CAZypedia celebrates the life of Senior Curator Emeritus Harry Gilbert, a true giant in the field, who passed away in September 2025.
CAZypedia needs your help!
We have many unassigned pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators. See a page that's out-of-date and just needs a touch-up? - You are also welcome to become a CAZypedian. Here's how.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute.
Learn more about CAZypedia's misson here and in this article. Totally new to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
Difference between revisions of "Carbohydrate Binding Module Family 105"
(Created page with " <!-- RESPONSIBLE CURATORS: Please replace the {{UnderConstruction}} tag below with {{CuratorApproved}} when the page is ready for wider public consumption --> {{UnderConstruc...") |
Guanchen Liu (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
== Ligand specificities == | == Ligand specificities == | ||
| − | + | The first member of family CBM105 (SoCBM) was identified in the [[PL29]] multidomain chondroitinase ChABC29So from ''Segatella oris'' <cite>Liu2024</cite>. SoCBM bound specifically to chondroitin sulfates (CSs) including CS-A and CS-C, while incapable of binding to other glycosaminoglycanss or polyuronic acid substrates. | |
| − | |||
| − | '' | ||
== Structural Features == | == Structural Features == | ||
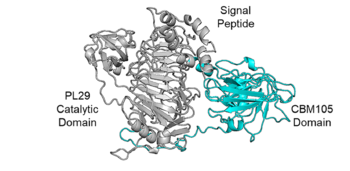
| − | + | [[File:CBM105 Fig.1.png|thumb|350px|right|'''Figure 1. Domain analysis of ChABC29So, the parent enzyme of SoCBM.'''The enzyme consists of a signal peptide (1-21 amino acids), a PL29 domain (66-380 amino acids) and a CBM105 domain (viz., SoCBM; 555-785 amino acids).]] | |
| − | + | An AlphaFold2 model predicts that SoCBM has a β-sandwich fold (Fig.1). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Functionalities == | == Functionalities == | ||
| − | + | SoCBM is the C-terminus domain of a [[PL29]] enzyme ChABC29So that displays chondroitin sulfate ABC activity, consistent with the SoCBM specificity. Biochemical characterization of ChABC29So and the CBM-truncated enzyme revealed that the SoCBM enhances the catalytic activity, thermostability, and disaccharide proportion in the final enzymatic products of ChABC29So. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Family Firsts == | == Family Firsts == | ||
;First Identified | ;First Identified | ||
| − | : | + | :The chondroitin sulfate binding SoCBM from the ''S. oris'' [[PL29]] chondroitinase was the first member of the family to be identified and characterized<cite>Liu2024</cite>. |
;First Structural Characterization | ;First Structural Characterization | ||
| − | : | + | :No experimentally determined three-dimensional structure has been solved in this CBM family. |
== References == | == References == | ||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
| − | # | + | #Liu2024 pmid=38777025 |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
Revision as of 19:09, 27 October 2024
This page is currently under construction. This means that the Responsible Curator has deemed that the page's content is not quite up to CAZypedia's standards for full public consumption. All information should be considered to be under revision and may be subject to major changes.
| CAZy DB link | |
| https://www.cazy.org/CBM105.html |
Ligand specificities
The first member of family CBM105 (SoCBM) was identified in the PL29 multidomain chondroitinase ChABC29So from Segatella oris [1]. SoCBM bound specifically to chondroitin sulfates (CSs) including CS-A and CS-C, while incapable of binding to other glycosaminoglycanss or polyuronic acid substrates.
Structural Features
An AlphaFold2 model predicts that SoCBM has a β-sandwich fold (Fig.1).
Functionalities
SoCBM is the C-terminus domain of a PL29 enzyme ChABC29So that displays chondroitin sulfate ABC activity, consistent with the SoCBM specificity. Biochemical characterization of ChABC29So and the CBM-truncated enzyme revealed that the SoCBM enhances the catalytic activity, thermostability, and disaccharide proportion in the final enzymatic products of ChABC29So.
Family Firsts
- First Identified
- The chondroitin sulfate binding SoCBM from the S. oris PL29 chondroitinase was the first member of the family to be identified and characterized[1].
- First Structural Characterization
- No experimentally determined three-dimensional structure has been solved in this CBM family.