CAZypedia needs your help!
We have many unassigned pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators. See a page that's out-of-date and just needs a touch-up? - You are also welcome to become a CAZypedian. Here's how.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute.
Learn more about CAZypedia's misson here and in this article.
Totally new to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
Difference between revisions of "Glycoside Hydrolase Family 162"
| (12 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!-- RESPONSIBLE CURATORS: Please replace the {{UnderConstruction}} tag below with {{CuratorApproved}} when the page is ready for wider public consumption --> | <!-- RESPONSIBLE CURATORS: Please replace the {{UnderConstruction}} tag below with {{CuratorApproved}} when the page is ready for wider public consumption --> | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{CuratorApproved}} |
| − | * [[Author]]: | + | * [[Author]]: [[User:Nobukiyo Tanaka|Nobukiyo Tanaka]] |
| − | * [[Responsible Curator]]: | + | * [[Responsible Curator]]: [[User:Masahiro Nakajima|Masahiro Nakajima]] |
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Clan''' | |'''Clan''' | ||
| − | | | + | |Clan-S |
|- | |- | ||
|'''Mechanism''' | |'''Mechanism''' | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
== Substrate specificities == | == Substrate specificities == | ||
| − | [[Image:The_phylogenetic_tree_of_GH162_homologs.png|thumb|500px|'''Figure 1. The phylogenetic tree of GH162 homologs.''' ]] | + | [[Image:The_phylogenetic_tree_of_GH162_homologs.png|thumb|500px|'''Figure 1. The phylogenetic tree of GH162 homologs.''' ]] |
| − | + | The defining member of [[glycoside hydrolase]] family 162, a β-1,2-glucanase from ''Talaromyces funiculosus'' (''Tf''SGL), was identified, characterized, and structurally analyzed as reported in 2019 <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. This enzyme specifically hydrolyzes both cyclic and linear β-1,2-glucans, which comprise a β-linked glucosyl backbone, and preferably releases sophorose (Glc-β-1,2-Glc) from the reducing end of linear β-1,2-glucan <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. Almost all of the family members are from Eukaryotes <cite>Tanaka2019</cite> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Kinetics and Mechanism == | == Kinetics and Mechanism == | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Catalytic_mechanism_of_Tfsgl.jpeg|thumb|right|350px|'''Figure 2. Active site and reaction mechanism.''' '''(A)''' The complex of the E262Q mutant with β-1,2-glucoheptaose. The numbers beside the substrate represent the positions of subsites. The ''red'' and ''blue'' dotted lines represent the hydrogen bonds between the ligands and D177 or E262, respectively. The β-1,2-glucotriose moiety in the observed substrate is represented by a ''yellow stick''. Candidate residues for a general acid are represented by ''brown sticks''. The 262th glutamine residue is represented as a glutamic acid. '''(B)''' E262 (general acid) indirectly protonates the glycosidic bond oxygen atom via the 3-hydroxy group of the Glc moiety at subsite +2 and D446 (general base) activates the nucleophilic water via another water <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>.]] |
| − | '''(A)''' The complex of the E262Q mutant with β-1,2-glucoheptaose. The numbers beside the substrate represent the positions of subsites. The ''red'' and ''blue dotted lines | + | Hydrolysis of cyclic β-1,2-glucan by ''Tf''SGL suggests that the enzyme is ''endo''-acting <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. The <sup>1</sup>H-NMR analysis of the anomeric configurations of hydrolysates indicates that ''Tf''SGL has an [[inverting]] mechanism. Analysis of the change of the degree of optical rotation during hydrolysis of β-1,2-glucan also supported this mechanism <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Structural analysis (see “Three-dimensional structures” below) and mutational analysis suggest that D446 activates the nucleophilic water via another water as a general acid <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. These analyses also suggest that D177 and/or E262 act as a general acid via the 3-hydroxy groups of the Glc moieties (see below) <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. According to action-pattern analysis using β-1,2-glucopentaose derivatives deoxygenated at their 3-hydroxy groups in the first or second Glc moiety from the reducing end, E262 was clearly determined to be a general acid. The 3-hydroxy group of the Glc moiety at subsite +2 mediates protonation of glycosidic bond oxygen atom <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. The reaction mechanism of ''Tf''SGL is quite unique in that both reaction pathways involving a general acid and a general base are non-canonical <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. | ||
== Catalytic Residues == | == Catalytic Residues == | ||
| − | The general acid and base of ''Tf''SGL are E262 and D446, respectively <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. Both residues are highly conserved in [[GH162]] enzymes. The general acid of ''Tf''SGL is well superimposed with an acidic residue in a [[GH144]] bacterial β-1,2-glucanase from ''Chitinophaga pinensis'' (''Cp''SGL), whereas the general base is not superimposed <cite>Tanaka2019, Abe2017</cite>. Although the reaction mechanisms of [[GH144]] are unclear, ''Tf''SGL | + | The general acid and base of ''Tf''SGL are E262 and D446, respectively <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. Both residues are highly conserved in [[GH162]] enzymes. The general acid of ''Tf''SGL is well superimposed with an acidic residue in a [[GH144]] bacterial β-1,2-glucanase from ''Chitinophaga pinensis'' (''Cp''SGL), whereas the general base is not superimposed <cite>Tanaka2019, Abe2017</cite>. Although the reaction mechanisms of [[GH144]] enzymes are currently unclear (June 2019), structural comparison of ''Tf''SGL and [[GH144]] suggests differences in reaction mechanisms <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | A structural comparison revealed that the position of the general acid residue in [[GH162]] and the candidate catalytic residue in [[GH144]] are well superimposed structurally <cite>Tanaka2024</cite>. In contrast, the positions of the other catalytic residues (or candidate catalytic residues) in [[GH162]] and [[GH144]] are completely different <cite>Tanaka2024</cite>. Furthermore, compared to clans GH-G, L, M, O, P and Q, which have the same overall structure (= (α/α)<sub>6</sub> fold) as [[GH162]] and [[GH144]], none of the positions of the catalytic residues in [[GH162]] and [[GH144]] are conserved <cite>Tanaka2024</cite>. A new clan GH-S was created for GH162 and GH144 based on these results <cite>Tanaka2024</cite>. | ||
== Three-dimensional structures == | == Three-dimensional structures == | ||
| − | [[Image:Overall_structure.jpg|thumb|350px|'''Figure 3. Overall structure of ''Tf''SGL (PDB [ | + | [[Image:Overall_structure.jpg|thumb|350px|'''Figure 3. Overall structure of ''Tf''SGL (PDB [{{PDBlink}}6IMU 6IMU]).''' ]] |
| − | + | The apo-structure of the recombinant ''Tf''SGL (''Tf''SGLr) was determined at 2.0 Å using the iodide single-wavelength anomalous diffraction phasing method (PDB [{{PDBlink}}6IMU 6IMU]) <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. The overall structure comprises an (α/α)<sub>6</sub> toroid fold <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. The complex structures with sophorose (PDB [{{PDBlink}}6IMV 6IMV]) and the Michaelis complex of an inactive ''Tf''SGLr-mutant (E262Q) with a β-1,2-glucoheptaose (PDB [{{PDBlink}}6IMW 6IMW]) were also determined by soaking of crystals in sophorose and β-1,2-glucan, respectively <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. ''Tf''SGLr has a cleft crossing the surface of the structure and there is a large active-site pocket at the center of the cleft <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. Interestingly, although ''Tf''SGL and [[GH144]] enzymes are quite different in their amino acid sequences, their overall structures and the positions of the substrates in their catalytic pockets are similar <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. ''Tf''SGLr has slight structural similarity to [[GH15]] and [[GH8]] enzymes. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Family Firsts == | == Family Firsts == | ||
| Line 92: | Line 53: | ||
;First general base residue identification: A fungal β-1,2-glucanase from ''Talaromyces funiculosus'' by the structural analysis and the mutational analysis <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. | ;First general base residue identification: A fungal β-1,2-glucanase from ''Talaromyces funiculosus'' by the structural analysis and the mutational analysis <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. | ||
;First 3-D structure: A fungal β-1,2-glucanase from ''Talaromyces funiculosus'' using the iodide single-wavelength anomalous diffraction phasing method <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. | ;First 3-D structure: A fungal β-1,2-glucanase from ''Talaromyces funiculosus'' using the iodide single-wavelength anomalous diffraction phasing method <cite>Tanaka2019</cite>. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 100: | Line 58: | ||
#Tanaka2019 pmid=30926603 | #Tanaka2019 pmid=30926603 | ||
#Abe2017 pmid=28270506 | #Abe2017 pmid=28270506 | ||
| + | #Tanaka2024 pmid=38300345 | ||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:03, 1 February 2024
This page has been approved by the Responsible Curator as essentially complete. CAZypedia is a living document, so further improvement of this page is still possible. If you would like to suggest an addition or correction, please contact the page's Responsible Curator directly by e-mail.
| Glycoside Hydrolase Family GH162 | |
| Clan | Clan-S |
| Mechanism | Inverting |
| Active site residues | Known |
| CAZy DB link | |
| https://www.cazy.org/GH162.html | |
Substrate specificities
The defining member of glycoside hydrolase family 162, a β-1,2-glucanase from Talaromyces funiculosus (TfSGL), was identified, characterized, and structurally analyzed as reported in 2019 [1]. This enzyme specifically hydrolyzes both cyclic and linear β-1,2-glucans, which comprise a β-linked glucosyl backbone, and preferably releases sophorose (Glc-β-1,2-Glc) from the reducing end of linear β-1,2-glucan [1]. Almost all of the family members are from Eukaryotes [1]
Kinetics and Mechanism
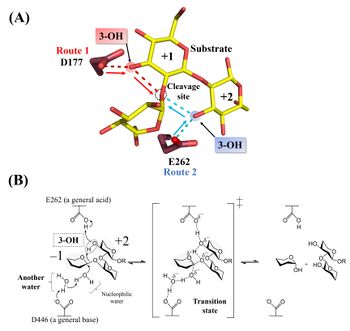
Hydrolysis of cyclic β-1,2-glucan by TfSGL suggests that the enzyme is endo-acting [1]. The 1H-NMR analysis of the anomeric configurations of hydrolysates indicates that TfSGL has an inverting mechanism. Analysis of the change of the degree of optical rotation during hydrolysis of β-1,2-glucan also supported this mechanism [1].
Structural analysis (see “Three-dimensional structures” below) and mutational analysis suggest that D446 activates the nucleophilic water via another water as a general acid [1]. These analyses also suggest that D177 and/or E262 act as a general acid via the 3-hydroxy groups of the Glc moieties (see below) [1]. According to action-pattern analysis using β-1,2-glucopentaose derivatives deoxygenated at their 3-hydroxy groups in the first or second Glc moiety from the reducing end, E262 was clearly determined to be a general acid. The 3-hydroxy group of the Glc moiety at subsite +2 mediates protonation of glycosidic bond oxygen atom [1]. The reaction mechanism of TfSGL is quite unique in that both reaction pathways involving a general acid and a general base are non-canonical [1].
Catalytic Residues
The general acid and base of TfSGL are E262 and D446, respectively [1]. Both residues are highly conserved in GH162 enzymes. The general acid of TfSGL is well superimposed with an acidic residue in a GH144 bacterial β-1,2-glucanase from Chitinophaga pinensis (CpSGL), whereas the general base is not superimposed [1, 2]. Although the reaction mechanisms of GH144 enzymes are currently unclear (June 2019), structural comparison of TfSGL and GH144 suggests differences in reaction mechanisms [1].
A structural comparison revealed that the position of the general acid residue in GH162 and the candidate catalytic residue in GH144 are well superimposed structurally [3]. In contrast, the positions of the other catalytic residues (or candidate catalytic residues) in GH162 and GH144 are completely different [3]. Furthermore, compared to clans GH-G, L, M, O, P and Q, which have the same overall structure (= (α/α)6 fold) as GH162 and GH144, none of the positions of the catalytic residues in GH162 and GH144 are conserved [3]. A new clan GH-S was created for GH162 and GH144 based on these results [3].
Three-dimensional structures
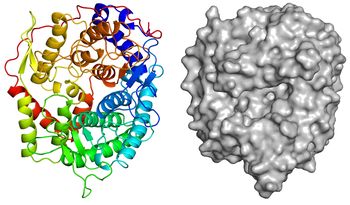
The apo-structure of the recombinant TfSGL (TfSGLr) was determined at 2.0 Å using the iodide single-wavelength anomalous diffraction phasing method (PDB 6IMU) [1]. The overall structure comprises an (α/α)6 toroid fold [1]. The complex structures with sophorose (PDB 6IMV) and the Michaelis complex of an inactive TfSGLr-mutant (E262Q) with a β-1,2-glucoheptaose (PDB 6IMW) were also determined by soaking of crystals in sophorose and β-1,2-glucan, respectively [1]. TfSGLr has a cleft crossing the surface of the structure and there is a large active-site pocket at the center of the cleft [1]. Interestingly, although TfSGL and GH144 enzymes are quite different in their amino acid sequences, their overall structures and the positions of the substrates in their catalytic pockets are similar [1]. TfSGLr has slight structural similarity to GH15 and GH8 enzymes.
Family Firsts
- First stereochemistry determination
- A fungal β-1,2-glucanase from Talaromyces funiculosus by the NMR analysis and the analysis of the change of the degree of optical rotation [1].
- First general acid residue identification
- A fungal β-1,2-glucanase from Talaromyces funiculosus by the structural analysis, the mutational analysis and the action pattern analysis of β-1,2-sophoropentaose derivatives [1].
- First general base residue identification
- A fungal β-1,2-glucanase from Talaromyces funiculosus by the structural analysis and the mutational analysis [1].
- First 3-D structure
- A fungal β-1,2-glucanase from Talaromyces funiculosus using the iodide single-wavelength anomalous diffraction phasing method [1].
References
- Tanaka N, Nakajima M, Narukawa-Nara M, Matsunaga H, Kamisuki S, Aramasa H, Takahashi Y, Sugimoto N, Abe K, Terada T, Miyanaga A, Yamashita T, Sugawara F, Kamakura T, Komba S, Nakai H, and Taguchi H. (2019). Identification, characterization, and structural analyses of a fungal endo-β-1,2-glucanase reveal a new glycoside hydrolase family. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(19):7942-7965. DOI:10.1074/jbc.RA118.007087 |
- Abe K, Nakajima M, Yamashita T, Matsunaga H, Kamisuki S, Nihira T, Takahashi Y, Sugimoto N, Miyanaga A, Nakai H, Arakawa T, Fushinobu S, and Taguchi H. (2017). Biochemical and structural analyses of a bacterial endo-β-1,2-glucanase reveal a new glycoside hydrolase family. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(18):7487-7506. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M116.762724 |
- Tanaka N, Saito R, Kobayashi K, Nakai H, Kamo S, Kuramochi K, Taguchi H, Nakajima M, and Masaike T. (2024). Functional and structural analysis of a cyclization domain in a cyclic β-1,2-glucan synthase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024;108(1):187. DOI:10.1007/s00253-024-13013-9 |