CAZypedia celebrates the life of Senior Curator Emeritus Harry Gilbert, a true giant in the field, who passed away in September 2025.
CAZypedia needs your help!
We have many unassigned pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators. See a page that's out-of-date and just needs a touch-up? - You are also welcome to become a CAZypedian. Here's how.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute.
Learn more about CAZypedia's misson here and in this article. Totally new to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
Difference between revisions of "General acid/base"
(Created page with ' * Author: Spencer Williams * Responsible Curator: Spencer Williams ---- == Overview == The term '''catalytic acid/base''' re…') |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
* Author: [[User:SpencerWilliams|Spencer Williams]] | * Author: [[User:SpencerWilliams|Spencer Williams]] | ||
| Line 6: | Line 5: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
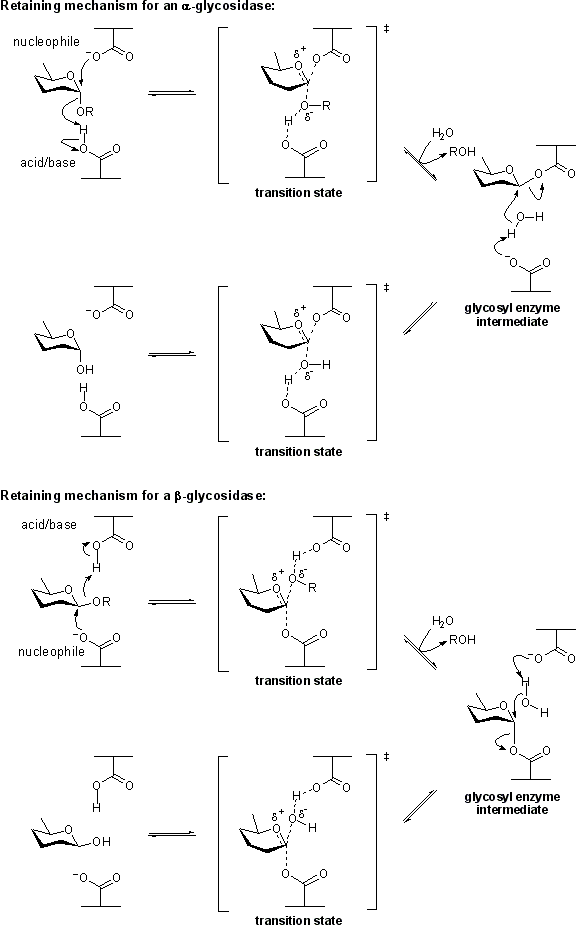
| − | The term ''' | + | The term '''general acid/base''' (also catalytic acid/base) refers to an amino acid residue in a [[glycoside hydrolase]] or a related enzyme that participates in the mechanism of hydrolysis by removing or adding a proton. The mechanism may be a [[retaining]] or [[inverting]] mechanism. General acid/base catalysis differs from specific acid/base catalysis as in the latter it is the solvent that acts as the acid or base. |
[[Image:Retaining_glycosidase_mechanism_1.png|centre]] | [[Image:Retaining_glycosidase_mechanism_1.png|centre]] | ||
| − | ==Methods for indentifying the | + | ==Methods for indentifying the general acid/base== |
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 18:01, 31 August 2009
- Author: Spencer Williams
- Responsible Curator: Spencer Williams
Overview
The term general acid/base (also catalytic acid/base) refers to an amino acid residue in a glycoside hydrolase or a related enzyme that participates in the mechanism of hydrolysis by removing or adding a proton. The mechanism may be a retaining or inverting mechanism. General acid/base catalysis differs from specific acid/base catalysis as in the latter it is the solvent that acts as the acid or base.