CAZypedia celebrates the life of Senior Curator Emeritus Harry Gilbert, a true giant in the field, who passed away in September 2025.
CAZypedia needs your help!
We have many unassigned pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators. See a page that's out-of-date and just needs a touch-up? - You are also welcome to become a CAZypedian. Here's how.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute.
Learn more about CAZypedia's misson here and in this article. Totally new to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
Difference between revisions of "Transglycosylases"
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
*[[GH13]], for example cyclodextran glucanotransferases that convert linear amylose to cyclodextrins; glycogen debranching enzyme, which transfers three glucose residues from the four-residue glycogen branch to a nearby branch; and trehalose synthase, which catalyzes the interconversion of maltose and trehalose.<br> | *[[GH13]], for example cyclodextran glucanotransferases that convert linear amylose to cyclodextrins; glycogen debranching enzyme, which transfers three glucose residues from the four-residue glycogen branch to a nearby branch; and trehalose synthase, which catalyzes the interconversion of maltose and trehalose.<br> | ||
*[[GH16]], for example xyloglucan endotransglycosylases, which cuts and rejoins xyloglucan chains in the plant cell wall. | *[[GH16]], for example xyloglucan endotransglycosylases, which cuts and rejoins xyloglucan chains in the plant cell wall. | ||
| + | *[[GH31]], for example, α-transglucosidases, which catalyze the transfer of individual glucosyl residues between α-(1→4)-glucans. | ||
*[[GH70]], for example glucansucrases, which catalyse the synthesis of high molecular weight glucans, from sucrose. | *[[GH70]], for example glucansucrases, which catalyse the synthesis of high molecular weight glucans, from sucrose. | ||
*[[GH77]], for examples amylomaltase, which catalyzes the synthesis of maltodextrins from maltose. | *[[GH77]], for examples amylomaltase, which catalyzes the synthesis of maltodextrins from maltose. | ||
Revision as of 20:50, 3 May 2013
This page has been approved by the Responsible Curator as essentially complete. CAZypedia is a living document, so further improvement of this page is still possible. If you would like to suggest an addition or correction, please contact the page's Responsible Curator directly by e-mail.
- Author: Spencer Williams
- Responsible Curator: Spencer Williams
Overview
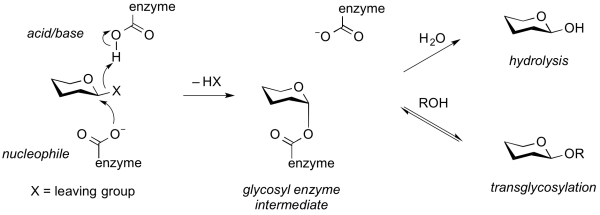
Transglycosylases are a class of GH enzymes that can catalyze the transformation of one glycoside to another. That is, these enzymes catalyze the substitution of a glycoside with another aglycon. Mechanistically, transglycosylases utilize the same mechanism as various retaining glycoside hydrolases. Thus, reaction of the nucleophile of a retaining glycoside hydrolase with a substrate gives a glycosyl-enzyme intermediate that can be intercepted either by water to give the hydrolysis product, or by another acceptor (often another carbohydrate alcohol), to give a new glycoside or oligosaccharide [1]. Alternatively, transglycosylation can occur by neighboring group participation, wherein a neighboring 2-acetamido group participates in the reaction to generate an oxazolinium ion intermediate, which can react with another acceptor other than water. Some transglycosidases possess substantial glycoside hydrolase activity, and some glycoside hydrolases possess transglycosylases activity. Indeed, in many cases it is unclear what the major role of an enzyme that possesses both activities may be. Transglycosylases are classified as glycoside hydrolases into various GH families on the basis of sequence similarity.
Families
GH families with notable transglycosylase activity include:
- GH2, for example LacZ β-galactosidase converts lactose to allolactose.
- GH13, for example cyclodextran glucanotransferases that convert linear amylose to cyclodextrins; glycogen debranching enzyme, which transfers three glucose residues from the four-residue glycogen branch to a nearby branch; and trehalose synthase, which catalyzes the interconversion of maltose and trehalose.
- GH16, for example xyloglucan endotransglycosylases, which cuts and rejoins xyloglucan chains in the plant cell wall.
- GH31, for example, α-transglucosidases, which catalyze the transfer of individual glucosyl residues between α-(1→4)-glucans.
- GH70, for example glucansucrases, which catalyse the synthesis of high molecular weight glucans, from sucrose.
- GH77, for examples amylomaltase, which catalyzes the synthesis of maltodextrins from maltose.
- GH23, GH102, GH103, and GH104 lytic transglycosylases, which convert peptidoglycan to 1,6-anhydrosugars.