydrolytic function of the enzyme and prevents transglycosylation reactions by preferentially binding the non-reducing end of β-mannans. Thus, the CBM32 may sterically block the access of longer manno-oligosaccharide acceptor molecules to the enzyme active site thereby enhancing hydrolysis and affecting the products of catalysis [5].
Alginate lyases may be mannuronate (EC 4.2.2.3), guluronate (EC 4.2.2.11) or mixed link (EC 4.2.2.-) specific lyases. The β-elimination of the 4-OH of the C5 epimers mannuronate or guluronate during alginate lyase activity results in the same 4,5-unsaturated uronate residue on the non-reducing end. Thus, alginate lyase released non-reducing end 4,5-unsaturated ManA and GulA have the same configuration and are identical. The Persicobacter sp CBM32 from AlyQ, a PL7, specifically targets this unsaturated non-reducing end uronate rather than the individual mannuronate or guluronate residues [7, 15].
CBM32s from the Gram-positive pathogen C. perfringens may well have a dual role as many of the enzymes containing CBM32s have an LPXTG motif at their C-terminal end, which generally signals for sortase-mediated anchoring to the bacterial cell wall [16]. Thus, not only would the catalytic modules be targeted to substrate, but also the bacterium as a whole, suggesting an adhesin-like activity for these CBMs [17].
The types of catalytic modules that the CBM32 members are associated with vary widely and include sialidases [8], β-N-acetylglucosaminidases [18], α-N-acetylglucosaminidases [19], alginate lyases [7], mannanases [5] and galactose oxidases [1]. In enteric bacteria the CBM32 motif may occur more than once in the same enzyme and they may or may not share the same ligand specifities; this suggests the possibility of heterogenic multivalent binding events [8, 9, 12]. Other modules that may be associated in the same enzymes are different families of CBMs, FNIII domains, and cohesin and dockerin domains [9, 17, 20, 21]. There are now examples of CBM32s that are independent of a catalytic module, such as the YeCBM32 periplasmic-binding protein [6].
As an example of an unusual biotechnological application, the ligand binding loops from CpCBM32-2 from the NagH enzyme were modified to create polyol-responsive antibody mimetics for affinity purification of specific proteins [22]. This CBM32 application speaks to the plasticity within the loop binding region.
Family Firsts
- First Identified
- The galactose-binding function of CBM32 was first suggested by crystallography of a galactose oxidase from the fungus Fusarium graminearum [1] (previously Dactylium dendroides [23]).
- First Structural Characterization
- In 1991, the first crystal structures of a galactose oxidase from the fungus F. graminearum (e.g. PDB ID 1GOF) revealed an N-terminal CBM32, although this study did not explore the carbohydrate-binding function of this module [24]. The first available complex structure of a CBM32 is from the same galactose oxidase soaked with galactose [1]; unfortunately, a corresponding entry in the RCSB Protein Data Bank is lacking.
References
- Ito N, Phillips SE, Yadav KD, and Knowles PF. (1994). Crystal structure of a free radical enzyme, galactose oxidase. J Mol Biol. 1994;238(5):794-814. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1994.1335 |
- Gaskell A, Crennell S, and Taylor G. (1995). The three domains of a bacterial sialidase: a beta-propeller, an immunoglobulin module and a galactose-binding jelly-roll. Structure. 1995;3(11):1197-205. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00255-6 |
- Newstead SL, Watson JN, Bennet AJ, and Taylor G. (2005). Galactose recognition by the carbohydrate-binding module of a bacterial sialidase. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2005;61(Pt 11):1483-91. DOI:10.1107/S0907444905026132 |
- Centeno MS, Goyal A, Prates JA, Ferreira LM, Gilbert HJ, and Fontes CM. (2006). Novel modular enzymes encoded by a cellulase gene cluster in Cellvibrio mixtus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006;265(1):26-34. DOI:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00464.x |
- Mizutani K, Fernandes VO, Karita S, Luís AS, Sakka M, Kimura T, Jackson A, Zhang X, Fontes CM, Gilbert HJ, and Sakka K. (2012). Influence of a mannan binding family 32 carbohydrate binding module on the activity of the appended mannanase. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012;78(14):4781-7. DOI:10.1128/AEM.07457-11 |
- Abbott DW, Hrynuik S, and Boraston AB. (2007). Identification and characterization of a novel periplasmic polygalacturonic acid binding protein from Yersinia enterolitica. J Mol Biol. 2007;367(4):1023-33. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.01.030 |
- Teh AH, Sim PF, and Hisano T. (2020). Structural basis for binding uronic acids by family 32 carbohydrate-binding modules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;533(3):257-261. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.09.064 |
- Boraston AB, Ficko-Blean E, and Healey M. (2007). Carbohydrate recognition by a large sialidase toxin from Clostridium perfringens. Biochemistry. 2007;46(40):11352-60. DOI:10.1021/bi701317g |
- Ficko-Blean E, Stuart CP, Suits MD, Cid M, Tessier M, Woods RJ, and Boraston AB. (2012). Carbohydrate recognition by an architecturally complex α-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Clostridium perfringens. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33524. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0033524 |
- Ficko-Blean E and Boraston AB. (2006). The interaction of a carbohydrate-binding module from a Clostridium perfringens N-acetyl-beta-hexosaminidase with its carbohydrate receptor. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(49):37748-57. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M606126200 |
- Ficko-Blean E and Boraston AB. (2009). N-acetylglucosamine recognition by a family 32 carbohydrate-binding module from Clostridium perfringens NagH. J Mol Biol. 2009;390(2):208-20. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.04.066 |
- Abbott DW, Eirín-López JM, and Boraston AB. (2008). Insight into ligand diversity and novel biological roles for family 32 carbohydrate-binding modules. Mol Biol Evol. 2008;25(1):155-67. DOI:10.1093/molbev/msm243 |
- Sim PF, Furusawa G, and Teh AH. (2017). Functional and Structural Studies of a Multidomain Alginate Lyase from Persicobacter sp. CCB-QB2. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):13656. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-13288-1 |
- Mazmanian SK, Liu G, Ton-That H, and Schneewind O. (1999). Staphylococcus aureus sortase, an enzyme that anchors surface proteins to the cell wall. Science. 1999;285(5428):760-3. DOI:10.1126/science.285.5428.760 |
- Ficko-Blean E, Gregg KJ, Adams JJ, Hehemann JH, Czjzek M, Smith SP, and Boraston AB. (2009). Portrait of an enzyme, a complete structural analysis of a multimodular {beta}-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Clostridium perfringens. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(15):9876-84. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M808954200 |
- Rao FV, Dorfmueller HC, Villa F, Allwood M, Eggleston IM, and van Aalten DM. (2006). Structural insights into the mechanism and inhibition of eukaryotic O-GlcNAc hydrolysis. EMBO J. 2006;25(7):1569-78. DOI:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601026 |
- Ficko-Blean E and Boraston AB. (2012). Structural analysis of a bacterial exo-α-D-N-acetylglucosaminidase in complex with an unusual disaccharide found in class III mucin. Glycobiology. 2012;22(5):590-5. DOI:10.1093/glycob/cwr165 |
- Chitayat S, Gregg K, Adams JJ, Ficko-Blean E, Bayer EA, Boraston AB, and Smith SP. (2008). Three-dimensional structure of a putative non-cellulosomal cohesin module from a Clostridium perfringens family 84 glycoside hydrolase. J Mol Biol. 2008;375(1):20-8. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.10.031 |
- Adams JJ, Gregg K, Bayer EA, Boraston AB, and Smith SP. (2008). Structural basis of Clostridium perfringens toxin complex formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(34):12194-9. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0803154105 |
- Suderman RJ, Rice DA, Gibson SD, Strick EJ, and Chao DM. (2017). Development of polyol-responsive antibody mimetics for single-step protein purification. Protein Expr Purif. 2017;134:114-124. DOI:10.1016/j.pep.2017.04.008 |
-
Ögel, Z.B. Brayford, D. and McPherson, M.J. (1994) Cellulose-Triggered Sporulation in the Galactose Oxidase-Producing Fungus Cladobotryum (Dactylium) Dendroides Nrrl-2903 and Its Reidentification as a Species of Fusarium. Mycological Research, 98(4):474-480. DOI:10.1016/S0953-7562(09)81207-0
- Ito N, Phillips SE, Stevens C, Ogel ZB, McPherson MJ, Keen JN, Yadav KD, and Knowles PF. (1991). Novel thioether bond revealed by a 1.7 A crystal structure of galactose oxidase. Nature. 1991;350(6313):87-90. DOI:10.1038/350087a0 |