CAZypedia celebrates the life of Senior Curator Emeritus Harry Gilbert, a true giant in the field, who passed away in September 2025.
CAZypedia needs your help!
We have many unassigned pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators. See a page that's out-of-date and just needs a touch-up? - You are also welcome to become a CAZypedian. Here's how.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute.
Learn more about CAZypedia's misson here and in this article. Totally new to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
Glycosyltransferases
This page is currently under construction. This means that the Responsible Curator has deemed that the page's content is not quite up to CAZypedia's standards for full public consumption. All information should be considered to be under revision and may be subject to major changes.
- Author: Spencer Williams
- Responsible Curator: Spencer Williams
Overview
Glycosyltransferases are enzymes that catalyze the formation of the glycosidic linkage to form a glycoside. These enzymes utilize 'activated' sugar phosphates as glycosyl donors, and catalyze glycosyl group transfer to a nucleophilic group, usually an alcohol. The product of glycosyl transfer may be an O-, N-, S-, or C-glycoside; the glycoside may be part of a monosaccharide glycoside, oligosaccharide, or polysaccharide ([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).
Donors
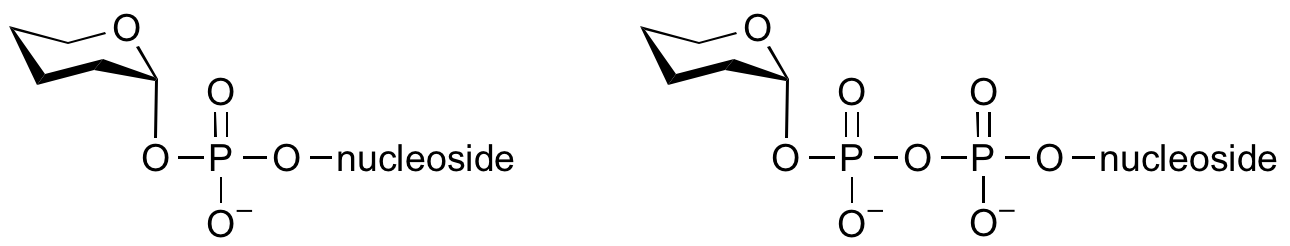
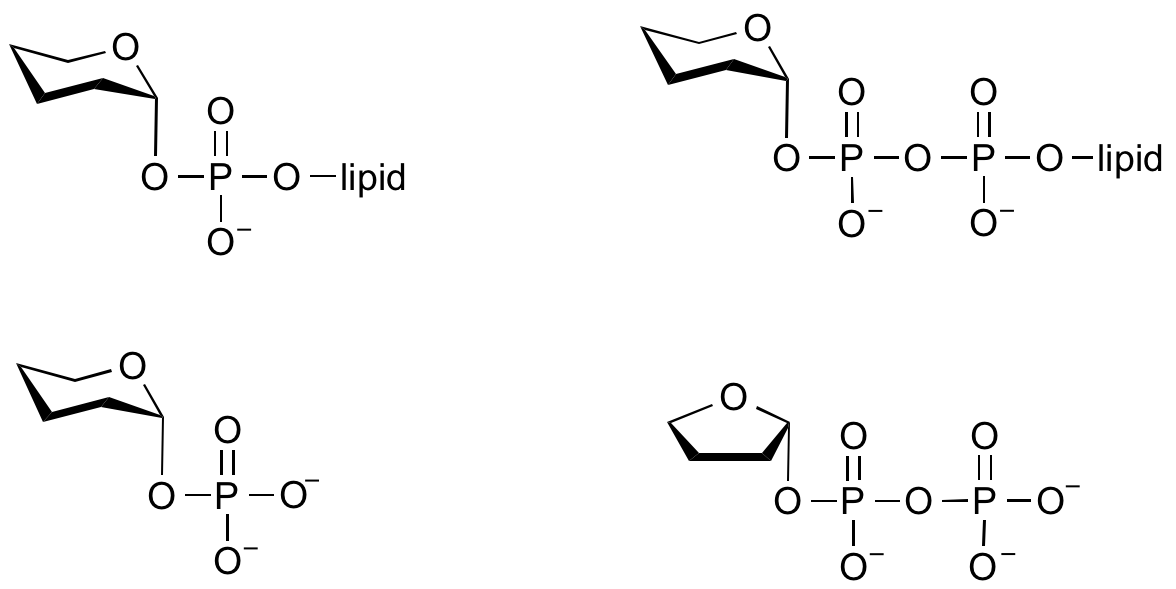
Glycosyltransferases can utilize a range of donor species. Sugar mono- or diphosphonucleotides are sometimes termed Leloir donors (after Nobel prize winner, Luis Leloir); the corresponding enzymes are termed Leloir donors.
Glycosyltransferases that utilize non-nucleotide donors, which may be polyprenol pyrophosphates, polyprenol phosphates, sugar-1-phosphates, or sugar-1-pyrophosphates, are termed non-Leloir glycosyltransferases.
Mechanism
Glycosyltransferases catalyze the transfer of glycosyl groups to a nucleophilic acceptor with either retention or inversion of configuration at the anomeric centre. This allows the classification of glycosyltransferases as either retaining or inverting enzymes.
Inverting glycosyltransferases
Structural and kinetic data for inverting glycosyltransferases support a mechanism that proceeds through a single nucleophilic substitution step, facilitated by an enzymic general base catalyst. The transition state is believed to possess substantial oxocarbenium ion character.
Retaining glycosyltransferases
Classification
Sequence based classification
Sequence-based classification uses algorithmic methods to assign sequences to various families. The glycosyltransferases have been classified into more than 90 families [6, 7]; this is permanently available through the Carbohydrate Active enZyme database [3]. Each family (GH family) contains proteins that are related by sequence, and by corollary, fold. This allows a number of useful predictions to be made since it has long been noted that the catalytic machinery and molecular mechanism is conserved for the vast majority of the glycosidase families [1] as well as the geometry around the glycosidic bond (irrespective of naming conventions) [4]. Usually, the mechanism used (ie retaining orinverting) is conserved within a GH family. One notable exception is the glycoside hydrolases of familyGH97, which contains both retaining and inverting enzymes; a glutamate acts as a general base in inverting members, whereas an aspartate likely acts as a catalytic nucleophilein retaining members[5]. Another mechanistic curiosity are the glycoside hydrolases of familes GH4 andGH109 which operate through an NAD-dependent hydrolysismechanism that proceeds through oxidation-elimination-addition-reduction steps via anionic transition states [6]. This allows a single enzyme to hydrolyze both alpha- and beta-glycosides.
Classification of families into larger groups, termed 'clans' has been proposed [7]. A 'clan' is a group of families that possess significant similarity in their tertiary structure, catalytic residues and mechanism. Families within clans are thought to have a common evolutionary ancestry. For an updated table of glycoside hydrolase clans see the CAZy Database [8].
3-D folds
Sugar nucleotide-dependent glycosyltransferases
<jmol> <jmolApplet> <color>white</color> <frame>true</frame> <uploadedFileContents>1h7l.pdb</uploadedFileContents> <script>cpk off; wireframe off; cartoon; color cartoon powderblue; select ligand; wireframe 0.3; select MG; spacefill;set spin Y 10; spin on; set antialiasDisplay ON</script> </jmolApplet> </jmol> |
<jmol> <jmolApplet> <color>white</color> <frame>true</frame> <uploadedFileContents>1bgt.pdb</uploadedFileContents> <script>cpk off; wireframe off; cartoon; color cartoon powderblue; select ligand; wireframe 0.3; select MG; spacefill;set spin Y 10; spin on; set antialiasDisplay ON</script> </jmolApplet> </jmol> |
Role of metals
Common sugar nucleotide donors
References
- Lairson LL, Henrissat B, Davies GJ, and Withers SG. (2008). Glycosyltransferases: structures, functions, and mechanisms. Annu Rev Biochem. 2008;77:521-55. DOI:10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.061005.092322 |
- Coutinho PM, Deleury E, Davies GJ, and Henrissat B. (2003). An evolving hierarchical family classification for glycosyltransferases. J Mol Biol. 2003;328(2):307-17. DOI:10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00307-3 |
Chapter 5: Coutinho PM, Rancurel C, Stam M, Bernard T, Couto FM, Danchin EGJ, Henrissat B. "Carbohydrate-active Enzymes Database: Principles and Classification of Glycosyltransferases."
- Campbell JA, Davies GJ, Bulone V, and Henrissat B. (1997). A classification of nucleotide-diphospho-sugar glycosyltransferases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem J. 1997;326 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):929-39. DOI:10.1042/bj3260929u |
- Campbell JA, Davies GJ, Bulone V, and Henrissat B. (1997). A classification of nucleotide-diphospho-sugar glycosyltransferases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem J. 1997;326 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):929-39. DOI:10.1042/bj3260929u |
- Coutinho PM, Deleury E, Davies GJ, and Henrissat B. (2003). An evolving hierarchical family classification for glycosyltransferases. J Mol Biol. 2003;328(2):307-17. DOI:10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00307-3 |
- Charnock SJ and Davies GJ. (1999). Structure of the nucleotide-diphospho-sugar transferase, SpsA from Bacillus subtilis, in native and nucleotide-complexed forms. Biochemistry. 1999;38(20):6380-5. DOI:10.1021/bi990270y |
- Vrielink A, Rüger W, Driessen HP, and Freemont PS. (1994). Crystal structure of the DNA modifying enzyme beta-glucosyltransferase in the presence and absence of the substrate uridine diphosphoglucose. EMBO J. 1994;13(15):3413-22. DOI:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06646.x |