CAZypedia celebrates the life of Senior Curator Emeritus Harry Gilbert, a true giant in the field, who passed away in September 2025.
CAZypedia needs your help!
We have many unassigned pages in need of Authors and Responsible Curators. See a page that's out-of-date and just needs a touch-up? - You are also welcome to become a CAZypedian. Here's how.
Scientists at all career stages, including students, are welcome to contribute.
Learn more about CAZypedia's misson here and in this article. Totally new to the CAZy classification? Read this first.
Difference between revisions of "Syn/anti lateral protonation"
Wim Nerinckx (talk | contribs) |
Wim Nerinckx (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1,163: | Line 1,163: | ||
| Asp90 | | Asp90 | ||
| <cite>Hehemann_2_2012</cite> | | <cite>Hehemann_2_2012</cite> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[GH123]] | ||
| + | | none | ||
| + | | (β/α)8 + β-sandwich | ||
| + | | beta | ||
| + | | retaining | ||
| + | | ''anti'' | ||
| + | | [{{PDBlink}}5fr0 5fr0] | ||
| + | | exo-β-N-acetylgalactosaminidase | ||
| + | | ''Clostridium perfringens'' | ||
| + | | N-difluoroacetyl-{{Smallcaps|d}}-galactosamine | ||
| + | | Glu345 | ||
| + | | internal | ||
| + | | <cite>Noach2016</cite> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[GH134]] | | [[GH134]] | ||
| Line 1,270: | Line 1,284: | ||
# Williams2014 pmid=24339341 | # Williams2014 pmid=24339341 | ||
# Hehemann_2_2012 pmid=22393053 | # Hehemann_2_2012 pmid=22393053 | ||
| + | # Noach2016 pmid=27038508 | ||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
[[Category:Definitions and explanations]] | [[Category:Definitions and explanations]] | ||
Revision as of 03:21, 17 December 2016
This page has been approved by the Responsible Curator as essentially complete. CAZypedia is a living document, so further improvement of this page is still possible. If you would like to suggest an addition or correction, please contact the page's Responsible Curator directly by e-mail.
- Author: ^^^Wim Nerinckx^^^
- Responsible Curator: ^^^Spencer Williams^^^
Overview
This page provides a table that summarizes the spatial positioning of the catalytic general acid residue in the active sites of glycoside hydrolases, relative to the substrate. The table below updates those found in the seminal paper on this concept by Heightman and Vasella [1], and a following paper by Nerinckx et al. [2].
Background
The "not from above, but from the side" concept of semi-lateral glycosidic oxygen protonation by glycoside hydrolases was introduced by Heightman and Vasella [1]. It was originally only described for beta-equatorial glycoside hydrolases, but appears to be equally applicable to enzymes acting on an alpha-axial glycosidic bond [2]. When dividing subsite -1 into half-spaces by a plane defined by the glycosidic oxygen and C1' and H1' of the –1 glycoside, many ligand-complexed structures reveal that the proton donor is positioned either in the syn half-space (near the ring-oxygen of the –1 glycoside), or in the anti half-space (on the opposite side of the ring-oxygen). Members of the same GH family appear to share a common syn or anti protonator arrangement and further, this specificity appears to be preserved within Clans of families. This page's compilation of subsite -1 occupied complexes shows that about 70% of all GH families are anti protonators.
Closer inspection of crystal structures of –1/+1 subsite-spanning substrates, or substrate-analogue ligands, in complex with enzymes reveals a further intriguing corollary [2, 3]. In substrate-bound complexes with anti protonating GH enzymes, the scissile anomeric bond (often studied using the thio-analogue) shows a dihedral angle φ (O5'-C1'-[O,S]x-Cx) that is in the lowest-energy synclinal (gauche) conformation. The rationale for this is that a minus synclinal dihedral angle φ for an equatorial glycosidic bond, or plus synclinal for an axial glycosidic bond [4], allows for hyperconjugative overlap of the C1'-O5' antibonding orbital with an antiperiplanar-oriented lone pair orbital lobe of the glycosidic oxygen, thereby creating partial double bond character and stabilization of the glycosidic bond by 4–5 kcal/mol; this ground-state stabilizing phenomenon is known as the ‘exo-anomeric effect’ [5, 6]. Anti protonation occurs on the glycosidic oxygen’s antiperiplanar lone pair, thereby removing the stabilizing exo-anomeric effect. This suggests that anti protonation is an enzymic approach for lowering the activation barrier leading to the transition state (Figure 1 centre).
Syn protonating glycoside hydrolases apparently make use of a different approach [2, 3]. In many –1/+1 subsite-spanning ligand complexes, the dihedral angle φ of the scissile anomeric bond has been rotated away from its lowest-energy synclinal position: clockwise to minus-anticlinal or antiperiplanar for beta-equatorial; counterclockwise to plus-anticlinal or antiperiplanar for alpha-axial anomeric bonds. This removes the hyperconjugative overlap and thus also the stabilizing exo-anomeric effect. And because of this rotation, a lone pair of the glycosidic oxygen is directed into the syn half-space, allowing it to be protonated by the syn-positioned proton donor (Figure 1 right).
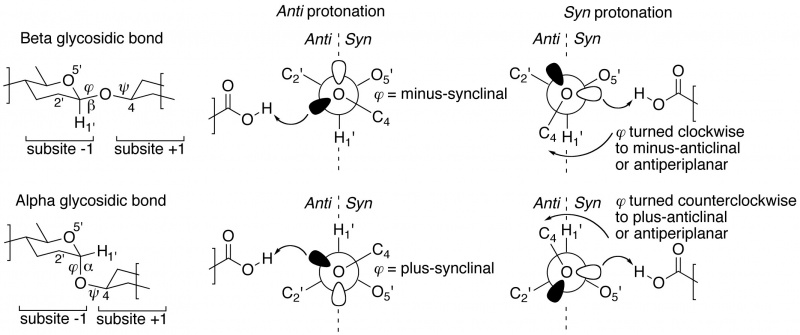
Table of syn/anti protonation examples
This table contains only one example per GH family of a ligand-complexed protein structure where the syn or anti positioning of the proton donor can be clearly observed; other examples may be available on a family-by-family basis. The reader is thus advised to consult the CAZy database for a current, comprehensive list of CAZyme structures. Where available, the selected examples are Michaelis-type complexes with the ligand spanning the -1/+1 subsites, since these have an intact glycosidic or thioglycosidic bond, or are N-analogs of the substrate (e.g. acarbose). In some examples, the proton donor has been mutated (e.g., to the corresponding amide or to an alanine), and in those cases one may wish to look at a superposition of the given PDB example with the structure of the native enzyme. If a Michaelis-type complex is not yet available, the second and third example choices, respectively, are trapped glycosyl-enzyme intermediates and product complexes where subsite -1 is occupied.
Please also be aware that this is a large table with many data. Please contact the page Author or Responsible Curator with corrections.
Table
This table can be re-sorted by clicking on the icons in the header (javascript must be turned on in your browser). To reset the page to be sorted by GH family, click the page tab at the very top of the page.
| Family | Clan | Structure fold | Anomeric specificity | Mechanism | Syn/anti protonator | Example PDB ID | Enzyme | Organism | Ligand | General acid | Nucleophile or General base | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH1 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 2cer | β-glycosidase S | Sulfolobus solfataricus P2 | phenethyl glucoimidazole | Glu206 | Glu387 | [7] | |
| GH2 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 2vzu | exo-β-glucosaminidase | Amicolatopsis orientalis | PNP-β-d-glucosamine | Glu469 | Glu541 | [8] | |
| GH3 | none | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 1iex | exo-1,3-1,4-glucanase | Hordeum vulgare | thiocellobiose | Glu491 | Asp285 | [9] | |
| GH5 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 1h2j | endo-β-1,4-glucanase | Bacillus agaradhaerens | 2',4'-DNP-2-F-cellobioside | Glu129 | Glu228 | [10] | |
| GH6 | none | (β/α)8 | beta | inverting | syn | 1qjw | cellobiohydrolase 2 | Hypocrea jecorina | (Glc)2-S-(Glc)2 | Asp221 | debated | [11] | |
| GH7 | B | β-jelly roll | beta | retaining | syn | 1ovw | endo-1,4-glucanase | Fusarium oxysporum | thio-(Glc)5 | Glu202 | Glu197 | [12] | |
| GH8 | M | (α/α)6 | beta | inverting | anti | 1kwf | endo-1,4-glucanase | Clostridium thermocellum | cellopentaose | Glu95 | Asp278 | [13] | |
| GH9 | none | (α/α)6 | beta | inverting | syn | 1rq5 | cellobiohydrolase | Clostridium thermocellum | cellotetraose | Glu795 | Asp383 | [14] | |
| GH10 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 2d24 | β-1,4-xylanase | Streptomyces olivaceoviridis E-86 | xylopentaose | Glu128 | Glu236 | [15] | |
| GH11 | C | β-jelly roll | beta | retaining | syn | 1bvv | xylanase | Bacillus circulans | Xyl-2-F-xylosyl | Glu172 | Glu78 | [16] | |
| GH12 | C | β-jelly roll | beta | retaining | syn | 1w2u | endoglucanase | Humicola grisea | thiocellotetraose | Glu205 | Glu120 | [17] | |
| GH13 | H | (β/α)8 | alpha | retaining | anti | 1cxk | β-cyclodextrin glucanotransferase | Bacillus circulans | maltononaose | Glu257 | Asp229 | [18] | |
| GH14 | none | (β/α)8 | alpha | inverting | syn | 1itc | β-amylase | Bacillus cereus | maltopentaose | Glu172 | Glu367 | [19] | |
| GH15 | L | (α/α)6 | alpha | inverting | anti | 1dog | glucoamylase | Aspergillus awamori | 1-deoxynojirimycin | Glu179 | Glu400 | [20] | |
| GH16 | B | β-jelly roll | beta | retaining | syn | 1urx | β-agarase A | Zobellia galactanivorans | oligoagarose | Glu152 | Glu147 | [21] | |
| GH17 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | predicted anti by clan | see e.g. at GH1 | |||||||
| GH18 | K | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 1ffr | chitinase A | Serratia marcescens | (NAG)6 | Glu315 | internal | [22] | |
| GH19 | none | lysozyme type | beta | inverting | syn | 3wh1 | chitinase | Bryum coronatum | (GlcNAc)4 | Glu61 | Glu70 | [23] | |
| GH20 | K | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 1c7s | chitobiase | Serratia marcescens | chitobiose | Glu540 | internal | [24] | |
| GH22 | none | lysozyme type | beta | retaining | syn | 1h6m | lysozyme C | Gallus gallus | Chit-2-F-chitosyl | Glu35 | Asp52 | [25] | |
| GH23 | none | lysozyme type | beta | inverting | syn | 1lsp | lysozyme G | Cygnus atratus | Bulgecin A | Glu73 | internal | [26] | |
| GH24 | I | α + β | beta | inverting | syn | 148l | lysozyme E | Bacteriophage T4 | chitobiosyl | Glu11 | Glu26 | [27] | |
| GH26 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 1gw1 | mannanase A | Cellvibrio japonicus | 2',4'-DNP-2-F-cellotrioside | Glu212 | Glu320 | [28] | |
| GH27 | D | (β/α)8 | alpha | retaining | anti | 1ktc | α-N-acetyl galactosaminidase | Gallus gallus | NAGal | Asp201 | Asp410 | [29] | |
| GH28 | N | β-helix | alpha | inverting | anti | 2uvf | exo-polygalacturonosidase | Yersinia enterocolitica ATCC9610D | digalacturonic acid | Asp402 | Asp381 Asp403 | [30] | |
| GH29 | none | (β/α)8 | alpha | retaining | syn | 1hl9 | α-l-fucosidase | Thermotoga maritima | 2-F-fuco- pyranosyl | Glu266 | Asp224 | [31] | |
| GH30 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 2v3d | glucocerebrosidase 1 | Homo sapiens | N-butyl-deoxynojirimycin | Glu235 | Glu340 | [32] | |
| GH31 | D | (β/α)8 | alpha | retaining | anti | 2qmj | maltase-glucoamylase | Homo sapiens | acarbose | Asp542 | Asp443 | [33] | |
| GH32 | J | 5-fold β-propeller | beta | retaining | anti | 2add | fructan β-(2,1)-fructosidase | Cichorium intybus | sucrose | Glu201 | Asp22 | [34] | |
| GH33 | E | 6-fold β-propeller | alpha | retaining | anti | 1s0i | trans-sialidase | Trypanosoma cruzi | sialyl-lactose | Asp59 | Tyr342 | [35] | |
| GH34 | E | 6-fold β-propeller | alpha | retaining | anti | 2bat | neuraminidase | Influenza A virus | sialic acid | Asp151 | Tyr406 | [36] | |
| GH35 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 1xc6 | β-galactosidase | Penicillium sp. | d-galactose | Glu200 | Glu299 | [37] | |
| GH36 | D | (β/α)8 | alpha | retaining | anti | 4fns | β-galactosidase | Geobacillus stearothermophilus | 1-deoxy galactonojirimycin | Asp584 | Asp478 | [38] | |
| GH37 | G | (α/α)6 | alpha | inverting | anti | 2jf4 | trehalase | Escherechia coli | validoxylamine | Asp312 | Glu496 | [39] | |
| GH38 | none | (β/α)7 | alpha | retaining | anti | 1qwn | α-mannosidase II | Drosophila melanogaster | 5-F-β-l-gulosyl | Asp341 | Asp204 | [40] | |
| GH39 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 1uhv | β-xylosidase | Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum | 2-F-xylosyl | Glu160 | Glu277 | [41] | |
| GH42 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 4ucf | β-galactosidase | Bifidobacterium bifidum | d-galactose | Glu161 | Glu320 | [42] | |
| GH44 | none | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 2eqd | endoglucanase | Clostridium thermocellum | cellooctaose | Glu186 | Glu359 | [43] | |
| GH45 | none | 6-strand. β-barrel | beta | inverting | syn | 4eng | endo-1,4-glucanase | Humicola insolens | cellohexaose | Asp121 | Asp10 | [44] | |
| GH46 | I | lysozyme type | beta | inverting | syn | 4olt | chitosanase | Pseudomonas sp. LL2(2010) | d-glucosamine | Glu25 | Asp43 | [45] | |
| GH47 | none | (α/α)7 | alpha | inverting | anti | 1x9d | α-mannosidase I | Homo sapiens | Me-2-S-(α-Man)-2-thio-α-Man | Asp463 | Glu599 | [46], [47] | |
| GH48 | M | (α/α)6 | beta | inverting | predicted anti by clan | see at GH8 | |||||||
| GH49 | N | β-helix | alpha | inverting | predicted anti by clan | see at GH28 | |||||||
| GH50 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 4bq5 | exo-β-agarase | Saccharophagus degradans | neoagarotetraose | Glu535 | Glu695 | [48] | |
| GH51 | A | (β/α)8 | alpha | retaining | anti | 1qw9 | α-l-arabino- furanosidase | Geobacillus stearothermophilus | PNP-l-arabino-furanoside | Glu175 | Glu294 | [49] | |
| GH52 | O | (α/α)6 | beta | retaining | anti | 4c1p | β-xylosidase | Geobacillus thermoglucosidasius | xylobiose | Asp517 | Glu537 | [50] | |
| GH53 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 2ccr | β-1,4-galactanase | Bacillus licheniformis | galactotriose | Glu165 | Glu263 | [51] | |
| GH54 | none | β-sandwich | alpha | retaining | anti | 1wd4 | α-l-arabino- furanosidase B | Aspergillus kawachii | l-arabinofuranose | Asp297 | Glu221 | [52] | |
| GH55 | none | β-helix | beta | inverting | anti | 3eqo | β-1,3-glucanase | Phanerochaete chrysosporium K-3 | d-gluconolacton | Glu633 | unknown | [53] | |
| GH56 | none | (β/α)7 | beta | retaining | anti | 1fcv | hyaluronidase | Apis mellifera | (hyaluron.)4 | Glu113 | internal | [54] | |
| GH57 | none | (β/α)7 | alpha | retaining | anti | 1k1y | glucanotransferase | Thermococcus litoralis | acarbose | Asp214 | Glu123 | [55] | |
| GH59 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 4ccc | β-galactocerebrosidase | Mus musculus | PNP-β-d-gal | Glu182 | Glu258 | [56] | |
| GH63 | G | (α/α)6 | alpha | inverting | predicted anti by clan | see at GH37 | |||||||
| GH65 | L | (α/α)6 | alpha | inverting | anti | 4ktr | 2-O-α-glucosylglycerol phosphorylase | Bacillus selenitireducens | isofagomine | Glu475 | phosphate | [57] | |
| GH66 | L | (β/α)8 | alpha | retaining | anti | 5axh | dextranase | Thermoanaerobacter pseudethanolicus | isomaltohexaose | Glu374 | Asp312 | [58] | |
| GH67 | none | (β/α)8 | alpha | inverting | syn | 1gql | α-glucuronidase | Cellvibrio japonicus Ueda107 | d-glucuronic acid | Glu292 | unknown | [59] | |
| GH68 | J | 5-fold β-propeller | beta | retaining | anti | 1pt2 | levansucrase | Bacillus subtilis | sucrose | Glu342 | Asp86 | [60] | |
| GH70 | H | (β/α)8 | alpha | retaining | anti | 3aic | glucansucrase | Streptococcus mutans | α-acarbose | Glu515 | Asp477 | [61] | |
| GH72 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 2w62 | β-1,3-glucano- transferase | Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C | laminaripentaose | Glu176 | Glu275 | [62] | |
| GH74 | none | 7-fold β-propeller | beta | inverting | syn | 2ebs | cellobiohydrolase (OXG-RCBH) | Geotrichum sp. m128 | xyloglucan heptasaccharide | Asp465 | Asp35 | [63] | |
| GH76 | none | (α/α)6 | alpha | retaining | anti | 5agd | endo-α-1,6-mannanase | Bacillus circulans | α-1,6-mannopentaose | Asp125 | Asp124 | [64] | |
| GH77 | H | (β/α)8 | alpha | retaining | anti | 1esw | amylomaltase | Thermus aquaticus | acarbose | Asp395 | Asp293 | [65] | |
| GH78 | H | (α/α)6 | alpha | inverting | anti | 3w5n | α-l-rhamnosidase | Streptomyces avermitilis | l-rhamnose | Glu636 | Glu895 | [66] | |
| GH79 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 5e9c | heparanase | Homo sapiens | heparin tetrasaccharide | Glu225 | Glu343 | [67] | |
| GH80 | I | α + β | beta | inverting | predicted syn by clan | see at GH24 | |||||||
| GH83 | E | 6-fold β-propeller | alpha | retaining | predicted anti by clan | see e.g. at GH33 | |||||||
| GH84 | none | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 2chn | β-N-acetyl- glucosaminidase | Bacteroides thetaiota- omicron VPI-5482 | NAG-thiazoline | Glu242 | internal | [68] | |
| GH85 | K | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 2w92 | endo-β-N-acetyl- glucosaminidase D | Streptococcus pneumoniae TIGR4 | NAG-thiazoline | Glu337 | internal | [69] | |
| GH86 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 4aw7 | β-porphyranase | Bacteroides plebeius | porphyran fragment | Glu152 | Glu279 | [70] | |
| GH89 | none | (β/α)8 | alpha | retaining | anti | 2vcb | α-N-acetyl- glucosaminidase | Clostridium perfringens | PUGNAc | Glu483 | Glu601 | [71] | |
| GH92 | none | (α/α)6 + β-sandw. | alpha | inverting | anti | 2ww1 | α-1,2-mannosidase | Bacteroides thetaiota- omicron VPI-5482 | thiomannobioside | Glu533 | Asp644 Asp642 | [72] | |
| GH93 | E | 6-bladed β-propeller | alpha | retaining | anti | 3a72 | exo-arabinanase | Penicillium chrysogenum | arabinobiose | Glu246 | Glu174 | [73] | |
| GH94 | none | (α/α)6 | beta | inverting | syn | 1v7x | chitobiose phosphorylase | Vibrio proteolyticus | GlcNAc | Asp492 | phosphate | [74] | |
| GH95 | none | (α/α)6 | alpha | inverting | anti | 2ead | α-1,2-l-fucosidase | Bifidobacterium bifidum | Fuc-α-1,2-Gal | Glu566 | Asn423 Asp766 | [75] | |
| GH97 | none | (β/α)8 | alpha | retaining + inverting | anti | 2zq0 | α-glucosidase | Bacteroides thetaiota- omicron VPI-5482 | acarbose | Glu532 | Glu508 | [76] | |
| GH99 | none | (β/α)8 | alpha | retaining | anti | 4ad4 | endo-α-mannosidase | Bacteroides xylanisolvens | glucose-1,3-isofagomine and α-1,2- mannobiose | Glu336 | debated | [77] | |
| GH100 | none | (α/α)6 core | beta | inverting | anti | 5gop | invertase | Anabaena (Nostoc) sp. pcc7120 | sucrose | Asp188 | Glu414 | [78] | |
| GH102 | none | double-ψ β-barrel | beta | retaining | syn | 2pi8 | lytic transglycosylase A | Escherichia coli | chitohexaose | Asp308 | none | [79] | |
| GH113 | A | (β/α)8 | beta | retaining | anti | 4cd8 | β-mannanase | Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius | mannobioimidazole | Glu151 | Glu231 | [80] | |
| GH117 | none | five-bladed β-propeller | alpha | inverting | anti | 4ak7 | α-1,3-3,6-anhydro-l-galactosidase | Bacteroides plebeius | neoagarobiose | His302 | Asp90 | [81] | |
| GH123 | none | (β/α)8 + β-sandwich | beta | retaining | anti | 5fr0 | exo-β-N-acetylgalactosaminidase | Clostridium perfringens | N-difluoroacetyl-d-galactosamine | Glu345 | internal | [82] | |
| GH134 | none | β + α | beta | inverting | anti | 5jug | β-mannanase | Streptomyces sp. | mannopentaose | Glu45 | Asp57 | [83] |
References
-
Heightman TD, and Vasella AT (1999) Recent Insights into Inhibition, Structure, and Mechanism of Configuration-Retaining Glycosidases. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 38(6), 750-770. Article online.
- Nerinckx W, Desmet T, Piens K, and Claeyssens M. (2005). An elaboration on the syn-anti proton donor concept of glycoside hydrolases: electrostatic stabilisation of the transition state as a general strategy. FEBS Lett. 2005;579(2):302-12. DOI:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.12.021 |
- Wu M, Nerinckx W, Piens K, Ishida T, Hansson H, Sandgren M, and Ståhlberg J. (2013). Rational design, synthesis, evaluation and enzyme-substrate structures of improved fluorogenic substrates for family 6 glycoside hydrolases. FEBS J. 2013;280(1):184-98. DOI:10.1111/febs.12060 |
-
Pérez S, and Marchessault RH (1978) The exo-anomeric effect: experimental evidence from crystal structures. Carbohydr res 65, 114-120.
-
Cramer CJ, Truhlar DG, and French AD (1997) Exo-anomeric effects on energies and geometries of different conformations of glucose and related systems in the gas phase and aqueous solution. Carbohydr res 298, 1-14.
- Johnson GP, Petersen L, French AD, and Reilly PJ. (2009). Twisting of glycosidic bonds by hydrolases. Carbohydr Res. 2009;344(16):2157-66. DOI:10.1016/j.carres.2009.08.011 |
- Gloster TM, Roberts S, Perugino G, Rossi M, Moracci M, Panday N, Terinek M, Vasella A, and Davies GJ. (2006). Structural, kinetic, and thermodynamic analysis of glucoimidazole-derived glycosidase inhibitors. Biochemistry. 2006;45(39):11879-84. DOI:10.1021/bi060973x |
- van Bueren AL, Ghinet MG, Gregg K, Fleury A, Brzezinski R, and Boraston AB. (2009). The structural basis of substrate recognition in an exo-beta-D-glucosaminidase involved in chitosan hydrolysis. J Mol Biol. 2009;385(1):131-9. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.10.031 |
- Hrmova M, Varghese JN, De Gori R, Smith BJ, Driguez H, and Fincher GB. (2001). Catalytic mechanisms and reaction intermediates along the hydrolytic pathway of a plant beta-D-glucan glucohydrolase. Structure. 2001;9(11):1005-16. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00673-6 |
- Varrot A and Davies GJ. (2003). Direct experimental observation of the hydrogen-bonding network of a glycosidase along its reaction coordinate revealed by atomic resolution analyses of endoglucanase Cel5A. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2003;59(Pt 3):447-52. DOI:10.1107/s0907444902023405 |
- Zou Jy, Kleywegt GJ, Ståhlberg J, Driguez H, Nerinckx W, Claeyssens M, Koivula A, Teeri TT, and Jones TA. (1999). Crystallographic evidence for substrate ring distortion and protein conformational changes during catalysis in cellobiohydrolase Ce16A from trichoderma reesei. Structure. 1999;7(9):1035-45. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80171-3 |
- Sulzenbacher G, Mackenzie LF, Wilson KS, Withers SG, Dupont C, and Davies GJ. (1999). The crystal structure of a 2-fluorocellotriosyl complex of the Streptomyces lividans endoglucanase CelB2 at 1.2 A resolution. Biochemistry. 1999;38(15):4826-33. DOI:10.1021/bi982648i |
- Guérin DM, Lascombe MB, Costabel M, Souchon H, Lamzin V, Béguin P, and Alzari PM. (2002). Atomic (0.94 A) resolution structure of an inverting glycosidase in complex with substrate. J Mol Biol. 2002;316(5):1061-9. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5404 |
- Schubot FD, Kataeva IA, Chang J, Shah AK, Ljungdahl LG, Rose JP, and Wang BC. (2004). Structural basis for the exocellulase activity of the cellobiohydrolase CbhA from Clostridium thermocellum. Biochemistry. 2004;43(5):1163-70. DOI:10.1021/bi030202i |
- Suzuki R, Fujimoto Z, Ito S, Kawahara S, Kaneko S, Taira K, Hasegawa T, and Kuno A. (2009). Crystallographic snapshots of an entire reaction cycle for a retaining xylanase from Streptomyces olivaceoviridis E-86. J Biochem. 2009;146(1):61-70. DOI:10.1093/jb/mvp047 |
- Sidhu G, Withers SG, Nguyen NT, McIntosh LP, Ziser L, and Brayer GD. (1999). Sugar ring distortion in the glycosyl-enzyme intermediate of a family G/11 xylanase. Biochemistry. 1999;38(17):5346-54. DOI:10.1021/bi982946f |
- Sandgren M, Berglund GI, Shaw A, Ståhlberg J, Kenne L, Desmet T, and Mitchinson C. (2004). Crystal complex structures reveal how substrate is bound in the -4 to the +2 binding sites of Humicola grisea Cel12A. J Mol Biol. 2004;342(5):1505-17. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.07.098 |
- Uitdehaag JC, Mosi R, Kalk KH, van der Veen BA, Dijkhuizen L, Withers SG, and Dijkstra BW. (1999). X-ray structures along the reaction pathway of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase elucidate catalysis in the alpha-amylase family. Nat Struct Biol. 1999;6(5):432-6. DOI:10.1038/8235 |
- Miyake H, Kurisu G, Kusunoki M, Nishimura S, Kitamura S, and Nitta Y. (2003). Crystal structure of a catalytic site mutant of beta-amylase from Bacillus cereus var. mycoides cocrystallized with maltopentaose. Biochemistry. 2003;42(19):5574-81. DOI:10.1021/bi020712x |
- Harris EM, Aleshin AE, Firsov LM, and Honzatko RB. (1993). Refined structure for the complex of 1-deoxynojirimycin with glucoamylase from Aspergillus awamori var. X100 to 2.4-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1993;32(6):1618-26. DOI:10.1021/bi00057a028 |
- Allouch J, Helbert W, Henrissat B, and Czjzek M. (2004). Parallel substrate binding sites in a beta-agarase suggest a novel mode of action on double-helical agarose. Structure. 2004;12(4):623-32. DOI:10.1016/j.str.2004.02.020 |
- Papanikolau Y, Prag G, Tavlas G, Vorgias CE, Oppenheim AB, and Petratos K. (2001). High resolution structural analyses of mutant chitinase A complexes with substrates provide new insight into the mechanism of catalysis. Biochemistry. 2001;40(38):11338-43. DOI:10.1021/bi010505h |
- Ohnuma T, Umemoto N, Nagata T, Shinya S, Numata T, Taira T, and Fukamizo T. (2014). Crystal structure of a "loopless" GH19 chitinase in complex with chitin tetrasaccharide spanning the catalytic center. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1844(4):793-802. DOI:10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.02.013 |
- Prag G, Papanikolau Y, Tavlas G, Vorgias CE, Petratos K, and Oppenheim AB. (2000). Structures of chitobiase mutants complexed with the substrate Di-N-acetyl-d-glucosamine: the catalytic role of the conserved acidic pair, aspartate 539 and glutamate 540. J Mol Biol. 2000;300(3):611-7. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2000.3906 |
- Vocadlo DJ, Davies GJ, Laine R, and Withers SG. (2001). Catalysis by hen egg-white lysozyme proceeds via a covalent intermediate. Nature. 2001;412(6849):835-8. DOI:10.1038/35090602 |
- Karlsen S, Hough E, Rao ZH, and Isaacs NW. (1996). Structure of a bulgecin-inhibited g-type lysozyme from the egg white of the Australian black swan. A comparison of the binding of bulgecin to three muramidases. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1996;52(Pt 1):105-14. DOI:10.1107/S0907444995008468 |
- Baldwin EP, Hajiseyedjavadi O, Baase WA, and Matthews BW. (1993). The role of backbone flexibility in the accommodation of variants that repack the core of T4 lysozyme. Science. 1993;262(5140):1715-8. DOI:10.1126/science.8259514 |
- Ducros VM, Zechel DL, Murshudov GN, Gilbert HJ, Szabó L, Stoll D, Withers SG, and Davies GJ. (2002). Substrate distortion by a beta-mannanase: snapshots of the Michaelis and covalent-intermediate complexes suggest a B(2,5) conformation for the transition state. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2002;41(15):2824-7. DOI:10.1002/1521-3773(20020802)41:15<2824::AID-ANIE2824>3.0.CO;2-G |
- Garman SC, Hannick L, Zhu A, and Garboczi DN. (2002). The 1.9 A structure of alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase: molecular basis of glycosidase deficiency diseases. Structure. 2002;10(3):425-34. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(02)00726-8 |
- Abbott DW and Boraston AB. (2007). The structural basis for exopolygalacturonase activity in a family 28 glycoside hydrolase. J Mol Biol. 2007;368(5):1215-22. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.02.083 |
- Sulzenbacher G, Bignon C, Nishimura T, Tarling CA, Withers SG, Henrissat B, and Bourne Y. (2004). Crystal structure of Thermotoga maritima alpha-L-fucosidase. Insights into the catalytic mechanism and the molecular basis for fucosidosis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(13):13119-28. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M313783200 |
- Brumshtein B, Greenblatt HM, Butters TD, Shaaltiel Y, Aviezer D, Silman I, Futerman AH, and Sussman JL. (2007). Crystal structures of complexes of N-butyl- and N-nonyl-deoxynojirimycin bound to acid beta-glucosidase: insights into the mechanism of chemical chaperone action in Gaucher disease. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(39):29052-29058. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M705005200 |
- Sim L, Quezada-Calvillo R, Sterchi EE, Nichols BL, and Rose DR. (2008). Human intestinal maltase-glucoamylase: crystal structure of the N-terminal catalytic subunit and basis of inhibition and substrate specificity. J Mol Biol. 2008;375(3):782-92. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.10.069 |
- Verhaest M, Lammens W, Le Roy K, De Ranter CJ, Van Laere A, Rabijns A, and Van den Ende W. (2007). Insights into the fine architecture of the active site of chicory fructan 1-exohydrolase: 1-kestose as substrate vs sucrose as inhibitor. New Phytol. 2007;174(1):90-100. DOI:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.01988.x |
- Amaya MF, Watts AG, Damager I, Wehenkel A, Nguyen T, Buschiazzo A, Paris G, Frasch AC, Withers SG, and Alzari PM. (2004). Structural insights into the catalytic mechanism of Trypanosoma cruzi trans-sialidase. Structure. 2004;12(5):775-84. DOI:10.1016/j.str.2004.02.036 |
- Varghese JN, McKimm-Breschkin JL, Caldwell JB, Kortt AA, and Colman PM. (1992). The structure of the complex between influenza virus neuraminidase and sialic acid, the viral receptor. Proteins. 1992;14(3):327-32. DOI:10.1002/prot.340140302 |
- Rojas AL, Nagem RA, Neustroev KN, Arand M, Adamska M, Eneyskaya EV, Kulminskaya AA, Garratt RC, Golubev AM, and Polikarpov I. (2004). Crystal structures of beta-galactosidase from Penicillium sp. and its complex with galactose. J Mol Biol. 2004;343(5):1281-92. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.09.012 |
- Merceron R, Foucault M, Haser R, Mattes R, Watzlawick H, and Gouet P. (2012). The molecular mechanism of thermostable α-galactosidases AgaA and AgaB explained by x-ray crystallography and mutational studies. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(47):39642-52. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M112.394114 |
- Gibson RP, Gloster TM, Roberts S, Warren RA, Storch de Gracia I, García A, Chiara JL, and Davies GJ. (2007). Molecular basis for trehalase inhibition revealed by the structure of trehalase in complex with potent inhibitors. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2007;46(22):4115-9. DOI:10.1002/anie.200604825 |
- Numao S, Kuntz DA, Withers SG, and Rose DR. (2003). Insights into the mechanism of Drosophila melanogaster Golgi alpha-mannosidase II through the structural analysis of covalent reaction intermediates. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(48):48074-83. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M309249200 |
- Yang JK, Yoon HJ, Ahn HJ, Lee BI, Pedelacq JD, Liong EC, Berendzen J, Laivenieks M, Vieille C, Zeikus GJ, Vocadlo DJ, Withers SG, and Suh SW. (2004). Crystal structure of beta-D-xylosidase from Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum, a family 39 glycoside hydrolase. J Mol Biol. 2004;335(1):155-65. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2003.10.026 |
- Godoy AS, Camilo CM, Kadowaki MA, Muniz HD, Espirito Santo M, Murakami MT, Nascimento AS, and Polikarpov I. (2016). Crystal structure of β1→6-galactosidase from Bifidobacterium bifidum S17: trimeric architecture, molecular determinants of the enzymatic activity and its inhibition by α-galactose. FEBS J. 2016;283(22):4097-4112. DOI:10.1111/febs.13908 |
- Kitago Y, Karita S, Watanabe N, Kamiya M, Aizawa T, Sakka K, and Tanaka I. (2007). Crystal structure of Cel44A, a glycoside hydrolase family 44 endoglucanase from Clostridium thermocellum. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(49):35703-11. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M706835200 |
- Davies GJ, Dodson G, Moore MH, Tolley SP, Dauter Z, Wilson KS, Rasmussen G, and Schülein M. (1996). Structure determination and refinement of the Humicola insolens endoglucanase V at 1.5 A resolution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1996;52(Pt 1):7-17. DOI:10.1107/S0907444995009280 |
- Lyu Q, Wang S, Xu W, Han B, Liu W, Jones DN, and Liu W. (2014). Structural insights into the substrate-binding mechanism for a novel chitosanase. Biochem J. 2014;461(2):335-45. DOI:10.1042/BJ20140159 |
- Karaveg K, Siriwardena A, Tempel W, Liu ZJ, Glushka J, Wang BC, and Moremen KW. (2005). Mechanism of class 1 (glycosylhydrolase family 47) {alpha}-mannosidases involved in N-glycan processing and endoplasmic reticulum quality control. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(16):16197-207. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M500119200 |
- Cantú D, Nerinckx W, and Reilly PJ. (2008). Theory and computation show that Asp463 is the catalytic proton donor in human endoplasmic reticulum alpha-(1-->2)-mannosidase I. Carbohydr Res. 2008;343(13):2235-42. DOI:10.1016/j.carres.2008.05.026 |
- Pluvinage B, Hehemann JH, and Boraston AB. (2013). Substrate recognition and hydrolysis by a family 50 exo-β-agarase, Aga50D, from the marine bacterium Saccharophagus degradans. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(39):28078-88. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M113.491068 |
- Hövel K, Shallom D, Niefind K, Belakhov V, Shoham G, Baasov T, Shoham Y, and Schomburg D. (2003). Crystal structure and snapshots along the reaction pathway of a family 51 alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase. EMBO J. 2003;22(19):4922-32. DOI:10.1093/emboj/cdg494 |
- Espina G, Eley K, Pompidor G, Schneider TR, Crennell SJ, and Danson MJ. (2014). A novel β-xylosidase structure from Geobacillus thermoglucosidasius: the first crystal structure of a glycoside hydrolase family GH52 enzyme reveals unpredicted similarity to other glycoside hydrolase folds. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014;70(Pt 5):1366-74. DOI:10.1107/S1399004714002788 |
- Le Nours J, De Maria L, Welner D, Jørgensen CT, Christensen LL, Borchert TV, Larsen S, and Lo Leggio L. (2009). Investigating the binding of beta-1,4-galactan to Bacillus licheniformis beta-1,4-galactanase by crystallography and computational modeling. Proteins. 2009;75(4):977-89. DOI:10.1002/prot.22310 |
- Miyanaga A, Koseki T, Matsuzawa H, Wakagi T, Shoun H, and Fushinobu S. (2004). Crystal structure of a family 54 alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase reveals a novel carbohydrate-binding module that can bind arabinose. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(43):44907-14. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M405390200 |
- Ishida T, Fushinobu S, Kawai R, Kitaoka M, Igarashi K, and Samejima M. (2009). Crystal structure of glycoside hydrolase family 55 {beta}-1,3-glucanase from the basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(15):10100-9. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M808122200 |
- Marković-Housley Z, Miglierini G, Soldatova L, Rizkallah PJ, Müller U, and Schirmer T. (2000). Crystal structure of hyaluronidase, a major allergen of bee venom. Structure. 2000;8(10):1025-35. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00511-6 |
- Imamura H, Fushinobu S, Yamamoto M, Kumasaka T, Jeon BS, Wakagi T, and Matsuzawa H. (2003). Crystal structures of 4-alpha-glucanotransferase from Thermococcus litoralis and its complex with an inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(21):19378-86. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M213134200 |
- Hill CH, Graham SC, Read RJ, and Deane JE. (2013). Structural snapshots illustrate the catalytic cycle of β-galactocerebrosidase, the defective enzyme in Krabbe disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(51):20479-84. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1311990110 |
- Touhara KK, Nihira T, Kitaoka M, Nakai H, and Fushinobu S. (2014). Structural basis for reversible phosphorolysis and hydrolysis reactions of 2-O-α-glucosylglycerol phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(26):18067-75. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M114.573212 |
- Suzuki N, Kishine N, Fujimoto Z, Sakurai M, Momma M, Ko JA, Nam SH, Kimura A, and Kim YM. (2016). Crystal structure of thermophilic dextranase from Thermoanaerobacter pseudethanolicus. J Biochem. 2016;159(3):331-9. DOI:10.1093/jb/mvv104 |
- Nurizzo D, Nagy T, Gilbert HJ, and Davies GJ. (2002). The structural basis for catalysis and specificity of the Pseudomonas cellulosa alpha-glucuronidase, GlcA67A. Structure. 2002;10(4):547-56. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(02)00742-6 |
- Meng G and Fütterer K. (2003). Structural framework of fructosyl transfer in Bacillus subtilis levansucrase. Nat Struct Biol. 2003;10(11):935-41. DOI:10.1038/nsb974 |
- Ito K, Ito S, Shimamura T, Weyand S, Kawarasaki Y, Misaka T, Abe K, Kobayashi T, Cameron AD, and Iwata S. (2011). Crystal structure of glucansucrase from the dental caries pathogen Streptococcus mutans. J Mol Biol. 2011;408(2):177-86. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.02.028 |
- Hurtado-Guerrero R, Schüttelkopf AW, Mouyna I, Ibrahim AF, Shepherd S, Fontaine T, Latgé JP, and van Aalten DM. (2009). Molecular mechanisms of yeast cell wall glucan remodeling. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(13):8461-9. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M807990200 |
- Yaoi K, Kondo H, Hiyoshi A, Noro N, Sugimoto H, Tsuda S, Mitsuishi Y, and Miyazaki K. (2007). The structural basis for the exo-mode of action in GH74 oligoxyloglucan reducing end-specific cellobiohydrolase. J Mol Biol. 2007;370(1):53-62. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.04.035 |
- Thompson AJ, Speciale G, Iglesias-Fernández J, Hakki Z, Belz T, Cartmell A, Spears RJ, Chandler E, Temple MJ, Stepper J, Gilbert HJ, Rovira C, Williams SJ, and Davies GJ. (2015). Evidence for a boat conformation at the transition state of GH76 α-1,6-mannanases--key enzymes in bacterial and fungal mannoprotein metabolism. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015;54(18):5378-82. DOI:10.1002/anie.201410502 |
- Przylas I, Terada Y, Fujii K, Takaha T, Saenger W, and Sträter N. (2000). X-ray structure of acarbose bound to amylomaltase from Thermus aquaticus. Implications for the synthesis of large cyclic glucans. Eur J Biochem. 2000;267(23):6903-13. DOI:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2000.01790.x |
- Fujimoto Z, Jackson A, Michikawa M, Maehara T, Momma M, Henrissat B, Gilbert HJ, and Kaneko S. (2013). The structure of a Streptomyces avermitilis α-L-rhamnosidase reveals a novel carbohydrate-binding module CBM67 within the six-domain arrangement. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(17):12376-85. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M113.460097 |
- Wu L, Viola CM, Brzozowski AM, and Davies GJ. (2015). Structural characterization of human heparanase reveals insights into substrate recognition. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015;22(12):1016-22. DOI:10.1038/nsmb.3136 |
- Dennis RJ, Taylor EJ, Macauley MS, Stubbs KA, Turkenburg JP, Hart SJ, Black GN, Vocadlo DJ, and Davies GJ. (2006). Structure and mechanism of a bacterial beta-glucosaminidase having O-GlcNAcase activity. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006;13(4):365-71. DOI:10.1038/nsmb1079 |
- Abbott DW, Macauley MS, Vocadlo DJ, and Boraston AB. (2009). Streptococcus pneumoniae endohexosaminidase D, structural and mechanistic insight into substrate-assisted catalysis in family 85 glycoside hydrolases. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(17):11676-89. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M809663200 |
- Hehemann JH, Kelly AG, Pudlo NA, Martens EC, and Boraston AB. (2012). Bacteria of the human gut microbiome catabolize red seaweed glycans with carbohydrate-active enzyme updates from extrinsic microbes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(48):19786-91. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1211002109 |
- Ficko-Blean E, Stubbs KA, Nemirovsky O, Vocadlo DJ, and Boraston AB. (2008). Structural and mechanistic insight into the basis of mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(18):6560-5. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0711491105 |
- Zhu Y, Suits MD, Thompson AJ, Chavan S, Dinev Z, Dumon C, Smith N, Moremen KW, Xiang Y, Siriwardena A, Williams SJ, Gilbert HJ, and Davies GJ. (2010). Mechanistic insights into a Ca2+-dependent family of alpha-mannosidases in a human gut symbiont. Nat Chem Biol. 2010;6(2):125-32. DOI:10.1038/nchembio.278 |
- Sogabe Y, Kitatani T, Yamaguchi A, Kinoshita T, Adachi H, Takano K, Inoue T, Mori Y, Matsumura H, Sakamoto T, and Tada T. (2011). High-resolution structure of exo-arabinanase from Penicillium chrysogenum. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2011;67(Pt 5):415-22. DOI:10.1107/S0907444911006299 |
- Hidaka M, Honda Y, Kitaoka M, Nirasawa S, Hayashi K, Wakagi T, Shoun H, and Fushinobu S. (2004). Chitobiose phosphorylase from Vibrio proteolyticus, a member of glycosyl transferase family 36, has a clan GH-L-like (alpha/alpha)(6) barrel fold. Structure. 2004;12(6):937-47. DOI:10.1016/j.str.2004.03.027 |
- Nagae M, Tsuchiya A, Katayama T, Yamamoto K, Wakatsuki S, and Kato R. (2007). Structural basis of the catalytic reaction mechanism of novel 1,2-alpha-L-fucosidase from Bifidobacterium bifidum. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(25):18497-18509. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M702246200 |
- Kitamura M, Okuyama M, Tanzawa F, Mori H, Kitago Y, Watanabe N, Kimura A, Tanaka I, and Yao M. (2008). Structural and functional analysis of a glycoside hydrolase family 97 enzyme from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(52):36328-37. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M806115200 |
- Thompson AJ, Williams RJ, Hakki Z, Alonzi DS, Wennekes T, Gloster TM, Songsrirote K, Thomas-Oates JE, Wrodnigg TM, Spreitz J, Stütz AE, Butters TD, Williams SJ, and Davies GJ. (2012). Structural and mechanistic insight into N-glycan processing by endo-α-mannosidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(3):781-6. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1111482109 |
- Xie J, Cai K, Hu HX, Jiang YL, Yang F, Hu PF, Cao DD, Li WF, Chen Y, and Zhou CZ. (2016). Structural Analysis of the Catalytic Mechanism and Substrate Specificity of Anabaena Alkaline Invertase InvA Reveals a Novel Glucosidase. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(49):25667-25677. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M116.759290 |
- van Straaten KE, Barends TR, Dijkstra BW, and Thunnissen AM. (2007). Structure of Escherichia coli Lytic transglycosylase MltA with bound chitohexaose: implications for peptidoglycan binding and cleavage. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(29):21197-205. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M701818200 |
- Williams RJ, Iglesias-Fernández J, Stepper J, Jackson A, Thompson AJ, Lowe EC, White JM, Gilbert HJ, Rovira C, Davies GJ, and Williams SJ. (2014). Combined inhibitor free-energy landscape and structural analysis reports on the mannosidase conformational coordinate. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014;53(4):1087-91. DOI:10.1002/anie.201308334 |
- Hehemann JH, Smyth L, Yadav A, Vocadlo DJ, and Boraston AB. (2012). Analysis of keystone enzyme in Agar hydrolysis provides insight into the degradation (of a polysaccharide from) red seaweeds. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(17):13985-95. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M112.345645 |
- Noach I, Pluvinage B, Laurie C, Abe KT, Alteen MG, Vocadlo DJ, and Boraston AB. (2016). The Details of Glycolipid Glycan Hydrolysis by the Structural Analysis of a Family 123 Glycoside Hydrolase from Clostridium perfringens. J Mol Biol. 2016;428(16):3253-3265. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2016.03.020 |
-
Jin Y, Petricevic M, John A, Raich L, Jenkins H, Portela De Souza L, Cuskin F, Gilbert HJ, Rovira C, Goddard-Borger ED, Williams SJ, and Davies GJ. A β-Mannanase with a Lysozyme-like Fold and a Novel Molecular Catalytic Mechanism. ACS Cent. Sci. 2016 Nov DOI:10.1021/acscentsci.6b00232